Blog SEO
What Is Blog SEO?
Blog SEO is the practice of optimizing a blog’s content, site architecture and HTML code for search engines. Common tasks associated with blog SEO include on-page optimization, installing plugins, improving page loading speed and internal linking.
Why Is Blog SEO Important?
Search engines are a super important traffic source for blogs.
In fact, a recent survey of over 1000 bloggers found that SEO was their 3rd most important source of traffic (just behind email marketing).
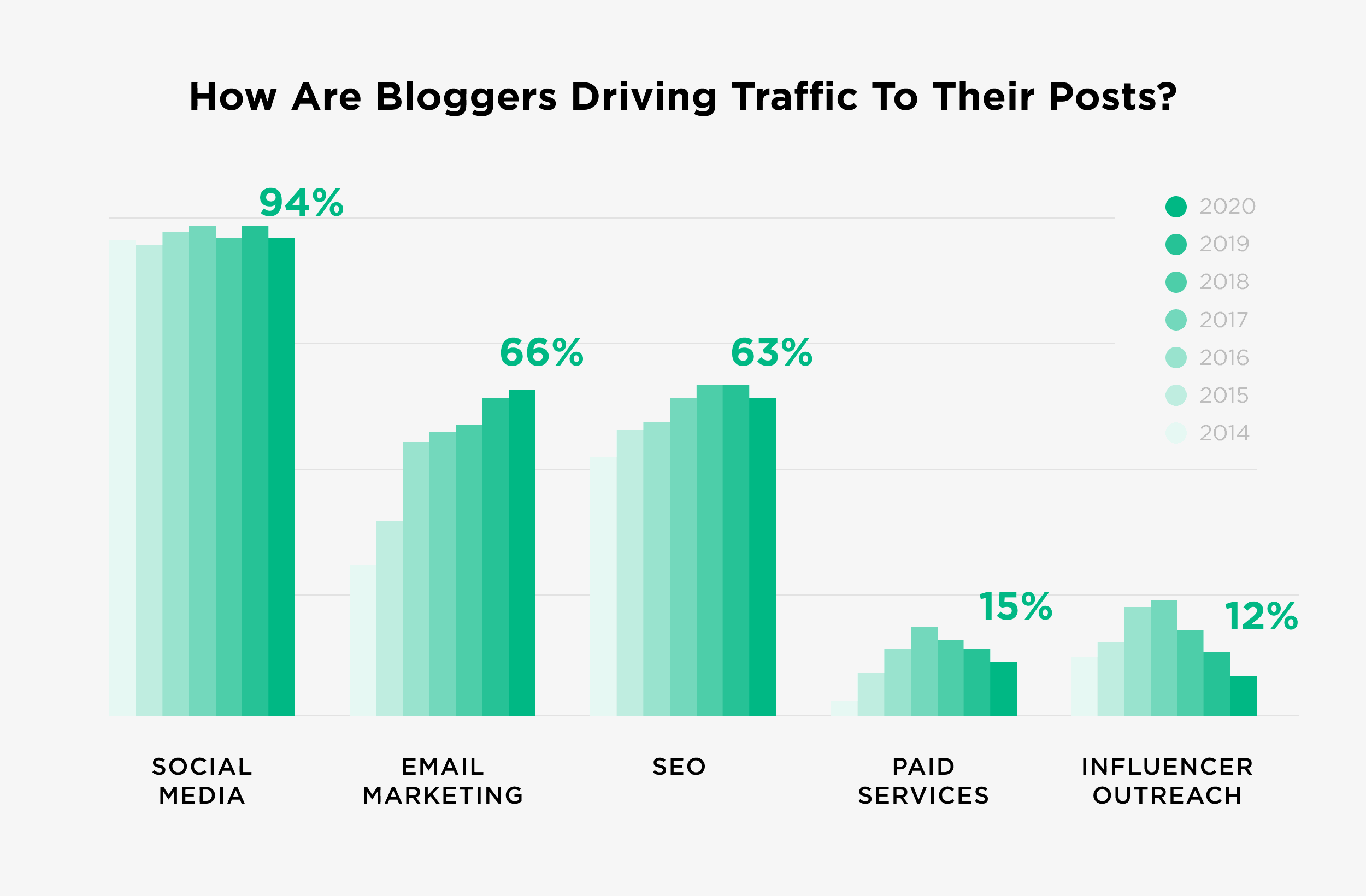
Our own blog is living proof of the power of SEO. Sure, we get a fair amount of traffic from Twitter, LinkedIn, email and direct traffic. And added together, these sources make up the majority of our monthly traffic.
But Google sends us over 396,000 visitors per month.
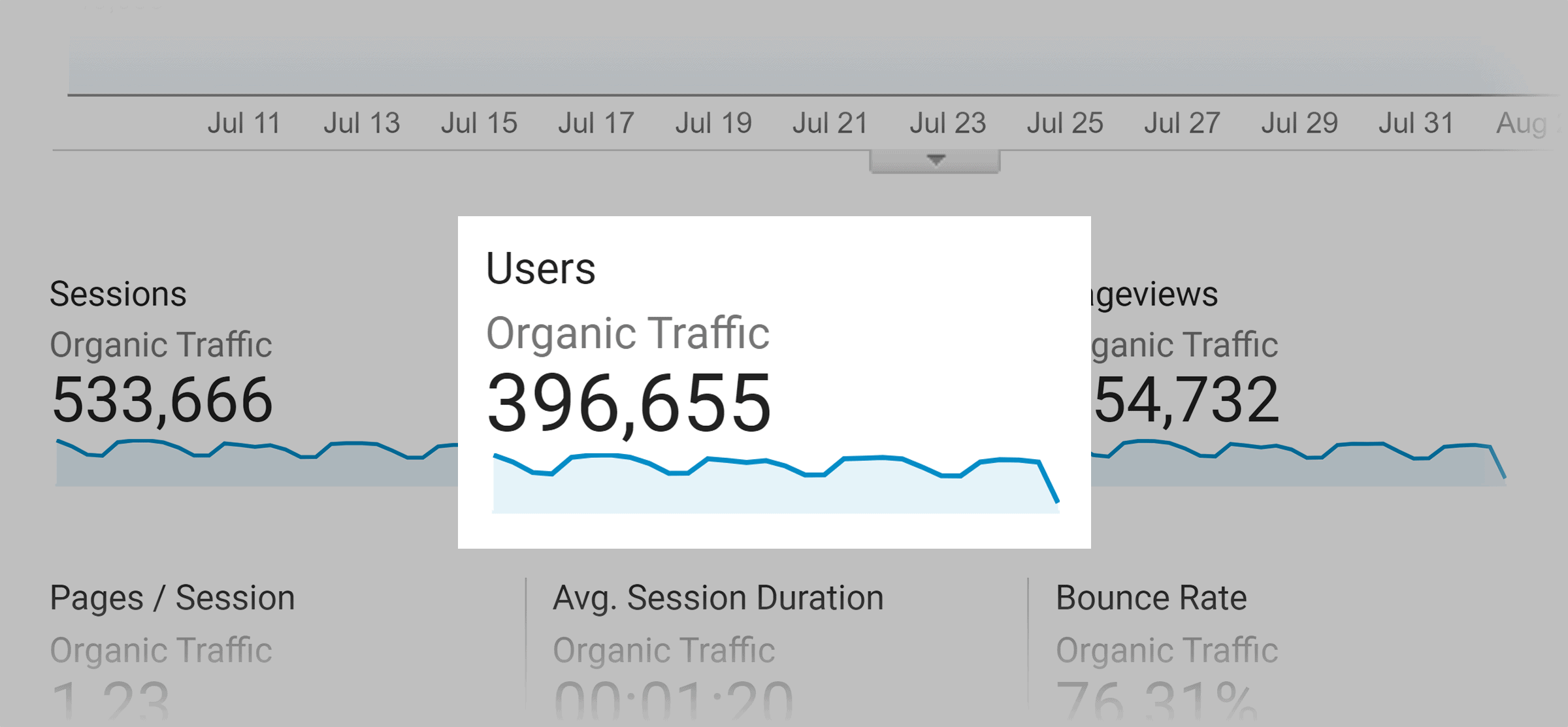
Without blog SEO, our site’s growth would have been much slower.
And if you want to learn how to optimize your blog for SEO, check out these tested SEO tips.
Best Practices
Find One Main Keyword For Each Post
Every blog post that you publish should be optimized around one keyword.
If you optimize your post around lots of different keywords, Google and other search engines get confused. They don’t know what your content is actually about.
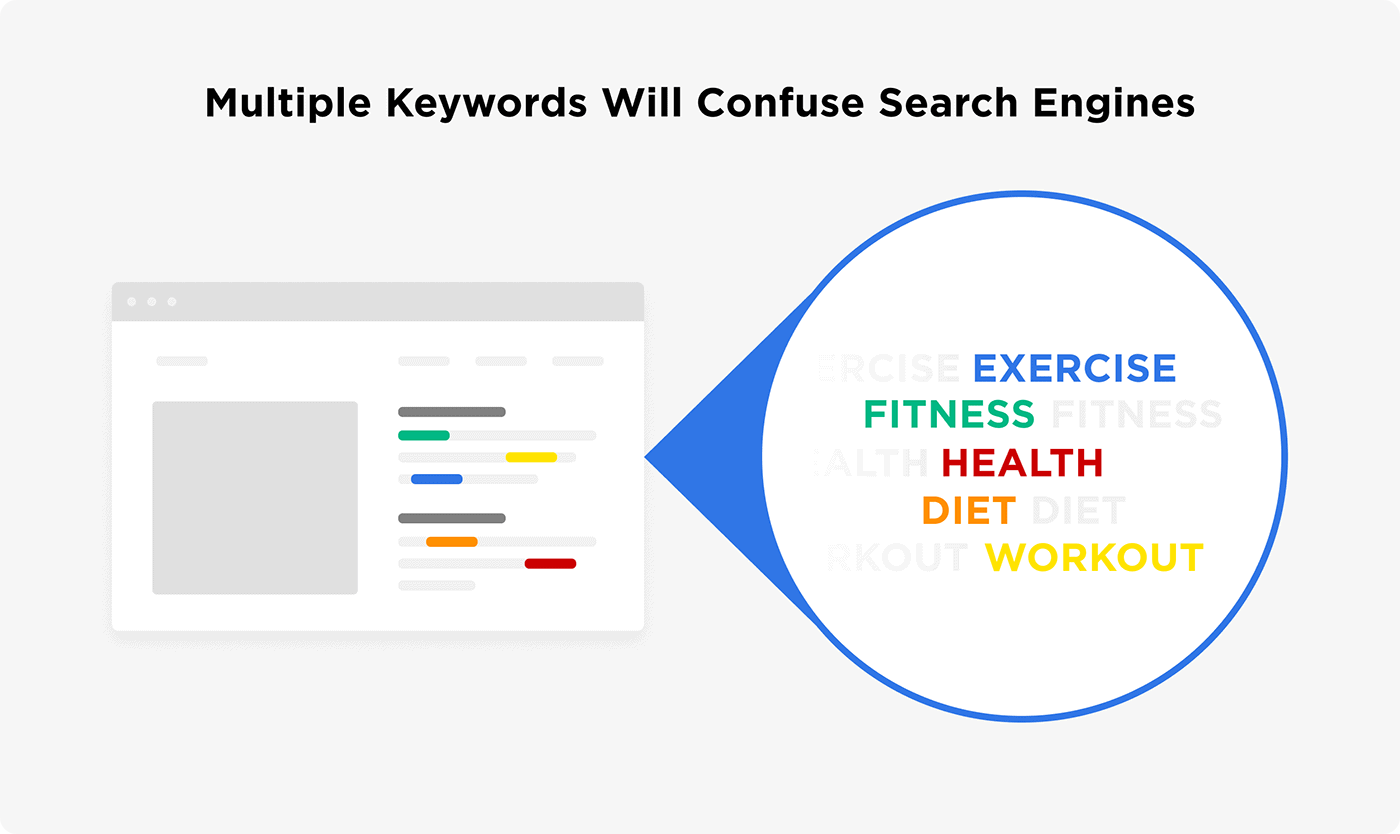
But when you focus on a single keyword, Google can easily understand that your post is about that one topic.
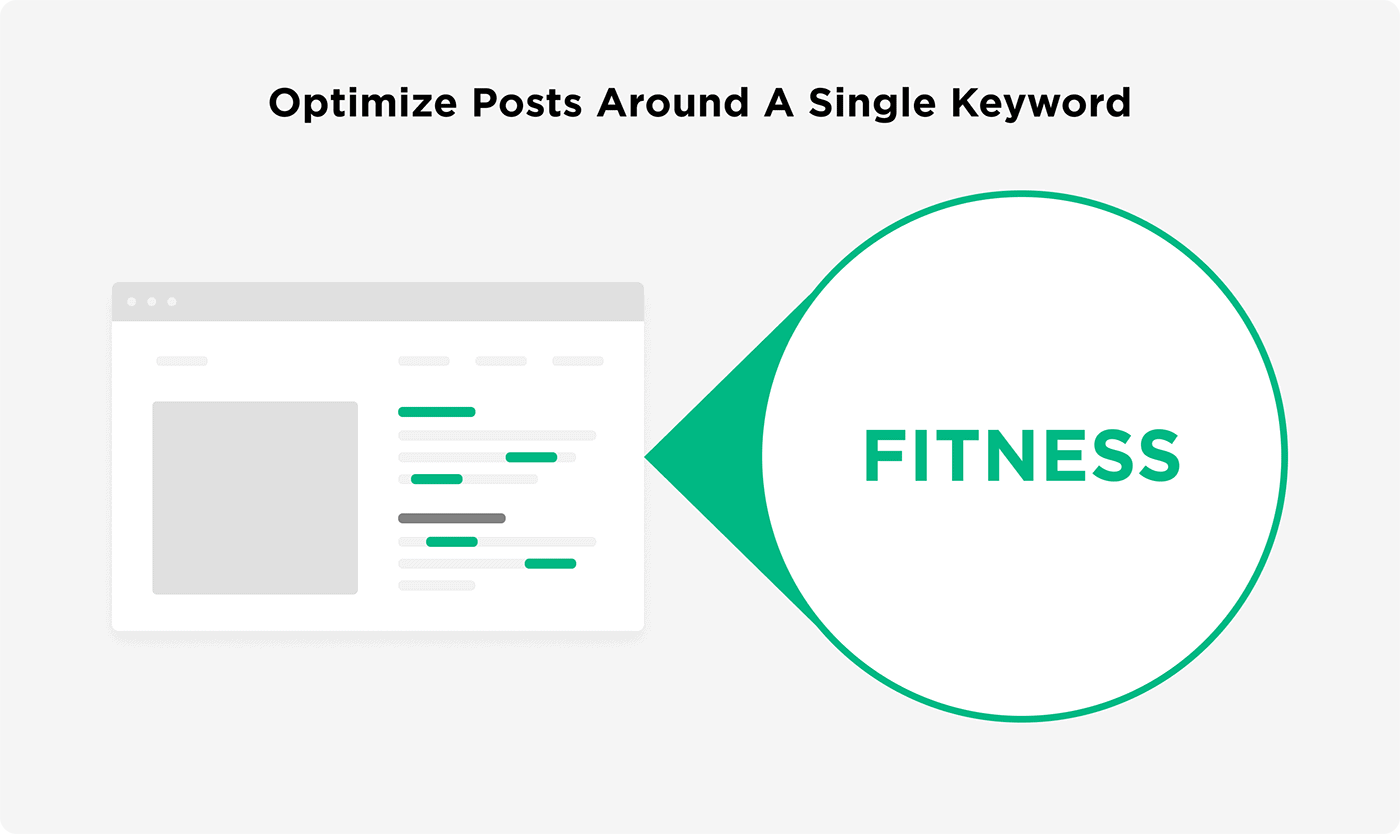
So your first step is to find one main keyword for your post.
If your blog is new, I recommend focusing on long tail keywords at first. That’s because long tail terms aren’t super competitive.
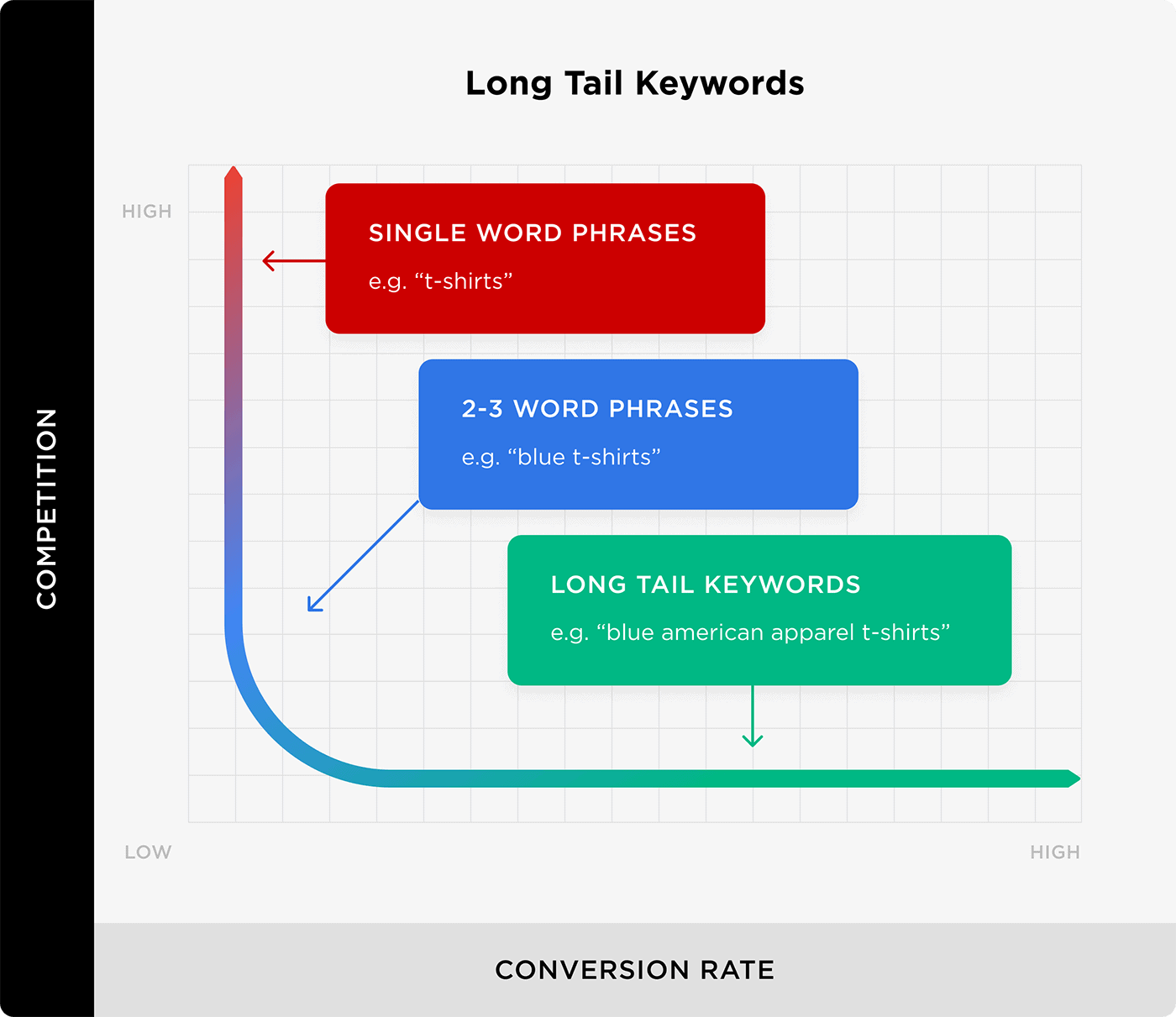
To find long tail keywords, type a term into Google search…
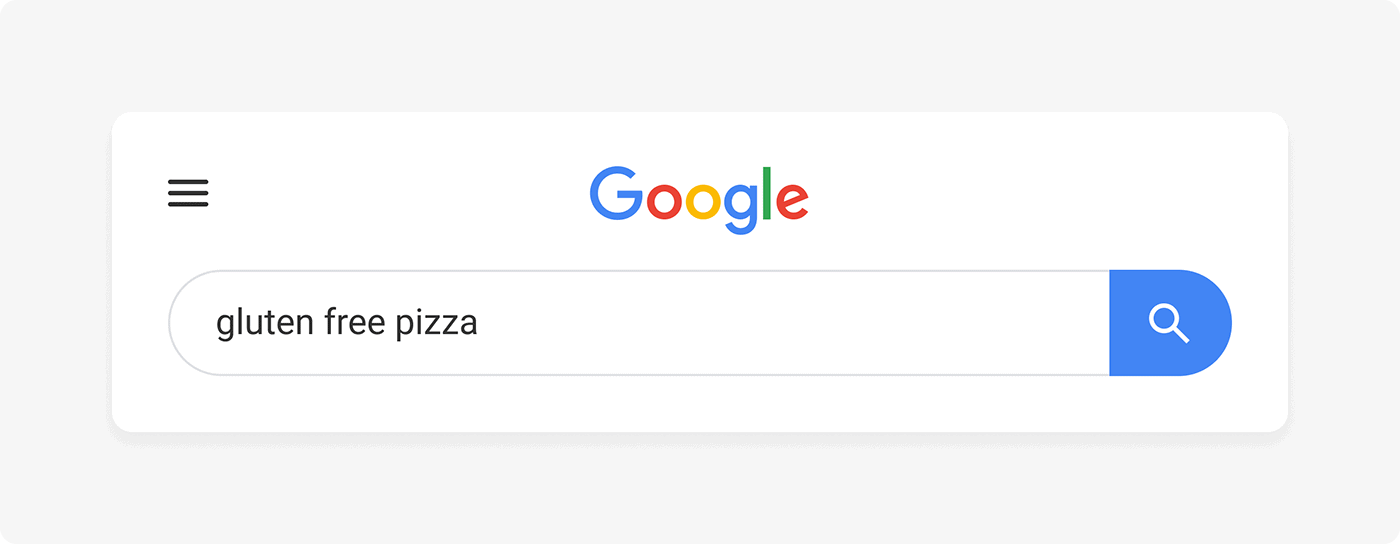
…and check out the keywords that Google suggests underneath the search bar.
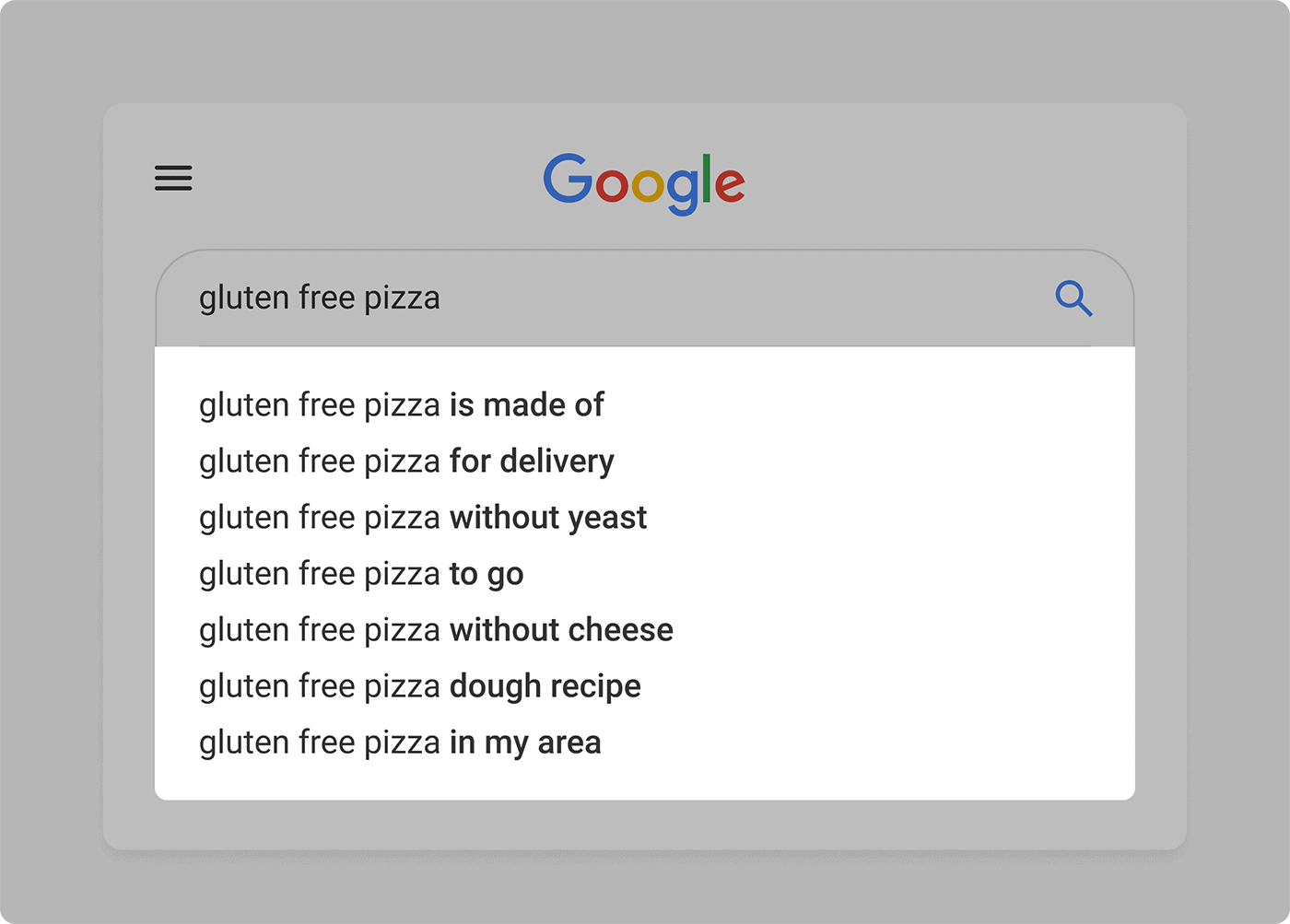
You can also use a nice little free tool called Answer The Public.
This tool generates a list of question-based keywords that you can optimize your post around.
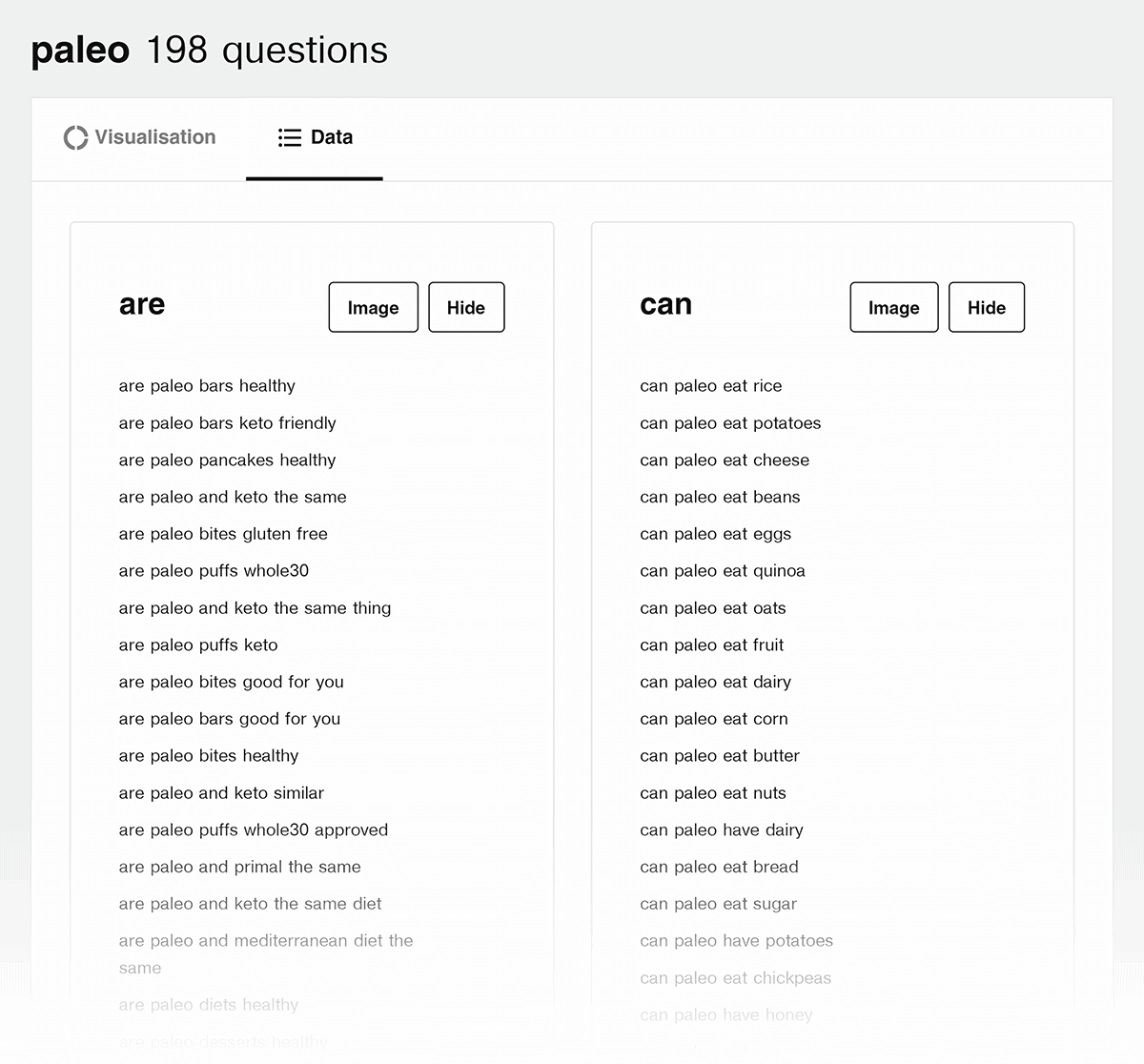
(Besides keyword research, this tool is great for coming up with content topic ideas.)
Optimize Your Blog Post
Now that you’ve found a long tail keyword, you want to optimize your post around that term.
There’s no need to stuff your keyword a million times on your page. That’s called “keyword stuffing”. Keyword stuffing used to work back in the day. But it can do more harm and good today.
Instead, you want to include your keyword in a few key places on your page.
Title and Title Tag
Most CMSs (like WordPress) have a title field at the top of the post.
And you want to include your keyword in your blog post title and your page’s title tag.

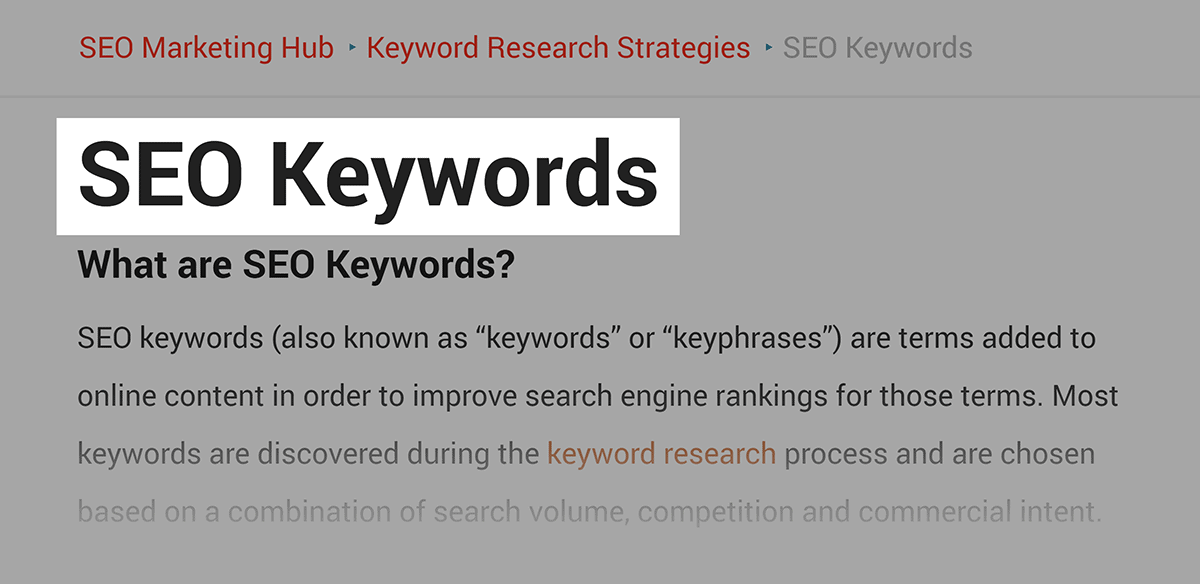
For example, on this page from our site, we include our target keyword “SEO keywords” in the post title:
And we use that same exact keyword in our title tag:

When it comes to blog SEO, your title tag is the most important of the two.
That’s because Google puts extra weight on terms that show up in your page’s title tag.
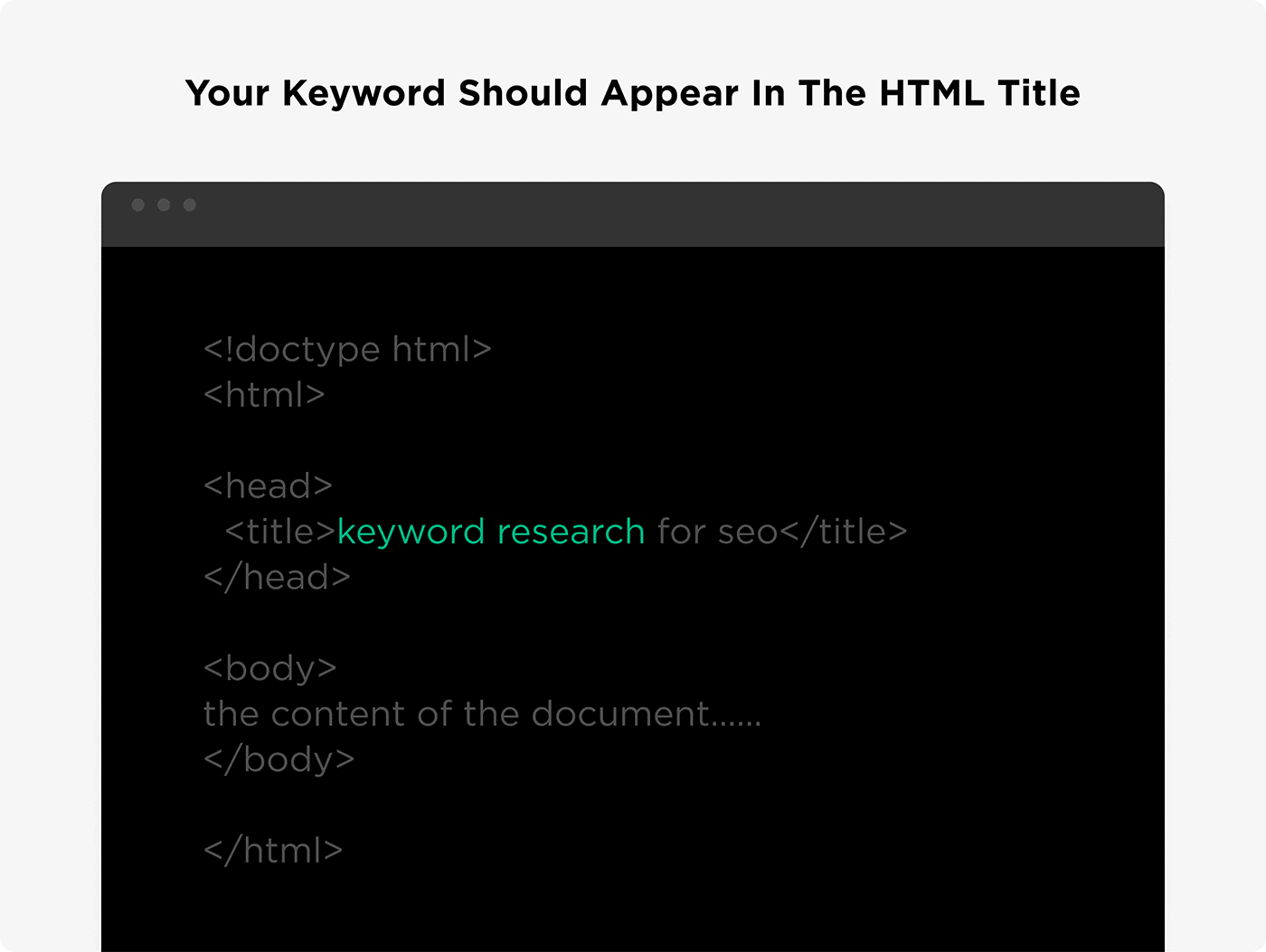
Certain WordPress themes and plugins automatically make your post your title tag. But others don’t. So you want to double-check your page’s HTML to make sure that your keyword ends up in your title.
Intro and Conclusion Sections
You also want to mention your keyword in your blog post intro and conclusion.
In my experience, placing your keyword in these two key areas helps a little bit with on-page SEO.
For example, I published a guide called Copywriting: The Definitive Guide.
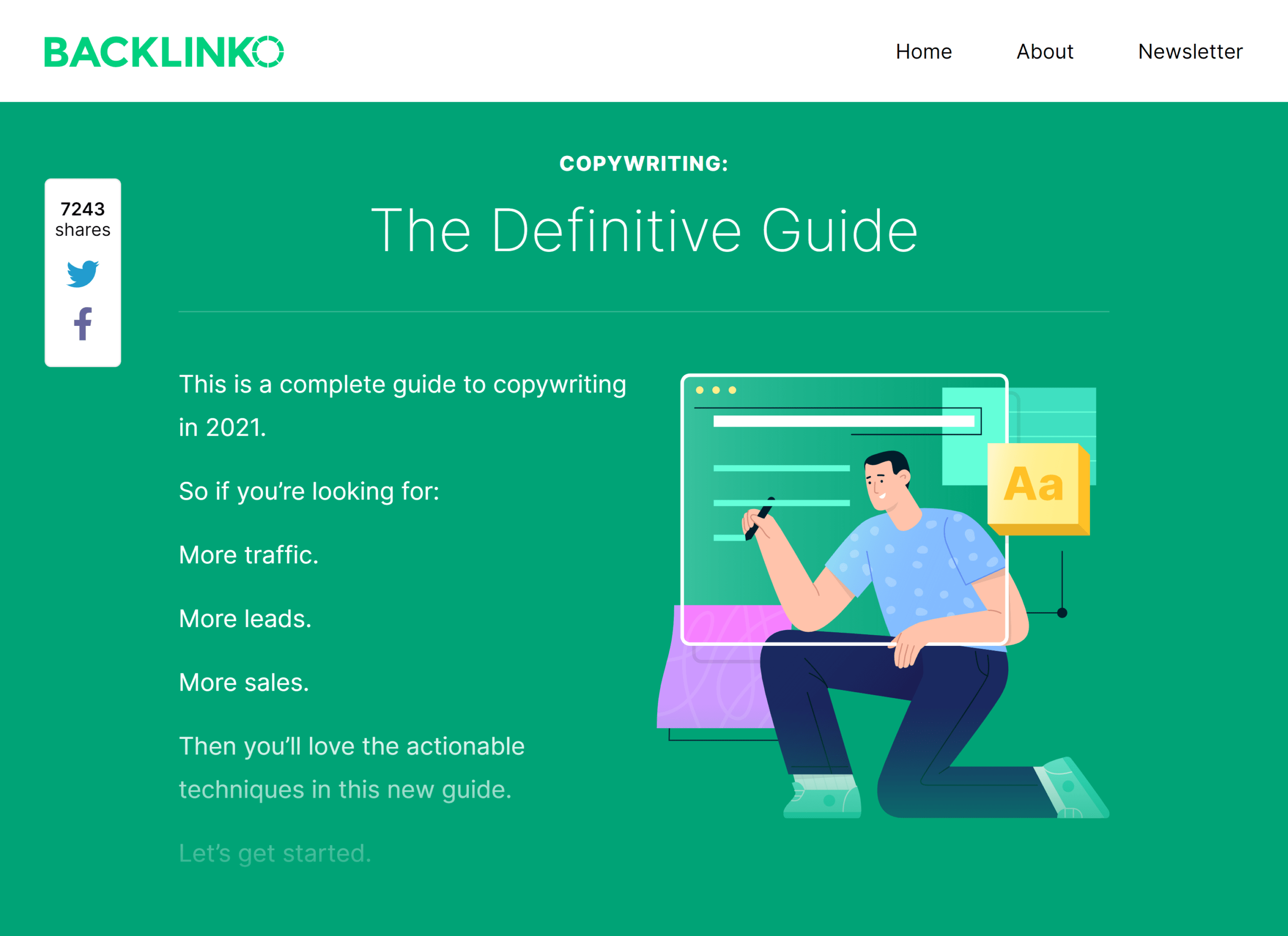
As you can see, I added my main keyword (“copywriting”) in my intro…

…and conclusion.

H1, H2 and H3 Subheadings
Use your keyword in an H1, H2 or H3 subheading.
Most WordPress themes automatically make your post title an H1.
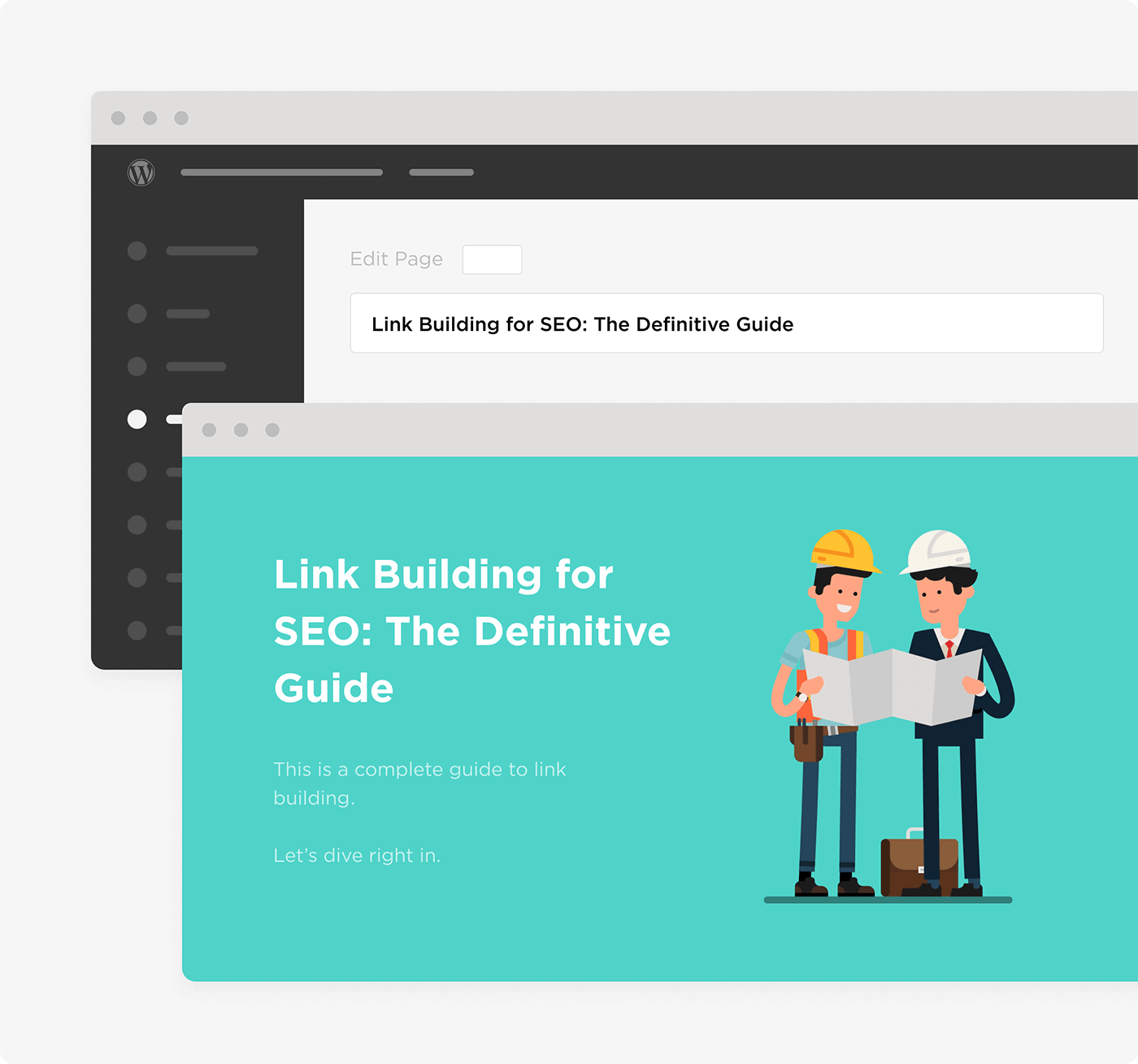
But, like your title tag, you need to check out your page’s HTML to be sure.
Besides an H1, add at least one subheading to your post that contains a keyword.
For example, I added my keyword in this H2 subheading:

These tips are the most important SEO best practices to keep in mind as you optimize your blog content.
But they only scratch the surface. When it comes to on-page SEO, you can also optimize your page’s alt text, sitespeed, responsive design, mobile optimization, and more.
And if you want to fully optimize each and every post, I recommend watching this video.
Setup SEO Plugins
Wix. Squarespace. Shopify. WordPress.
They all claim to be “SEO friendly” out of the box.
But no matter how SEO-friendly each one is, they usually need a little bit of help in the form of an SEO plugin or extension.
Yoast SEO is by far the most popular SEO plugin for WordPress. But there’s also All In One SEO and RankMath.
And there are similar SEO plugins for almost every blogging platform out there.
The exact plugin doesn’t matter all that much. The important thing is that you use the right types of SEO plugins on your blog.
Specifically, you want plugins that:
- Help you optimize your title and description tags: That way, you can write SEO-optimized titles and meta descriptions.
- Create a sitemap: An XML sitemap helps search engines find all of your blog’s post and pages
- Make it easy to create an SEO-friendly site structure: For blogs, this means being able to easily noindex pages and posts that you don’t want search engines to index.
- Compress images for speed: Page speed won’t make or break your rankings. But fast-loading pages can give you a slight boost.
Once you have those plugins in place, it’s time to…
Put Your Blog On a Subfolder
If your blog IS your site, you don’t need to worry about this.
But what if you’re a SaaS business? Or do you sell services?
Where do you put your blog?
Back in the day, people used to put their blogs on subdomains, like this:
blog.example.com
As it turns out, subdomains aren’t very SEO-friendly.
Instead, you want to put your blog on a subfolder, like this.
example.com/blog
In fact, that’s what we do at Backlinko.
In fact, John Doherty moved his client’s blog from a subdomain to a subfolder. And it helped boost their organic traffic by 98%.
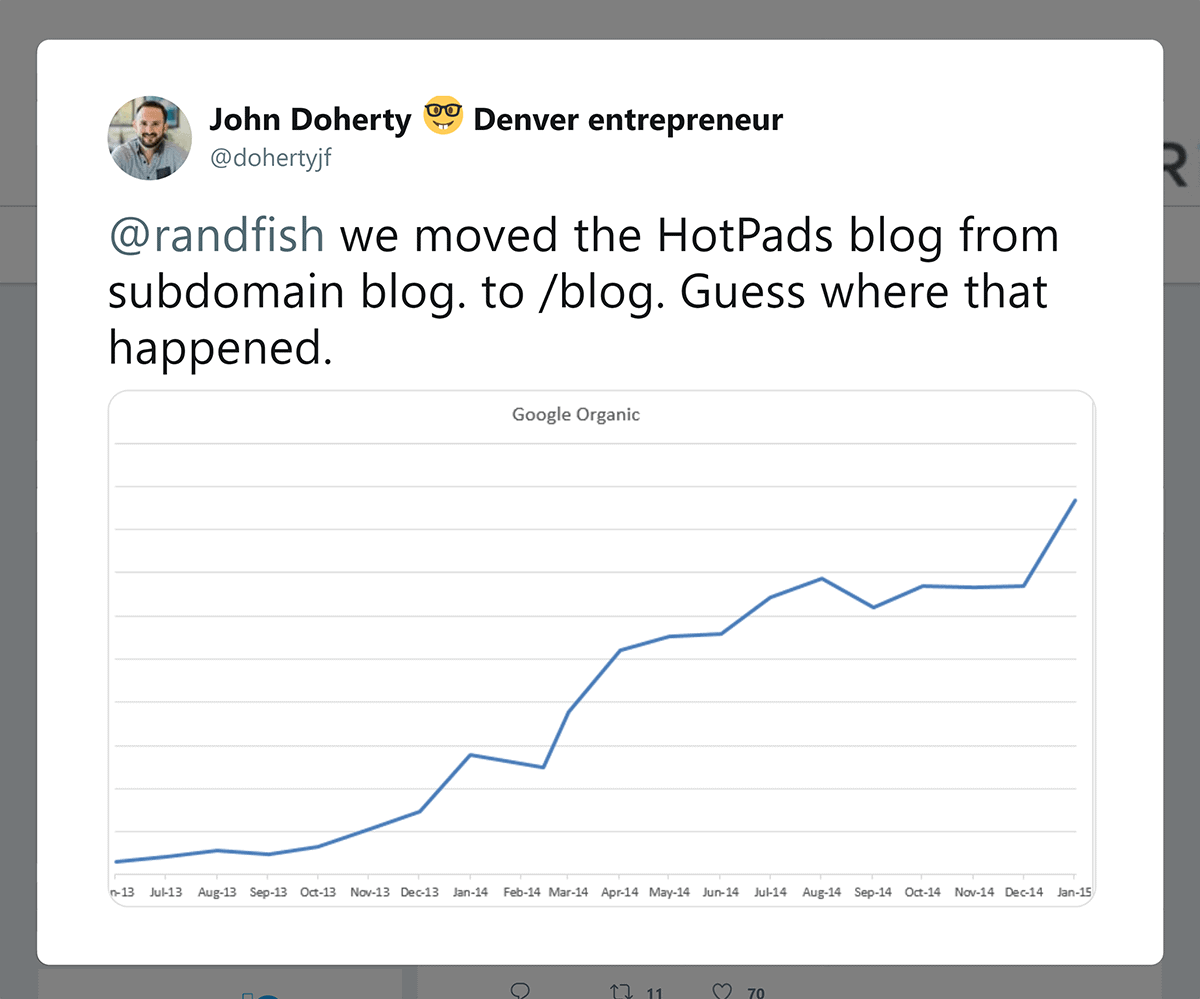
Use Evergreen URLs
Blog URLs can be super duper long.
And, as it turns out, long URLs aren’t great for SEO.
We found a correlation between short URLs and higher Google rankings.
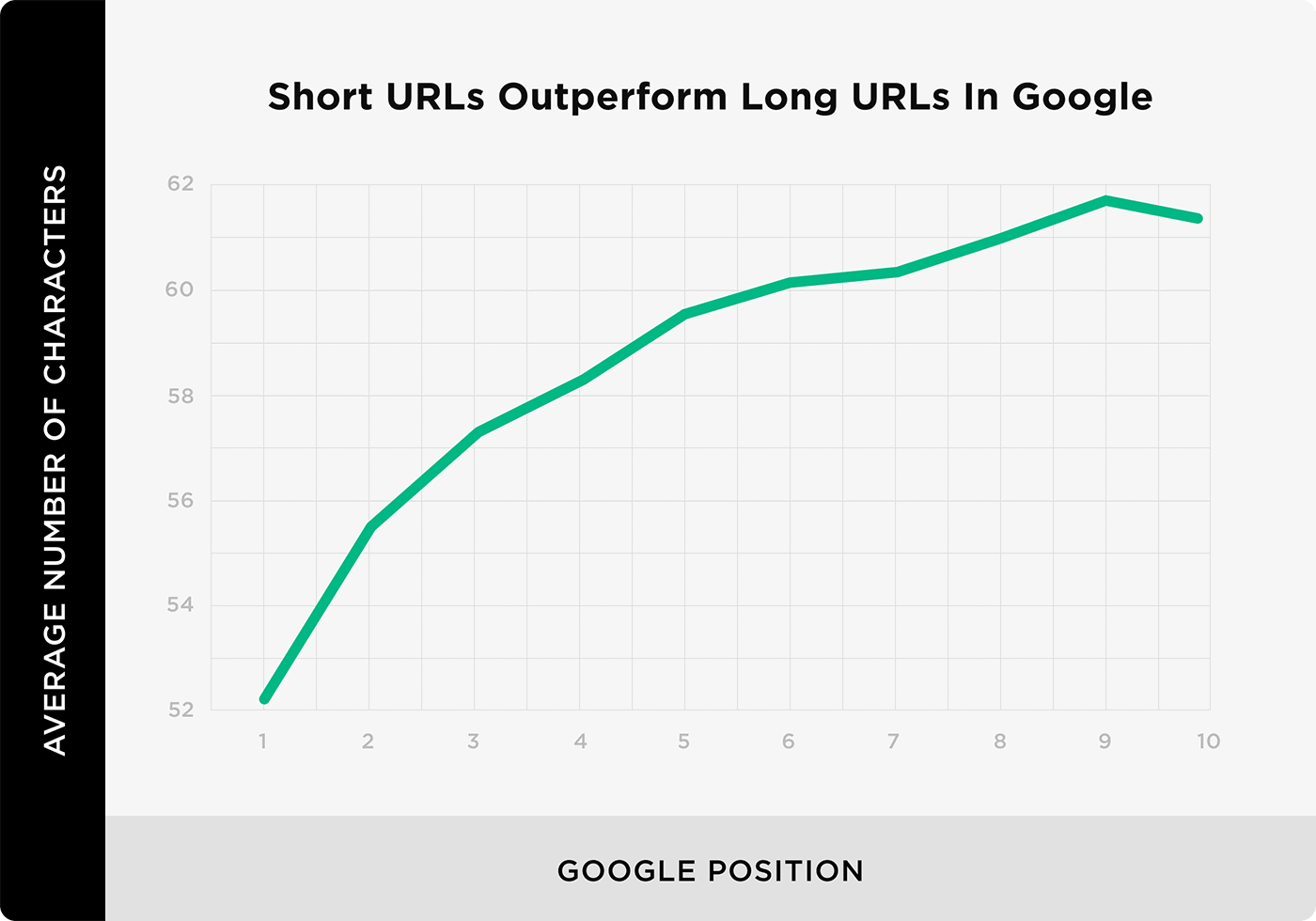
This is why I recommend short, custom URLs for every post.
For example, lots of blogging platforms (including WordPress), generate URLs based on your blog title.
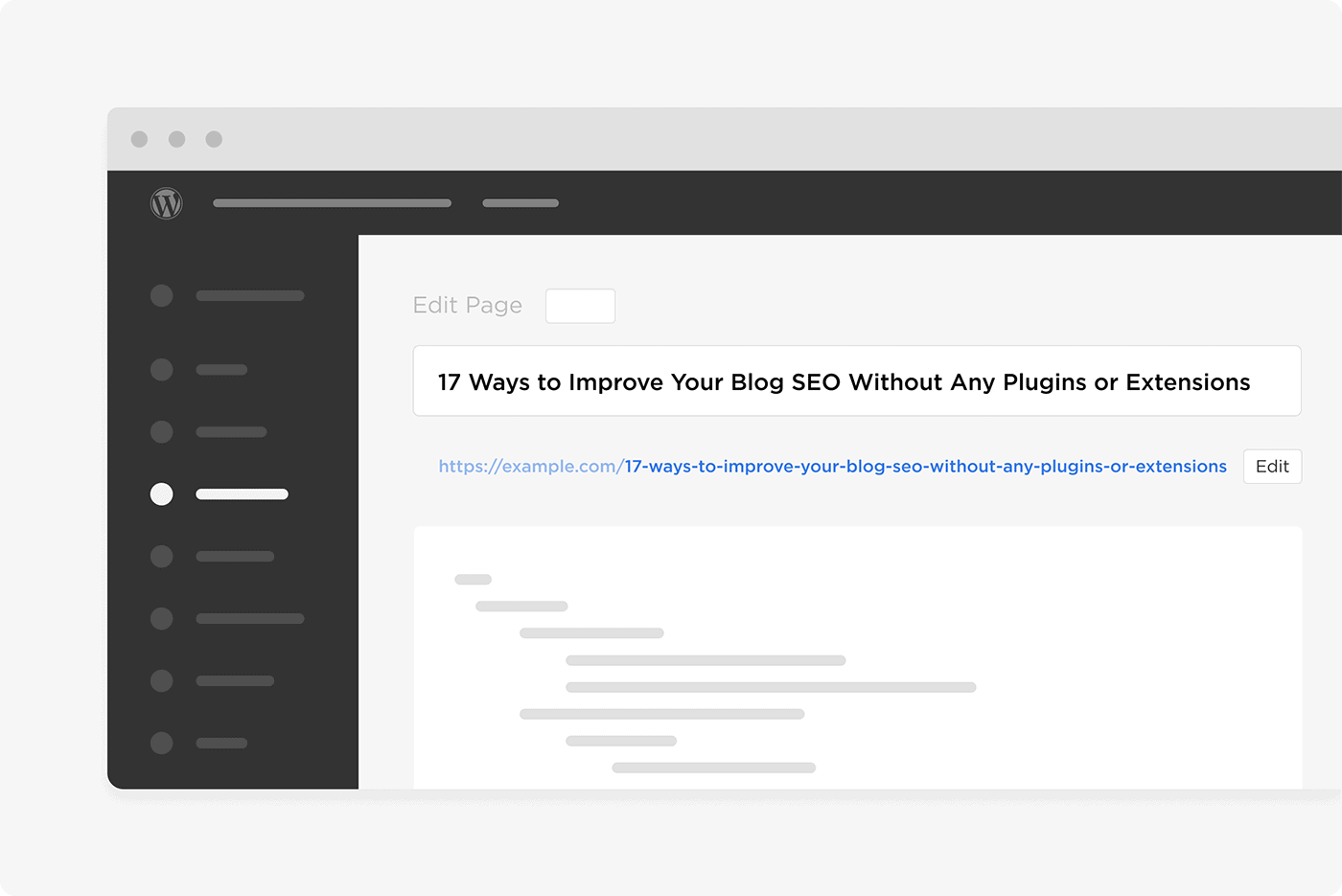
But you can easily edit your URL to make it shorter.
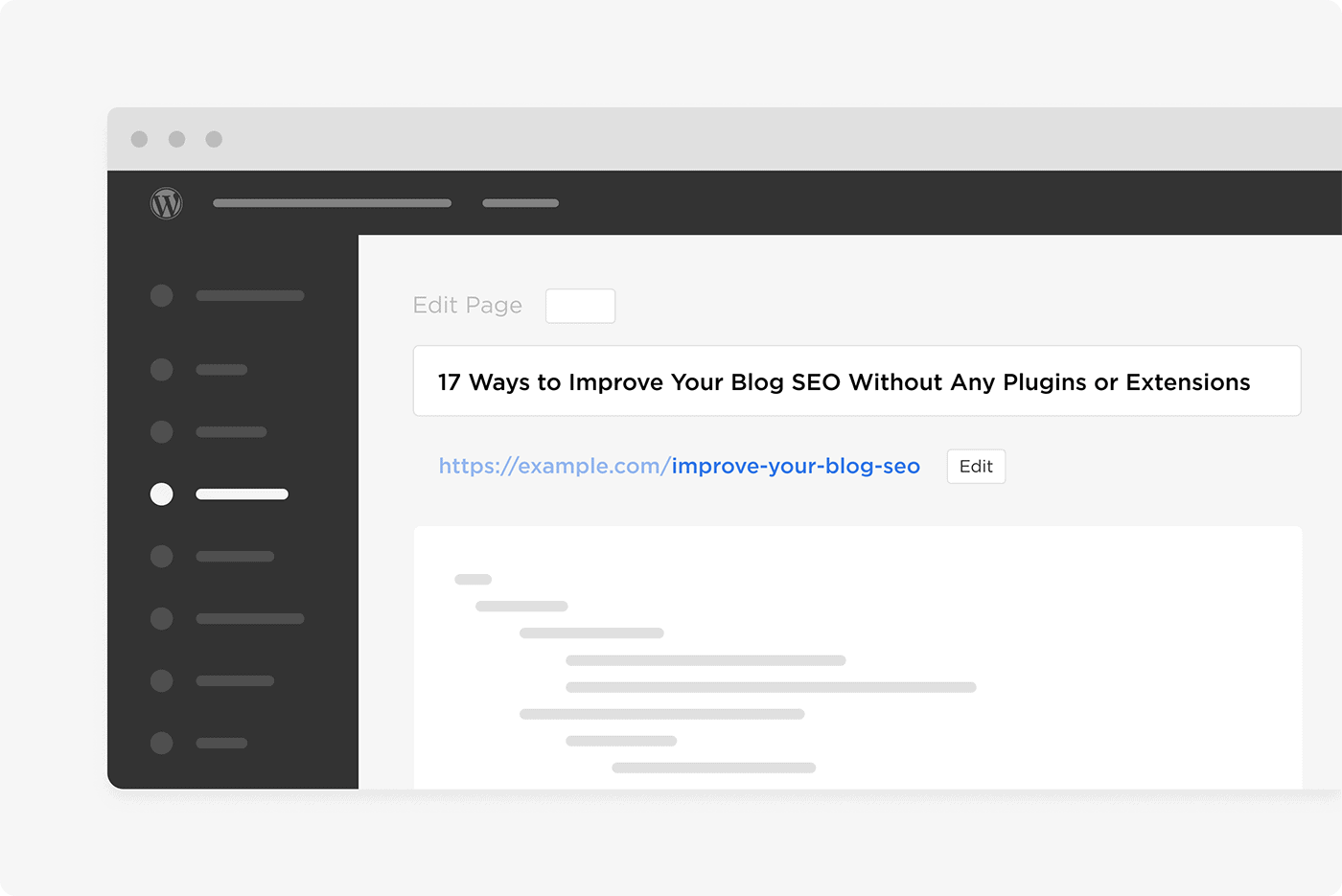
And as long as your URL contains a keyword, you’re good to go.
But that’s not the only issue with long URLs:
Depending on how your blog is setup, your posts can end up with dates in your URL.
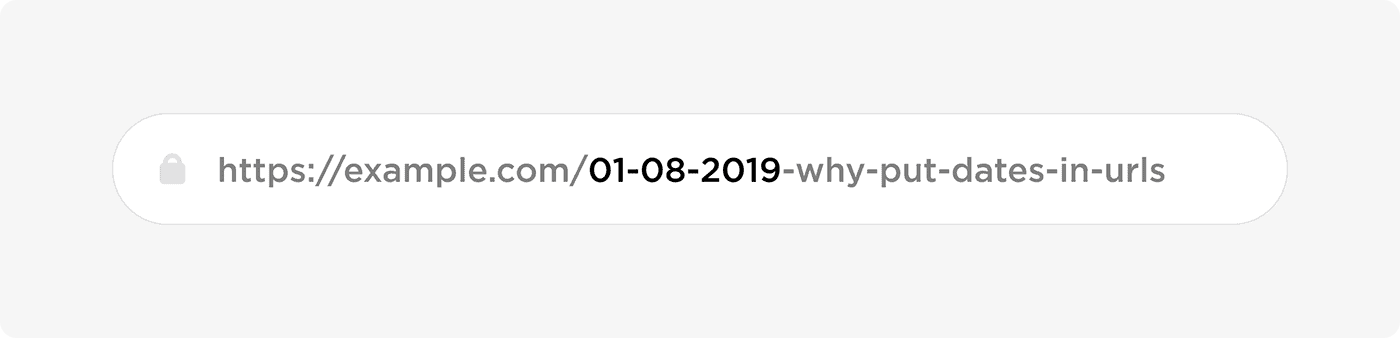
This adds extra junk to your URL that can hurt your SEO. But it also makes your older posts seem… old.
And even if you go back and update your old content, the date in the URL stays the same.
A custom, evergreen URL for every post sidesteps both of these issues.
Write Unique Meta Descriptions
We analyzed over 5 million Google search results.
And one of the most interesting findings from our study was that meta descriptions can increase organic click-through-rate.
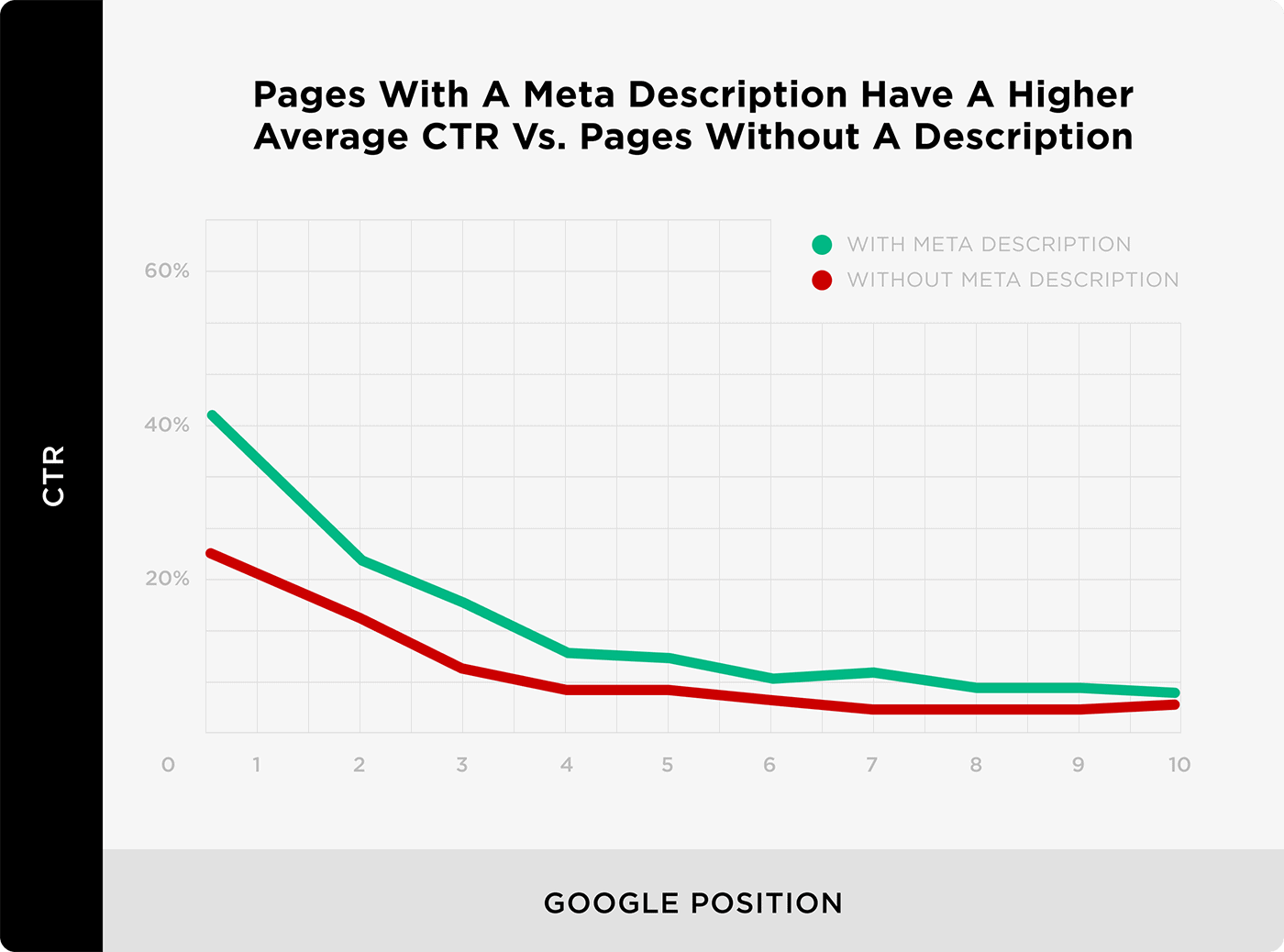
So you definitely want to write a custom meta description for every post that you publish on your blog.
If your page is missing a meta description, Google will create its own based on the content on your page.

Sometimes their description will encourage people to click. But most of the time, a hand-written description will work much better.
Note: You don’t need to include your keyword in your meta description. Google doesn’t use descriptions in their algorithm. This is purely to increase organic CTR in the SERPs.
Internal Link Between Posts
Want an easy, white hat SEO technique that actually works?
Try internal linking between different posts on your site.
The easiest way to take advantage of internal linking is to follow this 2-step process whenever you publish something new:
First, add 5-10 internal links to your new post. These links should point to older posts on your site.

Second, add 5-10 internal links from older posts to your new post.
And while you’re in there, make sure to use anchor text that describes your post. So instead of anchor text like: “this post”, use anchor text: “this post about user experience”.
That’s all there is to it.
Noindex Category and Tag Pages
Category and tag pages are almost 100% duplicate content. Which can cause serious SEO problems.
This is why I recommend that most sites add the “noindex” tag to category and tag pages. That way, these somewhat useless pages won’t get indexed by search engines.
The only exception to this rule is if these pages bring in traffic to your website. In that case, you can keep them around.
But if you’re like most bloggers, your category and tag pages should have the noindex tag applied to them.
Create a Blog Sitemap
One of the cool things about blogs is that, because they’re always putting out new stuff, Googlebot usually crawls them all the time.
But to make it super easy for Google to crawl and index all of your posts, I recommend using a sitemap. A sitemap is simply a list that links to all of your posts and pages.
Many SEO plugins will automatically create a sitemap for you. For example, Yoast created a plugin that links to posts and pages.

Speaking of pages, this is another reason to use a sitemap on your blog. Unlike blog posts that show up on your blog feed, pages are sometimes buried in your site.
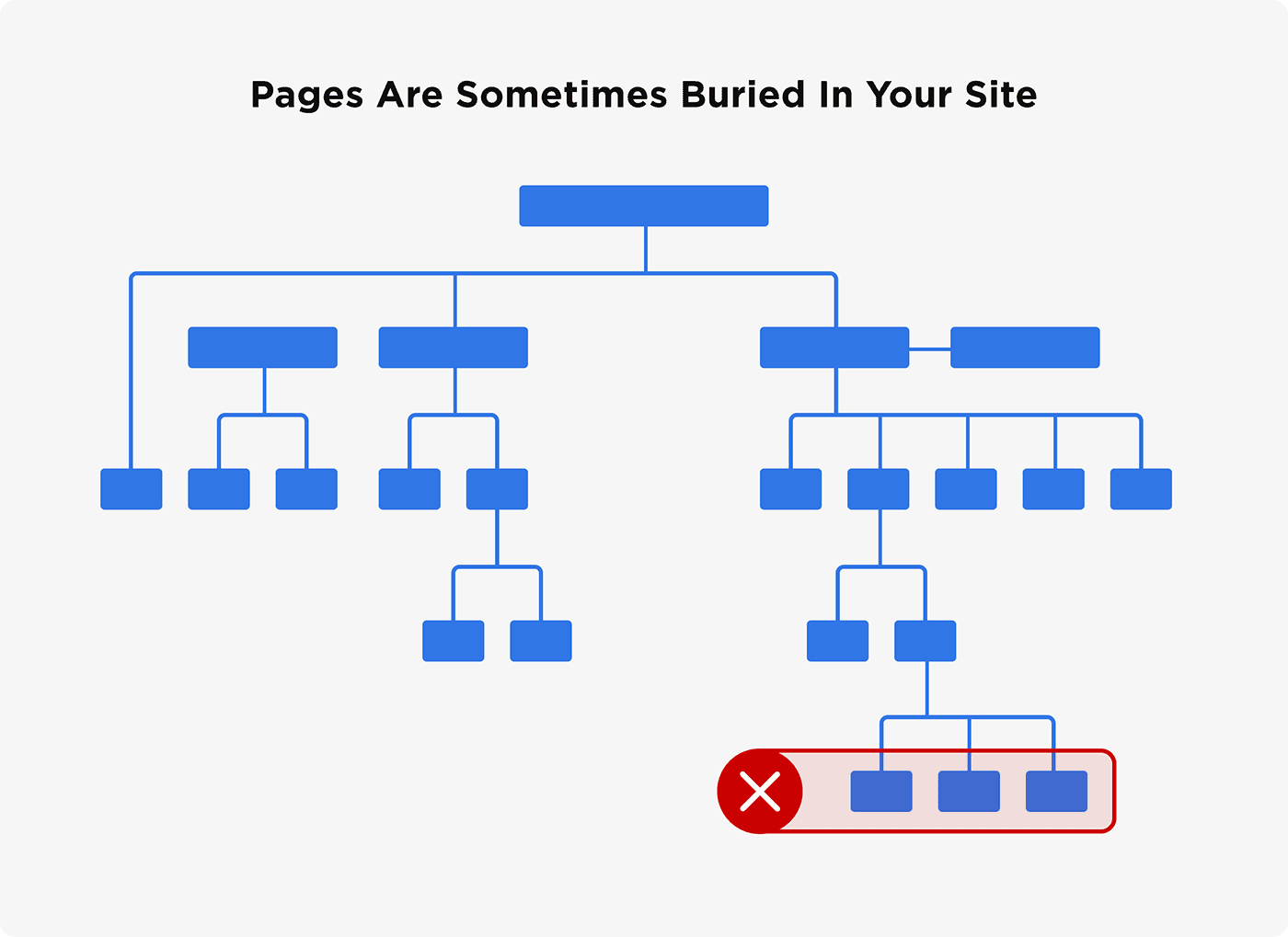
This can make it hard for search engines to find them. Internal linking to those pages can help. But again, it never hurts to also have your pages listed on a sitemap.
Monitor Your SEO With Search Console
Search Console is a must-have SEO tool for any blogger.
There are a ton of featured-packed into the GSC.
But there are only a few features that you need to pay attention to for blog SEO.
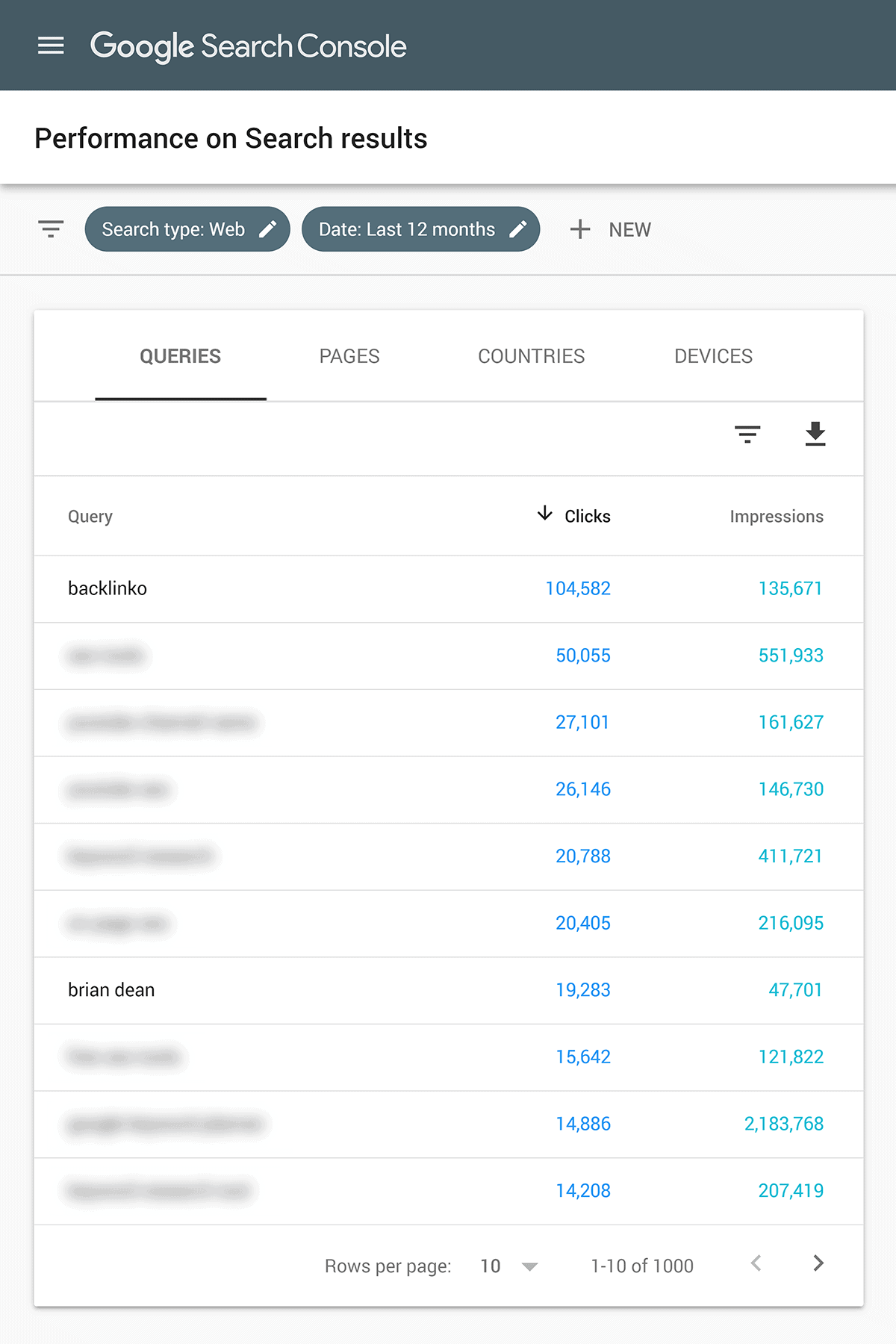
The first is the Performance Report.
This report shows you all the keywords that you currently rank for in Google (and how many people click on your result).
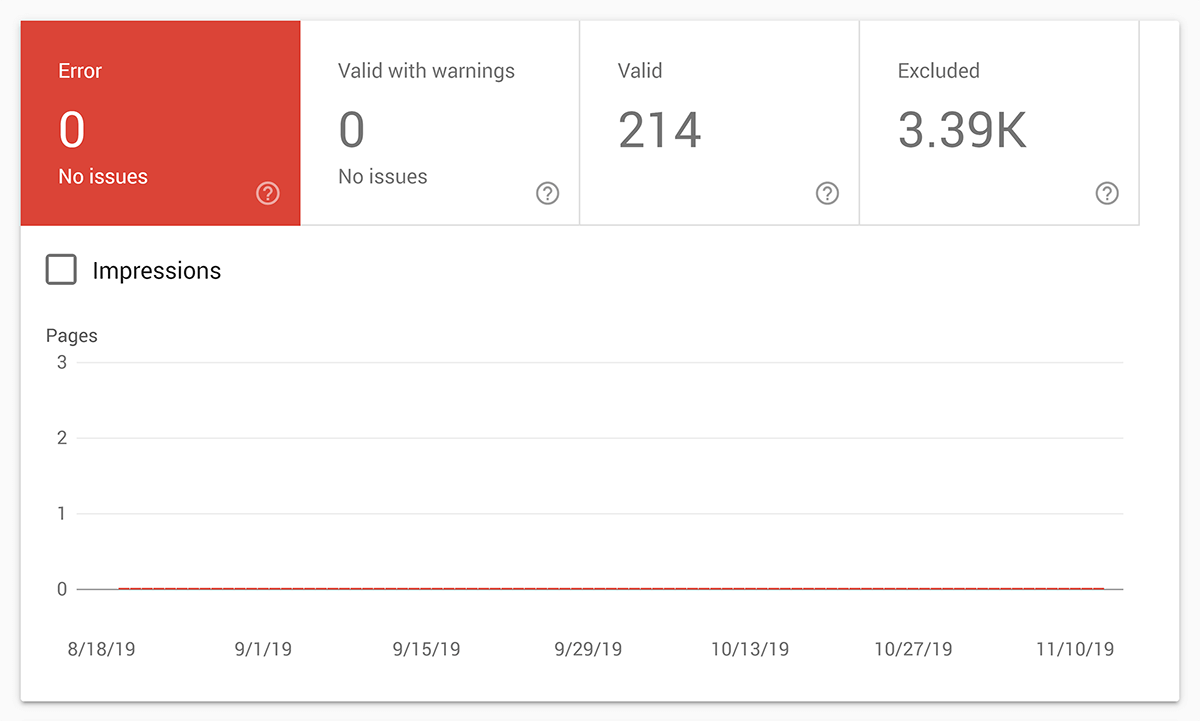
You also want to check out the “Coverage” and “Sitemap” sections.
The Coverage feature shows you how many pages you currently have indexed in Google.
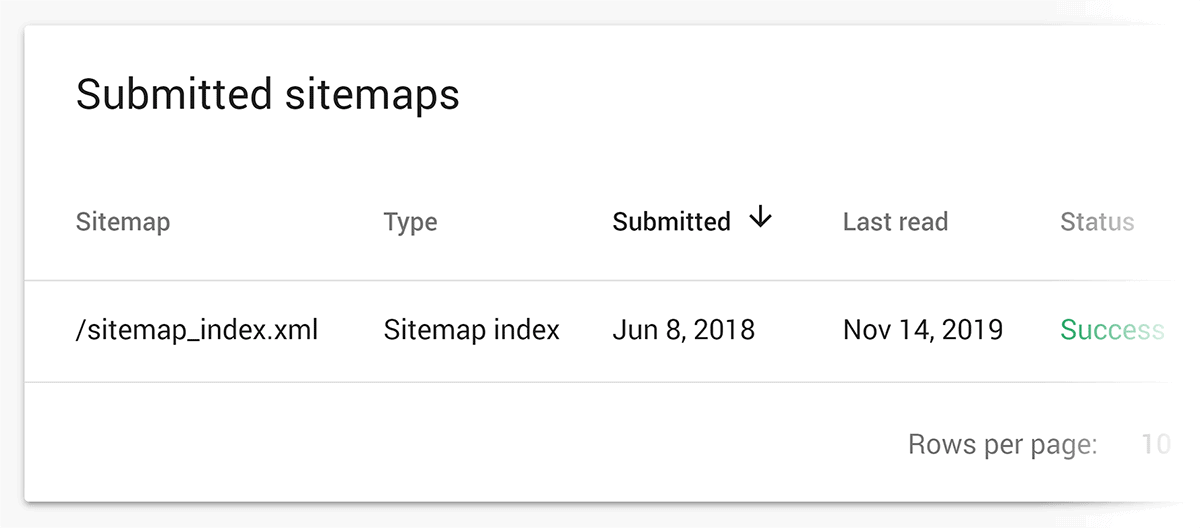
And the Sitemap feature shows you the latest sitemap Google has seen. It also lets you submit a new sitemap.
Optimize Your Posts for Featured Snippets
You’ve probably seen Featured Snippets before.
They’re short snippets of text that Google pulls from the search results. And they typically appear at the top of the organic results.
Google tends to grab text from blog posts and articles to use in Featured Snippets. And considering that blogs pretty much only publish articles, Featured Snippet optimization should be part of any blog’s SEO plan.
To tap into Featured Snippets, you need to first figure out what type of Featured Snippet that you’re aiming for.
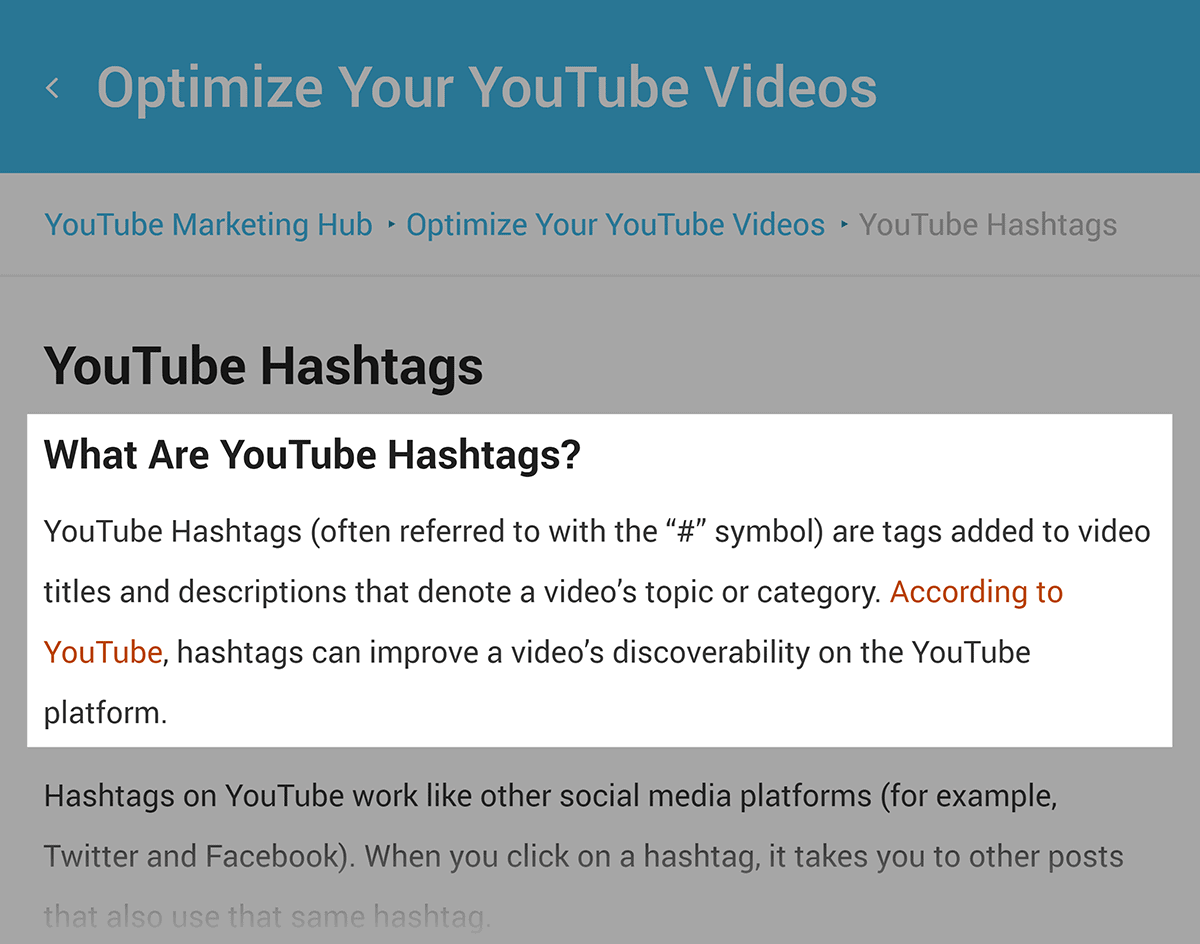
If you want to rank for a “Definition Snippet”, then make sure to include a definition that Google can use in your post.
Here’s an example:
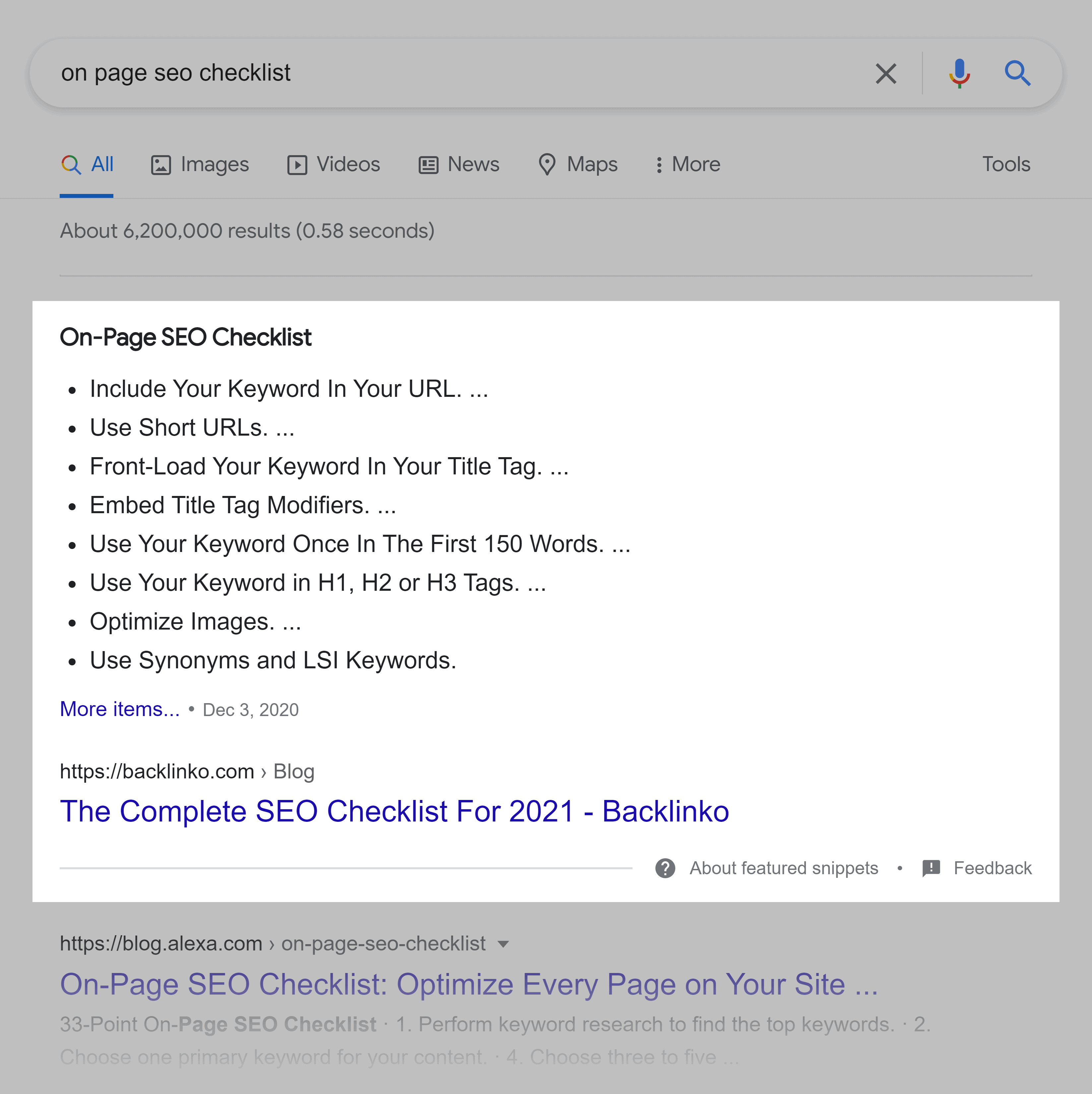
Another common form of Featured Snippet is a “List Snippet”.
The best way to optimize for these is to use lots of subheadings in your post.
For example, our content currently ranks in this Featured Snippet.
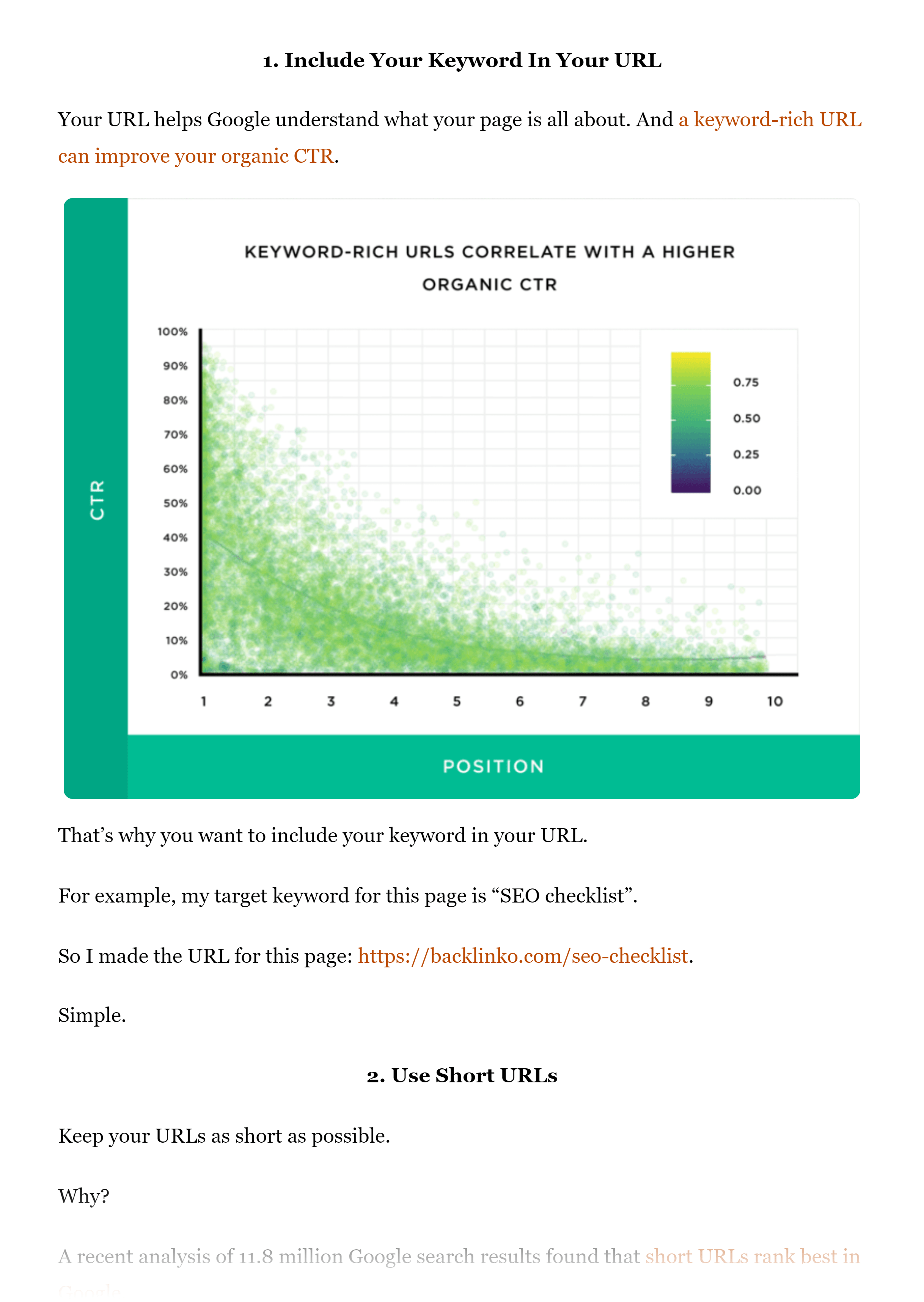
Each of the items that Google puts on that list is from a subheading from that post.
Reduce Your Bounce Rate
Whether or not Bounce Rate is a Google ranking factor is up for debate.
That said:
A handful of industry studies have found a correlation between bounce rate and rankings.
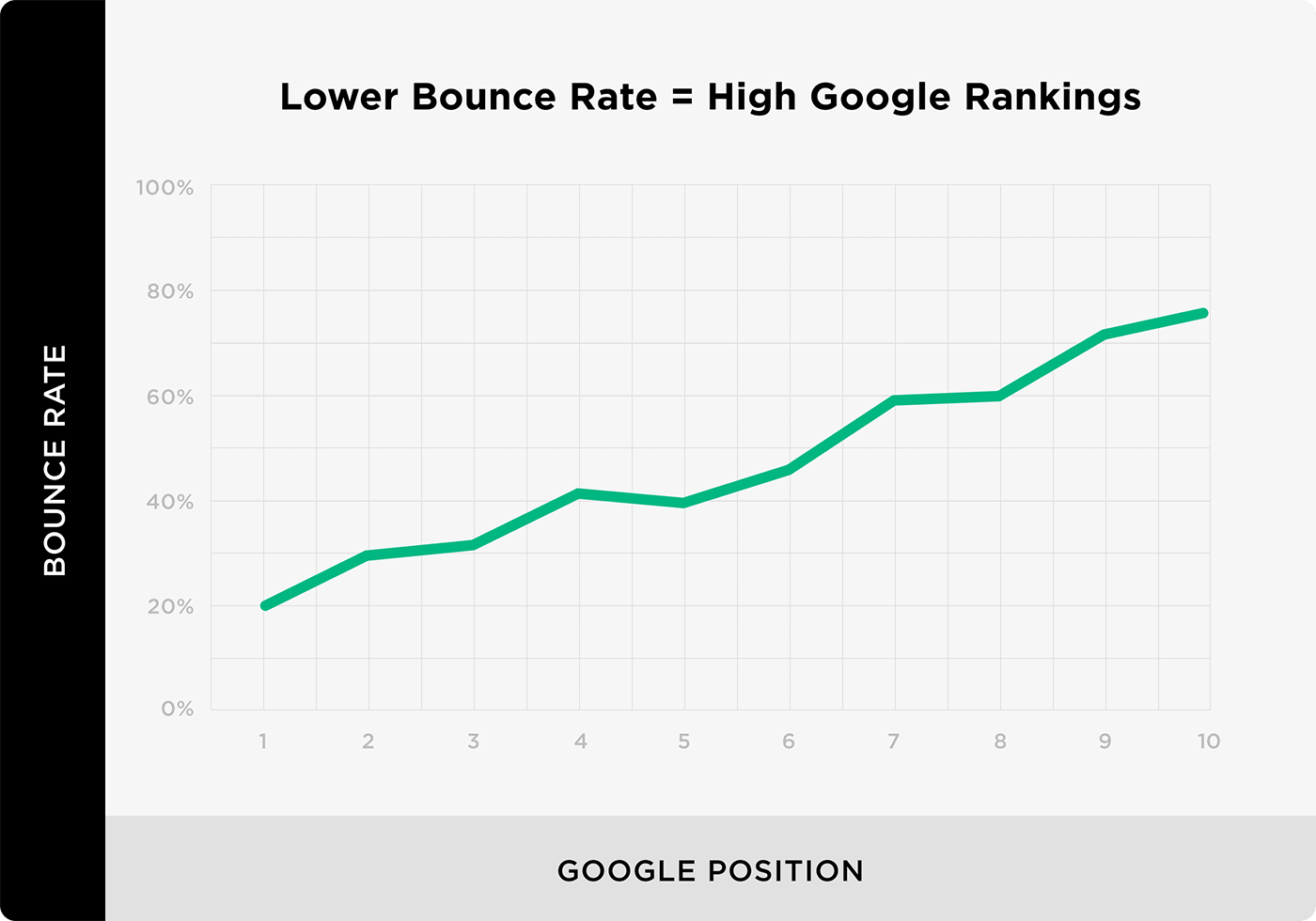
Does correlation mean causation? No.
But there’s really no downside to reducing your bounce rate. And it can help improve your SEO rankings.
So it makes sense to spend some time improving your bounce rate.
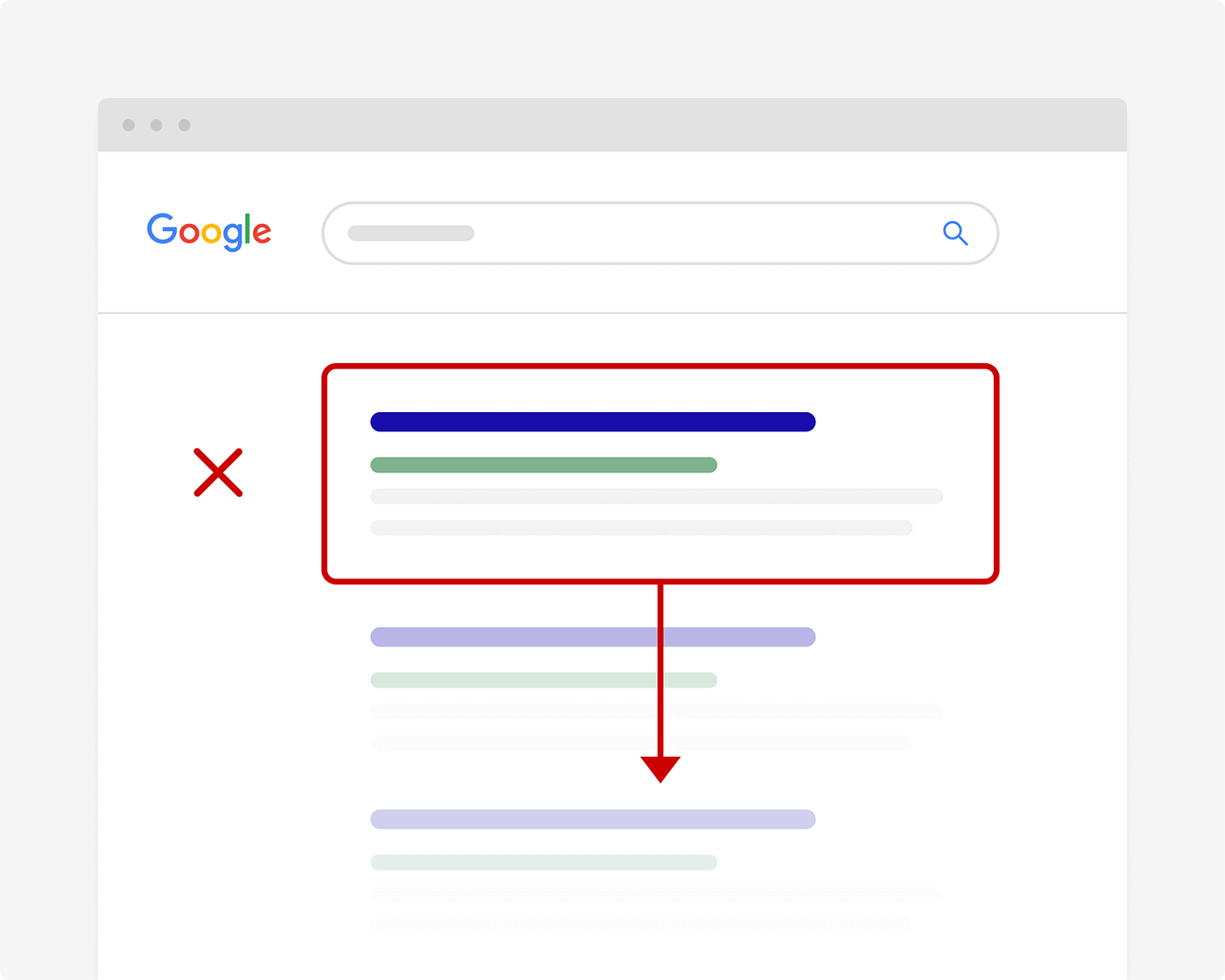
At a high level, the best way to reduce your site’s bounce rate is to publish content that gives Google searchers what they want.
(In other words: content that satisfies search intent.)
When someone lands on your post and says: “Nice! This is exactly what I’m looking for”, they’re going to stick around and read your stuff.
But if your post isn’t a great fit, they’ll bounce.
And if enough people bounce, Google will notice and downrank you.
Other than that, I recommend focusing on your blog design.
Users make a split-second decision to stay or leave your blog. And if your blog looks super professional, they’re more likely to stick around.
In fact, when I look at our Google Analytics data, I notice that our professionally designed guides tend to have a slightly lower bounce rate than normal posts.
Publish Content Designed for Link Building
At this point your blog is primed for SEO success.
That said:
Your blog can have amazing, world-class content. And you can apply every search engine optimization technique on the planet.
But for your blog to rank in Google, you need to build backlinks. And lots of them.
Fortunately, because you run a blog, your site is primed to get links. After all, you’re consistently publishing high-quality content. The exact type of content that other bloggers want to link to.
And if your main goal with content marketing is to get more links to your blog, then I recommend focusing on
An analysis of 900+ million posts found that these specific types of content got more links than average.
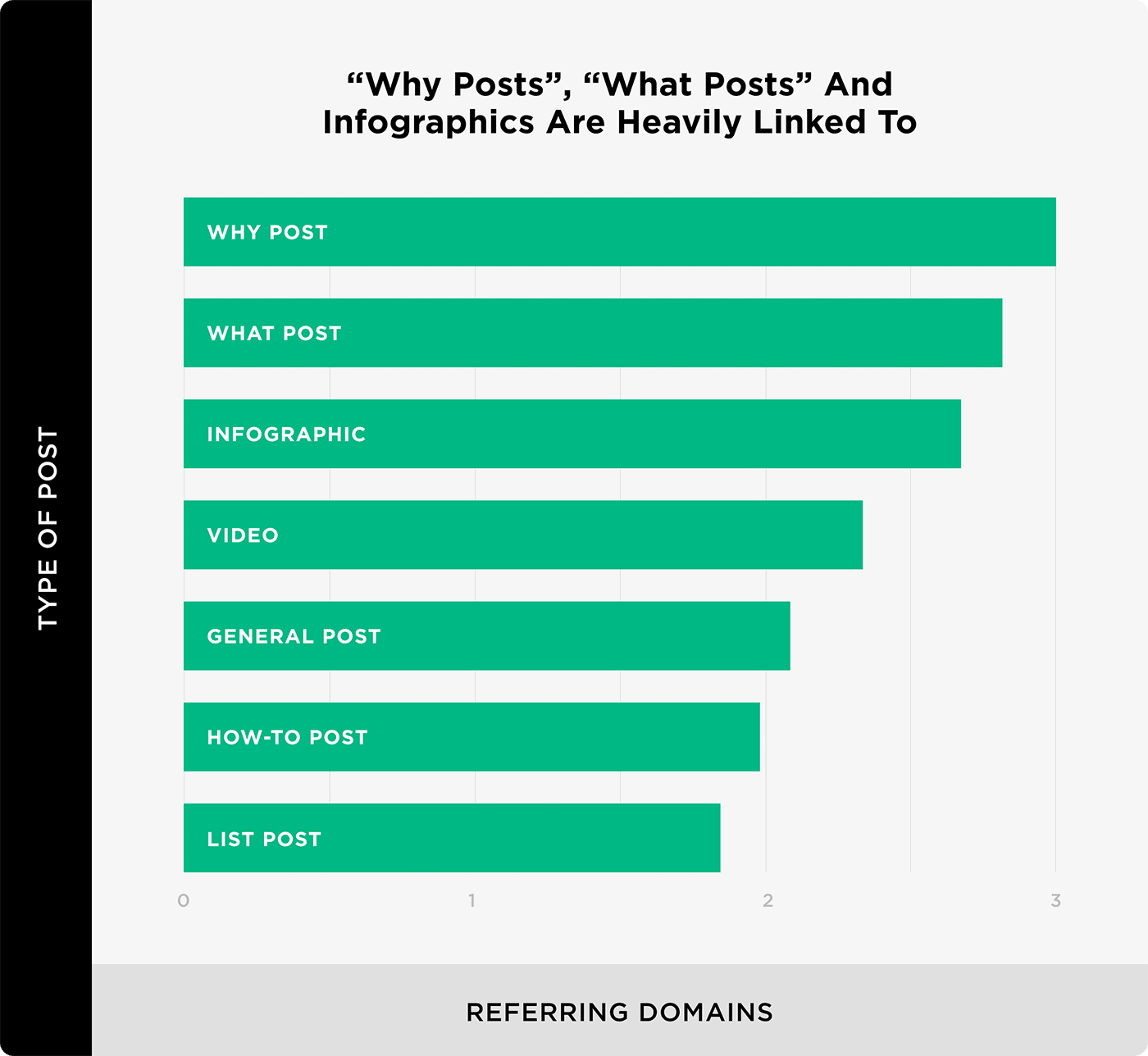
That’s not to say you should ONLY publish why posts and infographics. But when it comes to building links, these formats tend to perform best.
Learn More
On-Page SEO: Anatomy of a Perfectly Optimized Page: Everything you need to know about on-page optimization on a single page. Includes advanced strategies.
How to Write a Blog Post: A guide to writing, publishing and promoting blog content that generates shares and backlinks.
Advanced Keyword Research Tutorial: I didn’t have a ton of room to get into keyword research here. But if you want to learn how to find and choose keywords for SEO, you’ll learn a lot from this video.
Complete Guide to SEO Content: For many blogs, SEO isn’t just their #1 goal… but they’re only goal. And this in-depth guide shows you how to create content for SEO.