How to Launch an SEO Campaign
Written by Brian Dean
![How to Launch an SEO Campaign [Template Included]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fapi.backlinko.com%2Fapp%2Fuploads%2F2020%2F05%2Fseo-campaign.png&w=3840&q=75)
This post outlines exactly how to create a successful SEO campaign.
(Step-by-step)
The best part?
You’re going to see lots of real-life examples of these steps in action.
Let’s dive right in.
What Is an SEO Campaign?
An SEO campaign is a coordinated effort to improve a website’s search engine rankings. Common elements of SEO campaigns include finding keywords, publishing content, and creating backlinks, all with the goal of improving online presence.
With that basic explanation out of the way, let’s get into the specific steps:
Step #1: Find Keywords
Keyword research is the first step of any successful SEO campaign and SEO strategy.
Specifically, you want to generate a list of about 10 different keywords.
(These are keywords that you’ll optimize specific pages on your site around.)
1. Find Keyword Ideas With Google Keyword Planner
Google Keyword Planner is a free keyword research tool from Google.
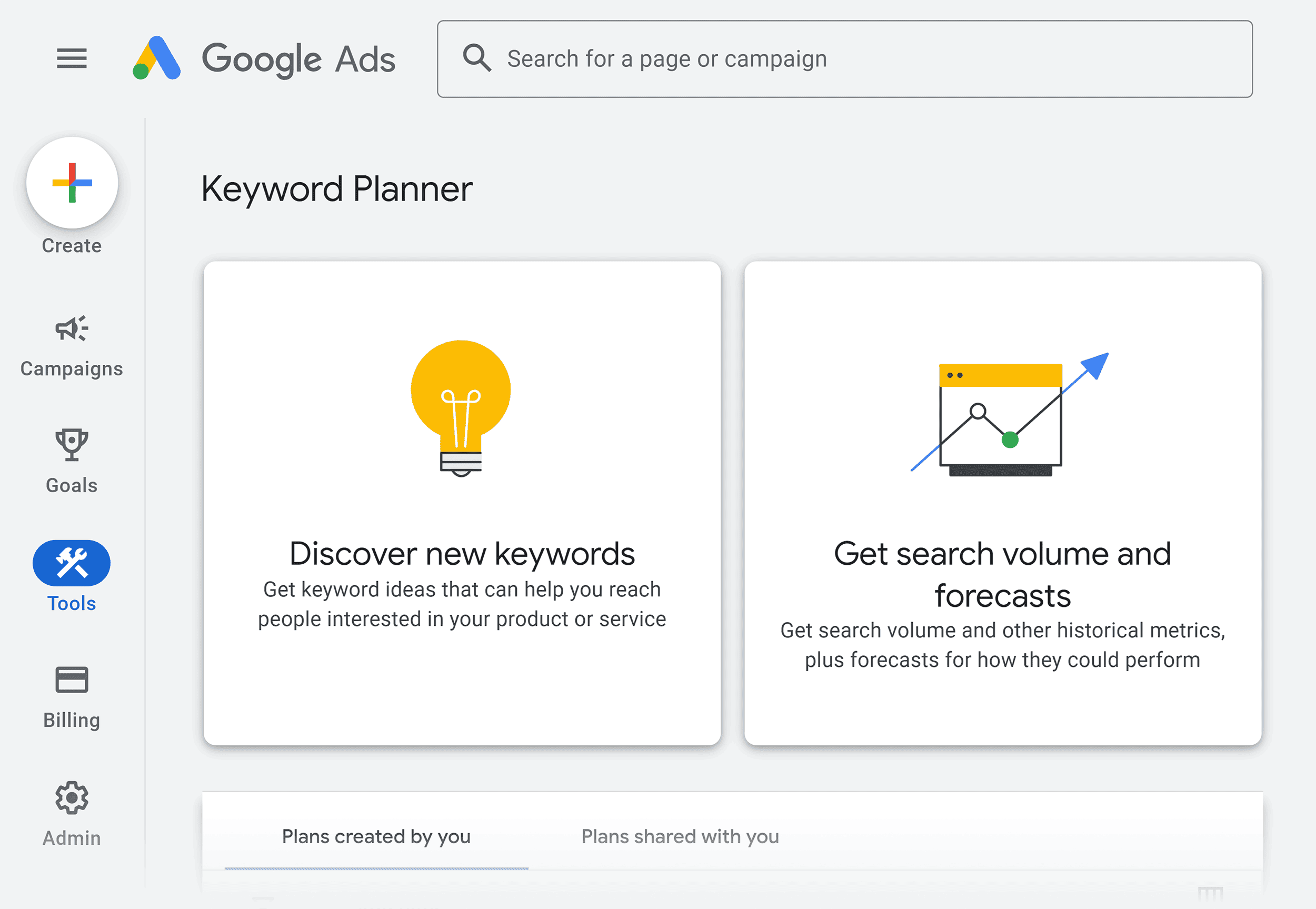
The great thing about the Google Keyword Planner is this:
All of the data comes straight from Google.
To use it, just enter a word or phrase and you’ll get a list of keyword ideas:

2. Find Long Tail Keywords With Backlinko
Our free keyword research tool is designed to generate lots of different keyword ideas.

Which means it’s great for uncovering low-competition, long tail keywords.

3. Copy Your Competitors’ Keywords
Here’s where you see the exact keywords that your competitors’ already rank for.
To do this, you’ll need to use a tool, like Semrush.
No matter which tool you end up using, the process is exactly the same.
First, find a competitor that’s doing really well with their SEO.
Then, pop that competitor’s homepage into the tool:

And you’ll get a complete list of keywords that the site ranks for:

4. Choose 10 Keywords
Now that you have a list of keywords, it’s time to choose the best 10 from your list.
But how do you choose the “best” keywords?
You want to pick keywords that have the best combination of these 3 key factors:
1. Low Competition: This is especially important if you’re just starting out. But even if your site is already established, you still want to go after keywords that aren’t super competitive.
So: how do you know if a keyword is competitive or not?
Your first option is to look at the search results:

If you notice that they’re packed with authoritative sites, you probably want to go with another keyword.
For more precise keyword competition analysis, look at Keyword Overview’s AI-powered metrics.

Personal Keyword Difficulty indicates how hard it’ll be to rank in the top 10 Google results, based on how well your content aligns with the keyword.
Topical Authority shows how well your domain’s content matches the keyword topic. Higher scores mean better chances of reaching the top 10.
Potential Traffic estimates the visitors you could get, based on your Topical Authority, SERP competitors, and potential position.
Potential Topic Traffic shows possible visitors from high-volume variations of your keyword.
Potential Position predicts where your domain might rank with quality content.
Compare these metrics to the current top 10 sites to gauge if the keyword is right for you.
2. High Search Volume: Now it’s time to see how many people search for the keywords on your list.
Obviously, the higher the search volume, the better.
That said, popular keywords also tend to be more competitive.
For example, 156.4K people search for “paleo diet” every month.

This partly explains why that search term is competitive.

So you’d want to go with a keyword that’s less popular… which means it’ll also be less competition:

3. Customer Fit: You want to find keywords that your customers actually search for.
That said, this doesn’t necessarily mean that they need to be ready to buy something right that second.
For example, take my site: Backlinko.com.
Backlinko is an SEO training company.
In my case, people that search for “best SEO courses” would probably have a really high conversion rate for me.
Unfortunately, very few people search for super-specific keywords like that:

That’s why I target keywords that my customers search for when they’re not looking for courses.
(Also known as “informational” keywords.)
In my case, I target terms like “on page seo”, “link building”, “seo tools” and more.

That said:
You still want to make sure people searching for information keywords will become buyers at some point.
To do that, just check out the “Top of page bid” in the Google Keyword Planner:
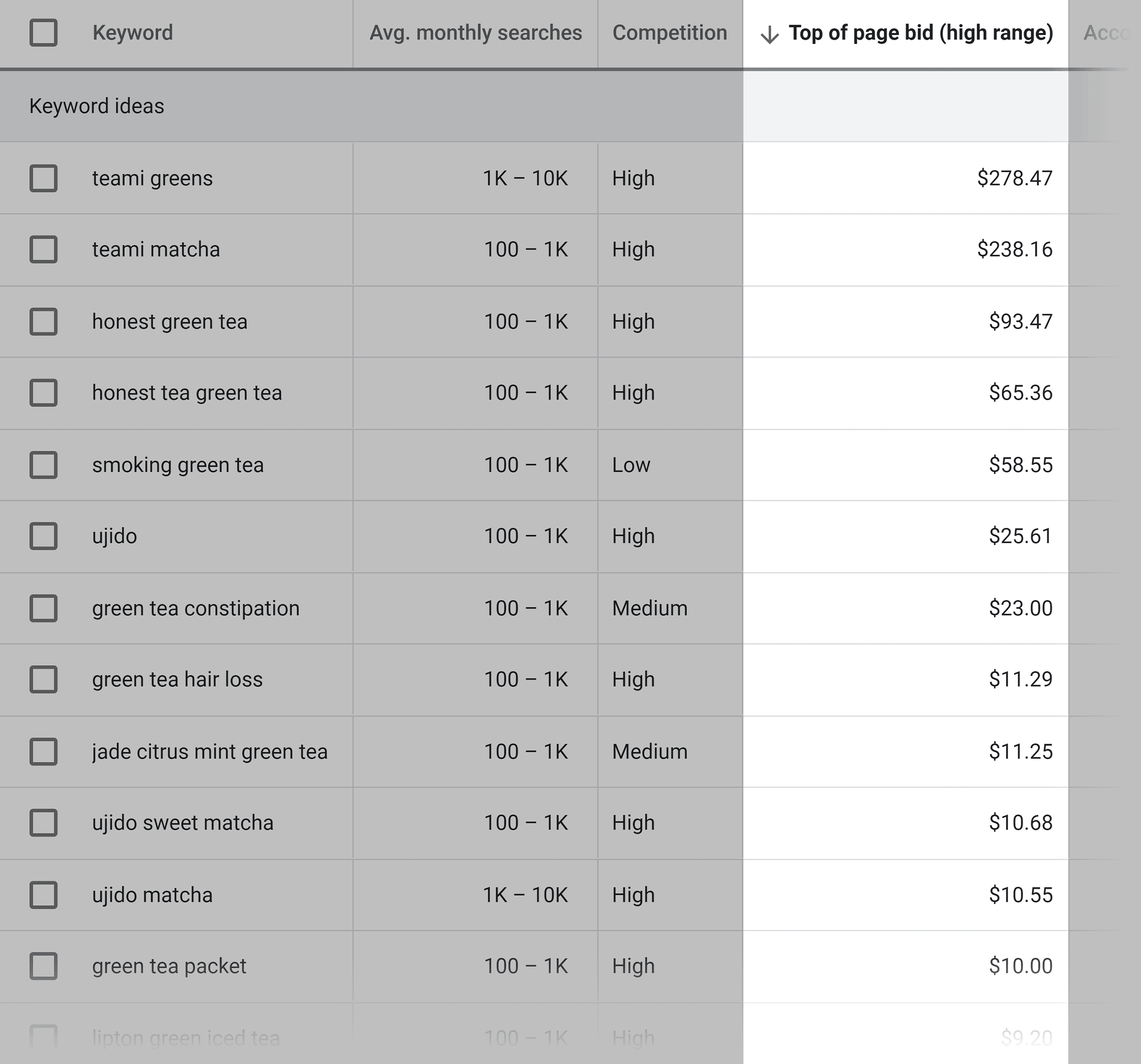
This represents the PPC cost for a single click in Google Ads.
Further reading: How to Align SEO and PPC
And if people are paying money to advertise for a keyword, that means that the traffic can be monetized.
Step #2: Publish High-Quality Content
Now that you have a list of 10 keywords, it’s time to publish content optimized around those terms.
Specifically, high-quality content that’s optimized for SEO and these relevant keywords.
1. Write Long, Comprehensive Content
Back in the day publishing short, 500-word blog posts worked really well for SEO.
Not anymore.
In fact, one industry study found that longer content clearly ranks best in Google.
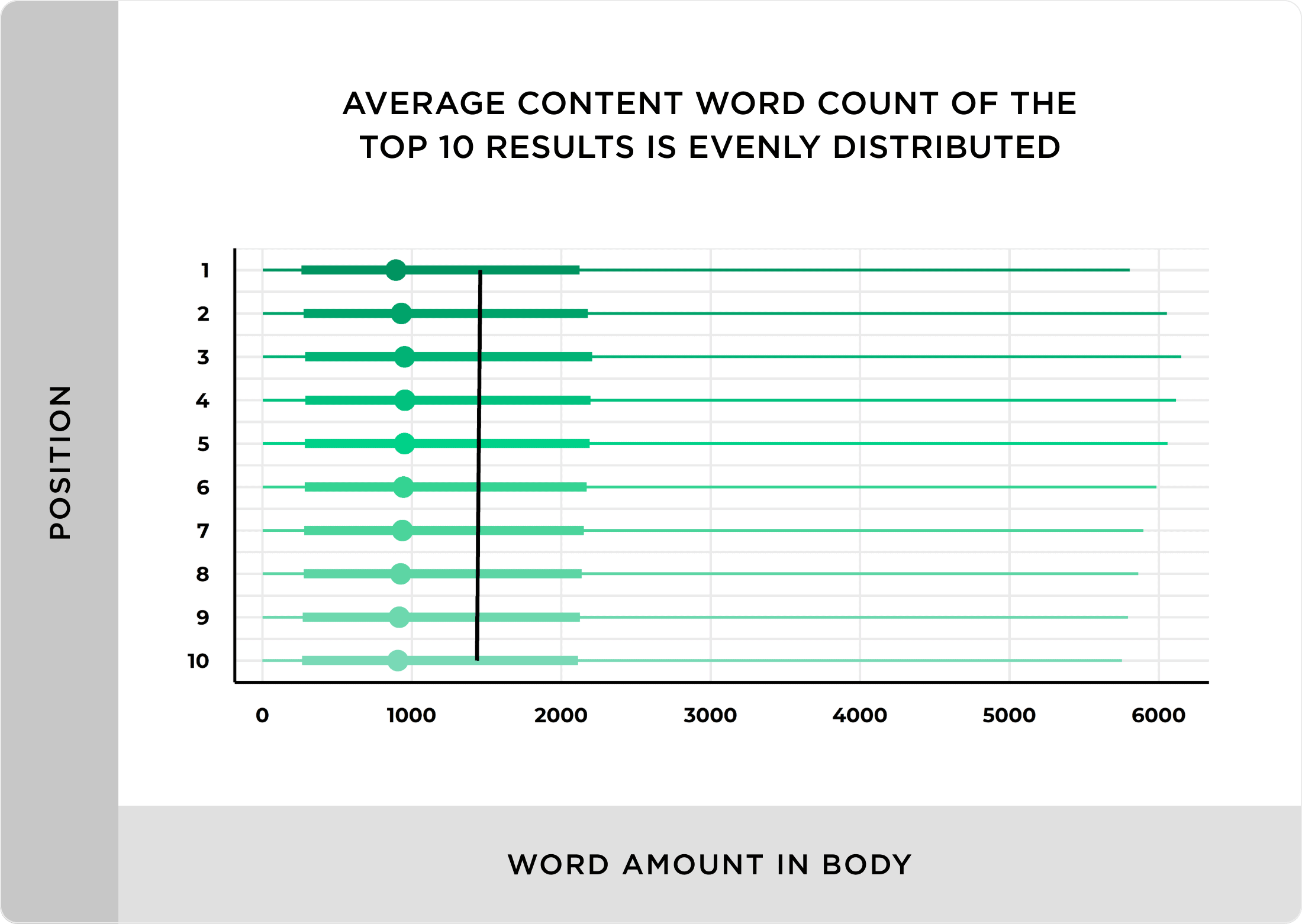
As you can see in that chart, there’s a correlation between word count and search engine rankings.
I’m not saying that you should write 3,000 words of fluff.
Instead, your goal is to cover an entire topic on one page.
(And it usually requires a lot of words to do that.)
For example, some time ago I decided to write a post about Mobile SEO.
Instead of a post like “5 tips for optimizing your site for mobile devices”, I wrote a complete guide:

And because my content covers pretty much everything there is to know about mobile SEO, it ranks #2 on Google for my target keyword:

2. Create Visual and Data-Driven Content
Visual content can be a great way to get more social media shares and backlinks.
For example, Digitaloft is an SEO and digital PR agency in England.
A few years ago, they were approached by a company that launched an awesome platform that helps beauty shoppers find the best prices on their favorite products.
The problem was:
The coverage the client was getting often didn’t include links, missing the opportunities to add more SEO value.
To solve this, Digitaloft developed a metric to rank and compare various global beauty brands based on search trends, social followings, and engagement metrics:

This metric was also packaged with visually appealing graphics and charts, enhancing its attractiveness and shareability.
How did this content do?
Six years since the launch, the campaign they created has generated over 1,000 social shares:

An influx of backlinks from almost 200 referring domains:

As you might expect, these links and shares boosted his client’s search engine traffic:

Since the index and visuals are updated yearly, the client has repeated opportunities to get more page visits, social shares, and backlinks.
3. Publish “Authoritative” Content
A few years ago, BuzzSumo analyzed 100 milion articles.
And they discovered two interesting things:
First, most content gets “zero” links or social shares.
Second, “authoritative” content is great for acquiring links.
What is “authoritative” content?
It’s content that:
- Is written by a legit expert
- Isn’t regurgitated info
- Brings something completely new to the table
Let me illustrate this with an example…
In 2019 I realized that voice search was growing fast.
But when I read articles about voice search, they tended to repeat the same info.
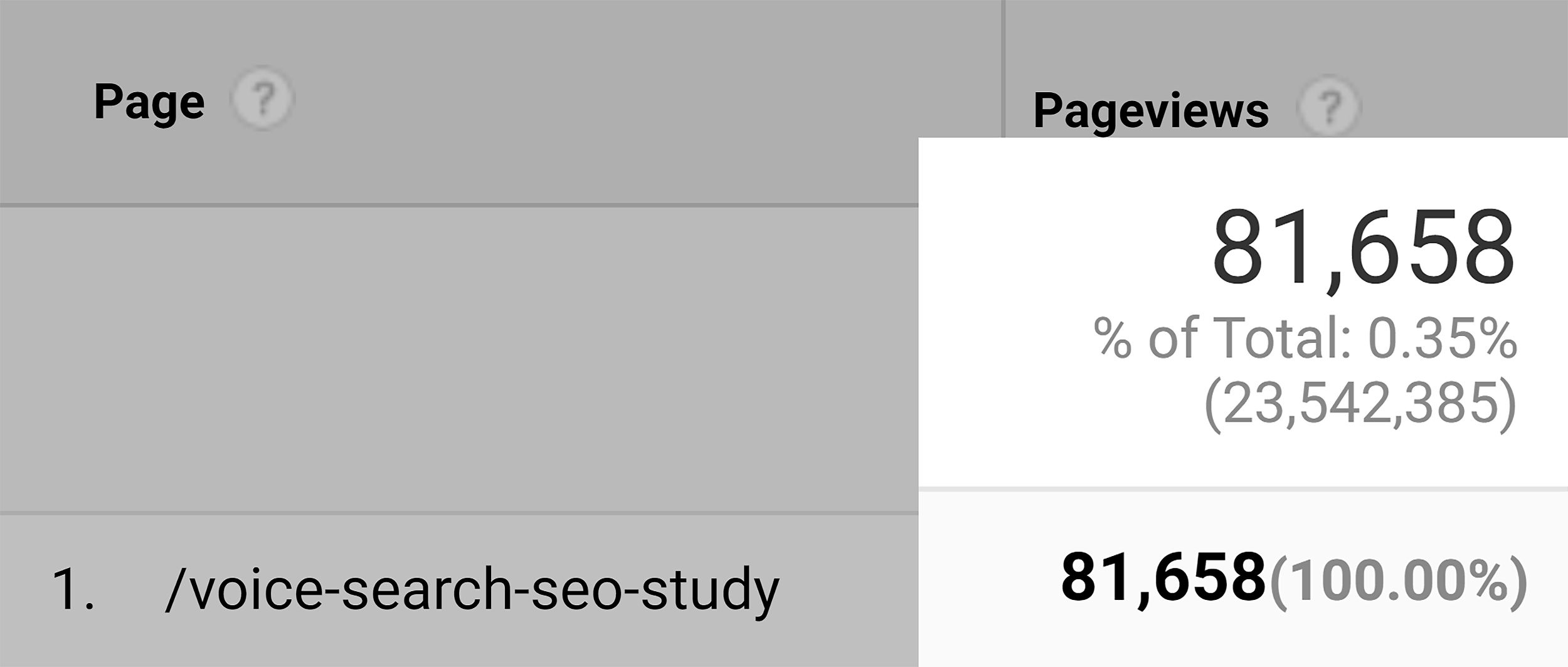
So I decided to create a piece of authoritative content on voice search SEO.

And because that content contained so much original stuff (and was written by an authority in the field), it generated 3.7K backlinks so far:

And ton of traffic:
Step #3: On-Site Optimization
Now that you’ve created a piece of high-quality content, it’s time for the next phase of your SEO campaign: optimizing content.
As you probably know, search engine optimization has changed a lot over the last few years.
And in this step, I’ll show you exactly how to optimize your site the right way in 2026.
1. Short, Keyword-Rich URLs
When it comes to on-page SEO, most people underestimate their URLs.
But as it turns out, your URLs are really important.
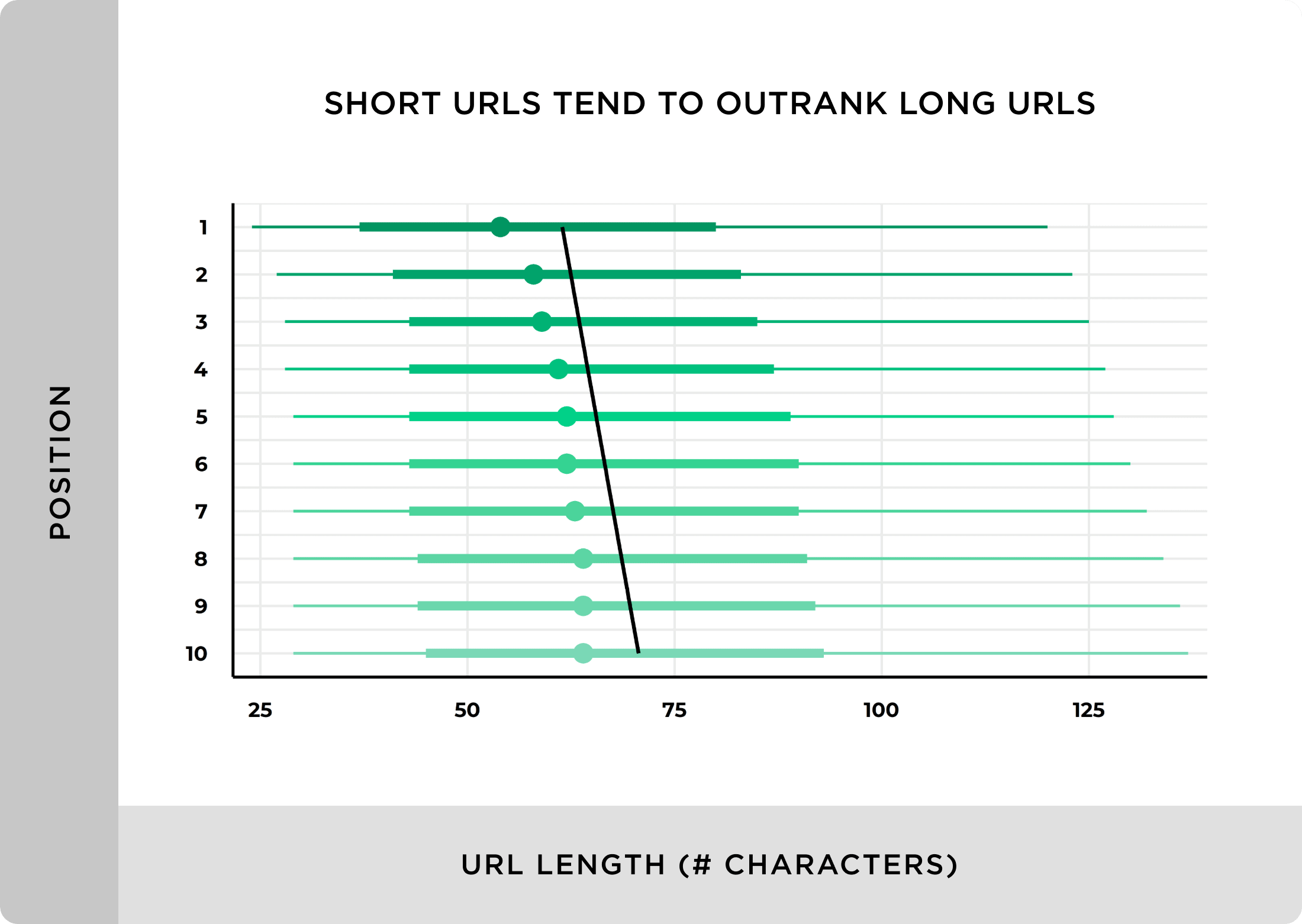
Specifically, you want your URLS to be short and keyword-rich.
For example, take this post from my site about SEO copywriting.

As you can see, the URL is only two words… and contains my main keyword.

2. “Frontload” Your Target Keyword
Whenever possible, put your keyword at the beginning of your title tag.
(Why? Search engines put more weight on terms that show up early on in your meta title.)
Going back to my SEO copywriting post, you can see that I include that keyword early on in my title tag:

(In fact, my title tag starts off with that term.)
3. Use Keyword in First 150 Words
Next, use your target keyword in the first 150 words of your content.
Why?
When Google sees a keyword early in your page’s HTML, it lets them know that term is important.
For example, you can see that I use my target keyword within the first 20 words of this post:
4. Internal Link
Now it’s time to use internal linking.
Specifically, you want to:
- Link from your new post to other pages on your site
- Link from other pages to your new content
These internal links help Google find and index all of your pages. They also send link authority around your site, which helps all of your pages rank better.
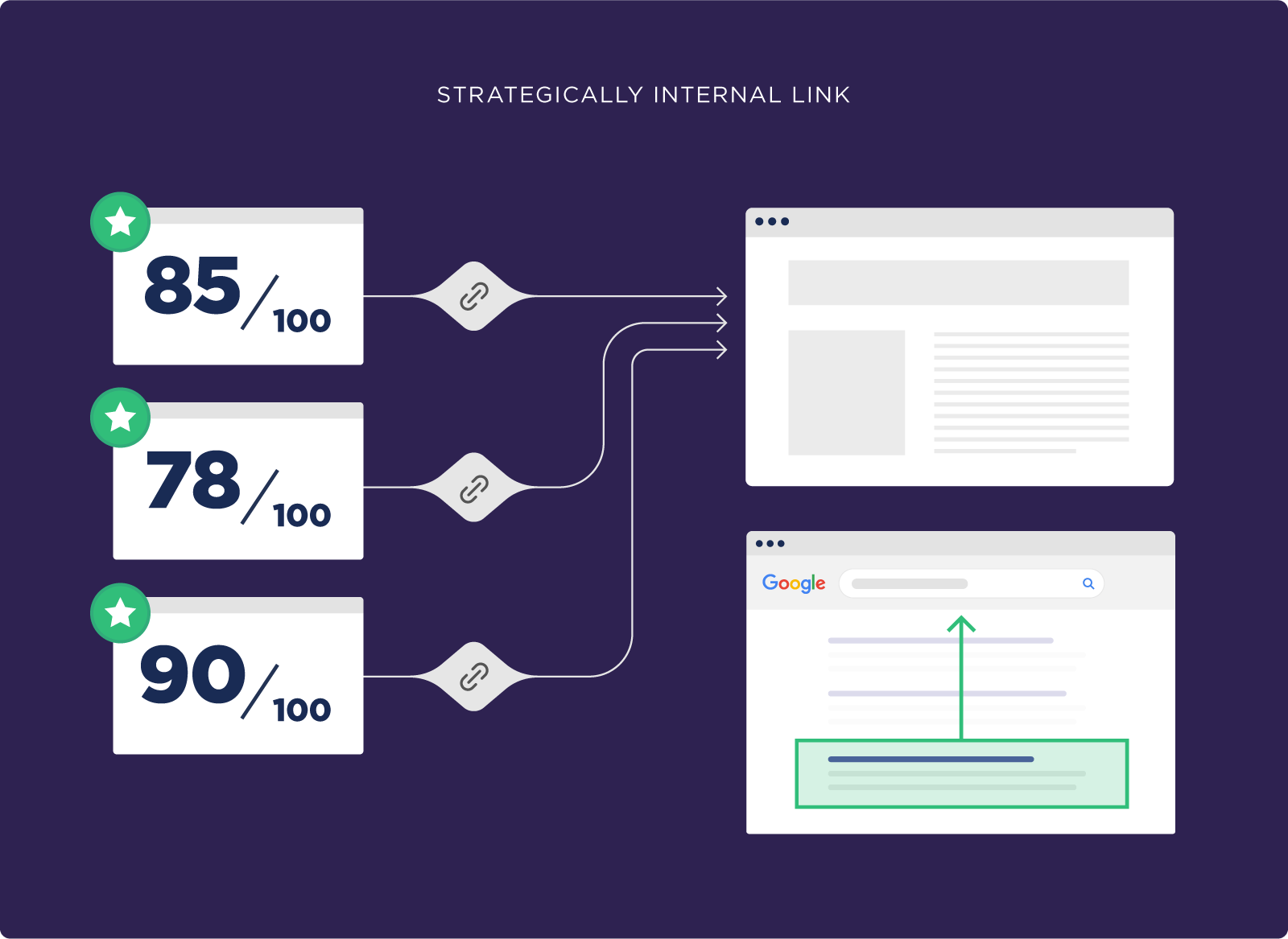
For example, let’s look at this post from my site.

As you can see, I included internal links that point to other pages on my site:

And I also link from other pages to that post:

5. Sprinkle In Synonyms
Finally, include synonyms of the main keyword on your page.
This helps give Google a deeper understanding of your content.
For example, let’s look at my post: 19 New SEO Techniques.

My target keyword for this page is “SEO Techniques”.
So I made sure to optimize my content using the 4 tips I already showed you.
But I also sprinkled in synonyms of “SEO Techniques”, like “search engine optimization strategies”:

Step #4: Build Backlinks
No SEO campaign would be complete without a bit of off-page SEO, in this case – link building.
That’s because links are still an integral part of Google’s ranking algorithm.
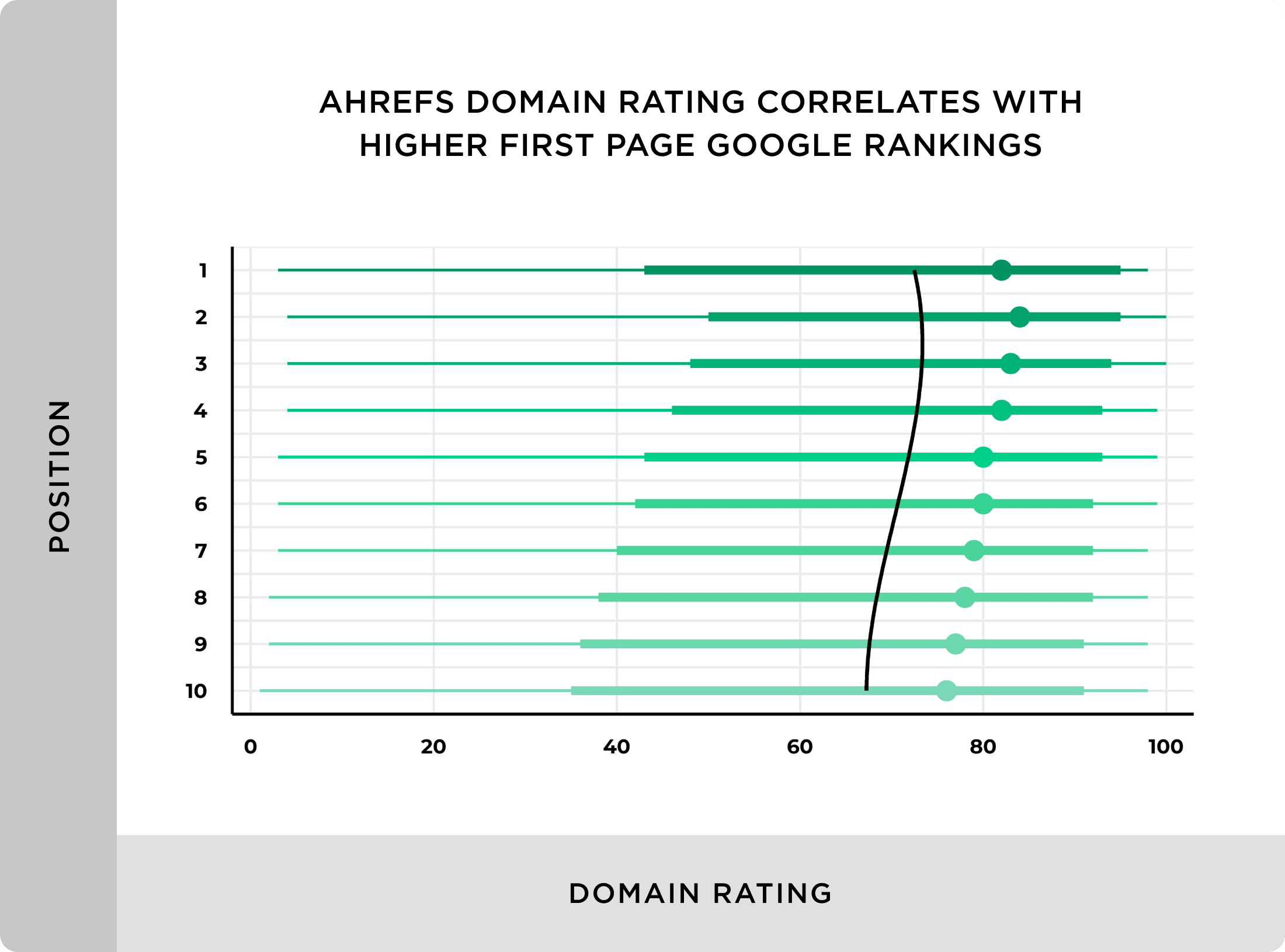
And in this step I’ll show you how to build quality backlinks, as part of your SEO efforts.
1. Email Outreach
If you want to get backlinks to your site, you’ll usually need outreach to do it.
(At least at first.)
In other words: when you promote your content to people that have the power to share it, you can get legit links from authority sites.
For example…
Mike Bonadio runs a digital marketing agency in NYC.
A few years ago one of his clients asked him to improve their SEO.
The problem was:
His client was in one of the most boring industries imaginable: pest control.
Which meant traditional content formats (like blog posts) were out.
Instead, Mike decided to create a piece of visual content: DIY Pest Control for the Savvy Gardener.

Well, Mike didn’t just publish his infographic and hope for the best.
Instead, he actively promoted it with email outreach:
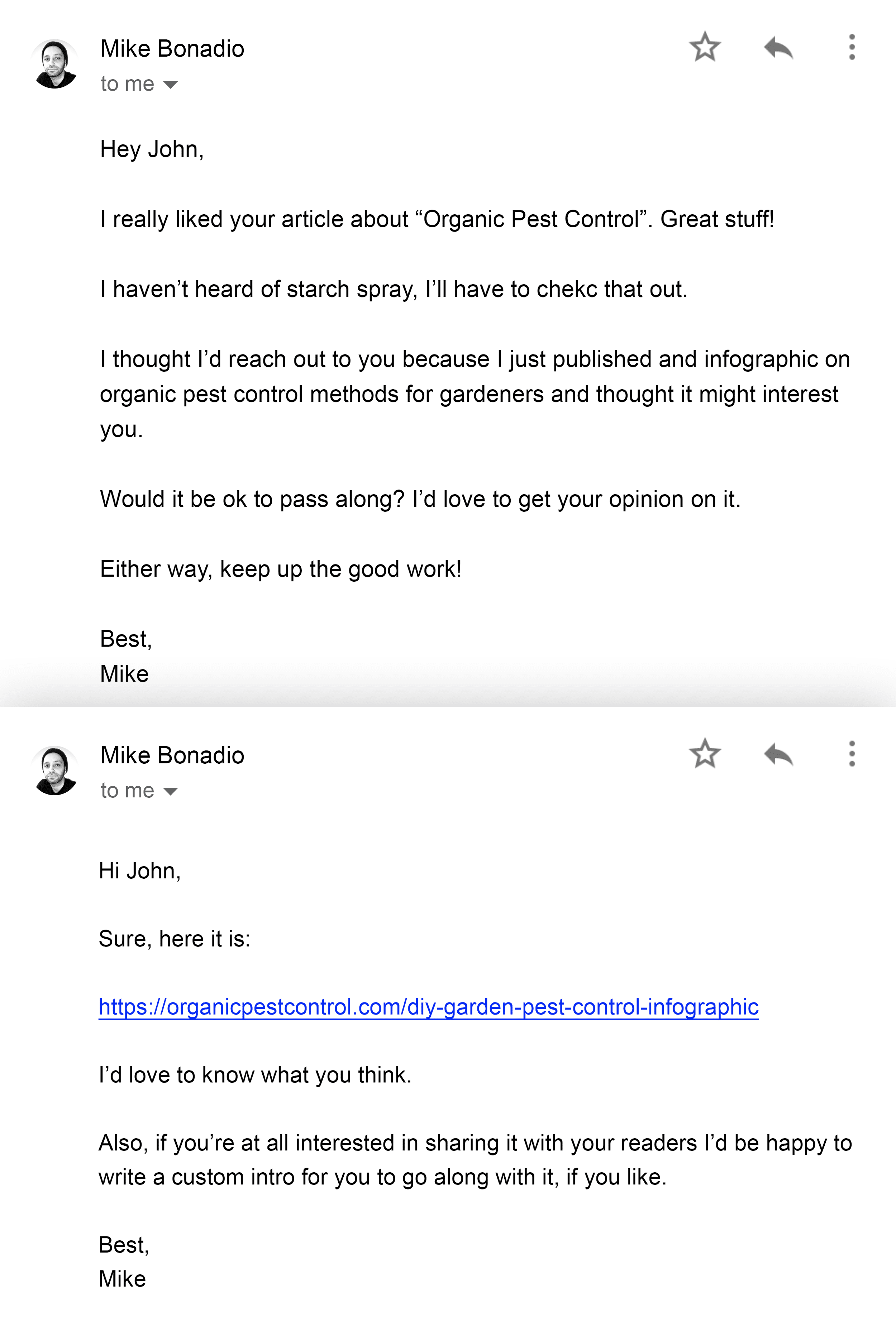
Because Mike wasn’t pushy or spammy, his campaign landed him backlinks from Lifehacker…

…and a popular newspaper website in Maine called The Bangor Daily News:

2. Guest Posting
Guest posting doesn’t work as well as it used to.
That said, it’s still a solid link-building strategy.
(When done right.)
Specifically, to get the most out of guest blogging, follow these 2 simple rules:
Rule #1: Don’t use exact match anchor text.
Google doesn’t want your guest post links to use exact match anchor text, like this:

Instead, use branded anchor text, like this:

Rule #2: Post on related sites.
If your site is about coffee, don’t guest post on a site about digital marketing.
(Even if you can find a way to “make it work”.)
Why? Guest posting on unrelated sites can get your site penalized.
For example, my site is about SEO.
So I make sure to only guest post on sites that are about SEO or closely related topics like social media, blogging, and content marketing.
3. Copy Your Competitor’s Links (Reverse Engineering)
Reverse engineering is a tried-and-true link-building strategy.
All you need to do is use a tool like Semrush to find a competitor’s inbound links.

For example, my site has a link from this page:

And let’s say that you’re one of my competitors.
Do you have a digital marketing trend on your site worthy of this list? Could you find one?
If so, you’d have a good chance of getting a link from that page too.
Step #5: Track Your SEO Results
Your last step is to see how your SEO campaign is performing.
To do that, we’re going to use two excellent (free) SEO tools: Google Analytics and the Google Search Console.
Let’s dive right in.
1. Track Organic Traffic With Google Analytics
How do you know if SEO is working or not?
My answer? Check your organic traffic in Google Analytics.
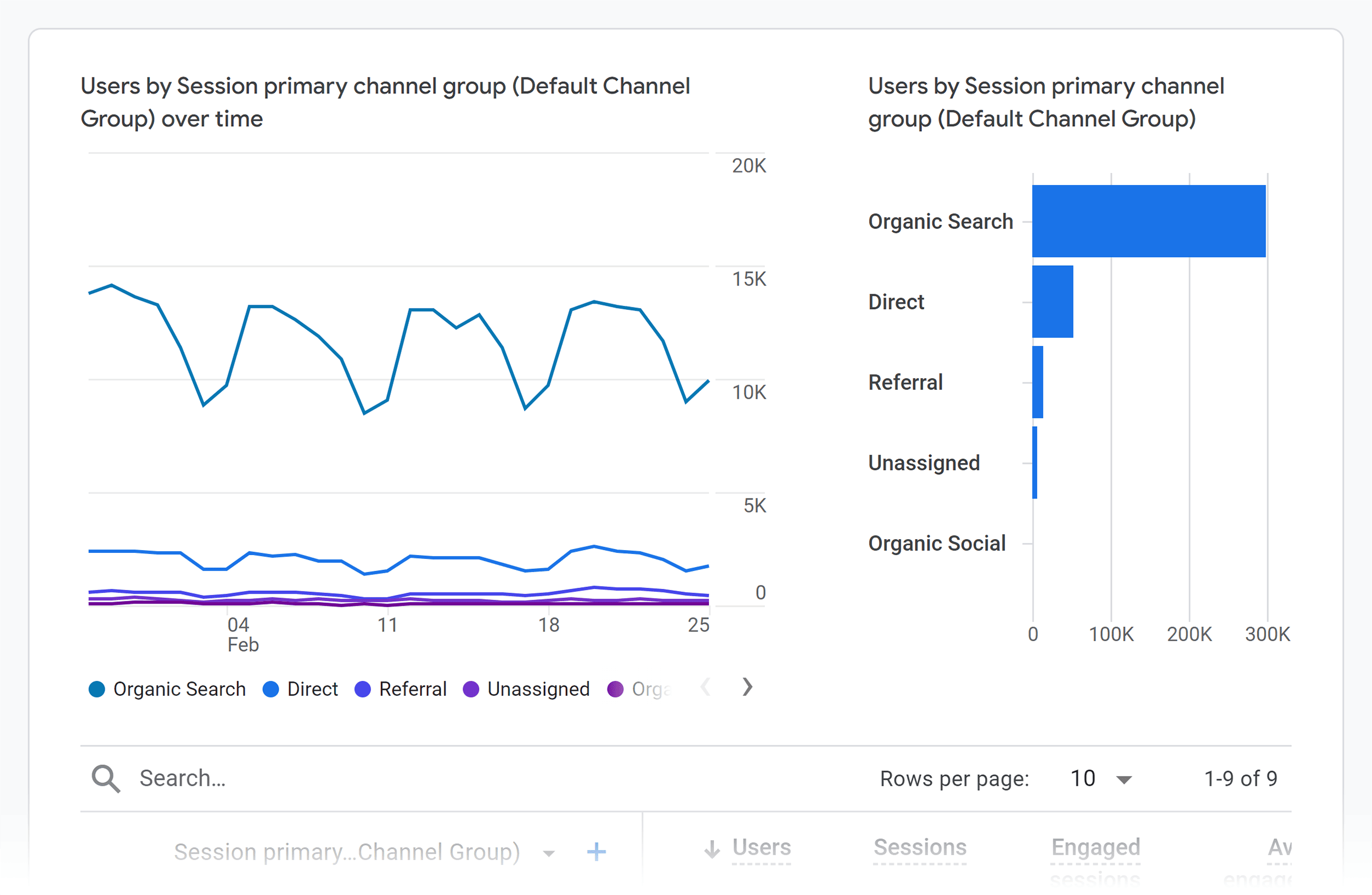
If it went up, then you’re on the right track.
If it went down? Then you probably want to change your approach.
Note: SEO results don’t happen overnight. Depending on the niche, it can take weeks or months to see changes kick in. That said, if you followed the steps above, you should see some positive movement within 4-6 weeks.
2. Track Keyword Rankings With The Google Search Console
Google Analytics gives you a high-level overview of how your search engine traffic changes over time.
But if you want to dig deeper, check out the Google Search Console.
Just like with Google Analytics, the Google Search Console tells you how many people came to your site from Google:
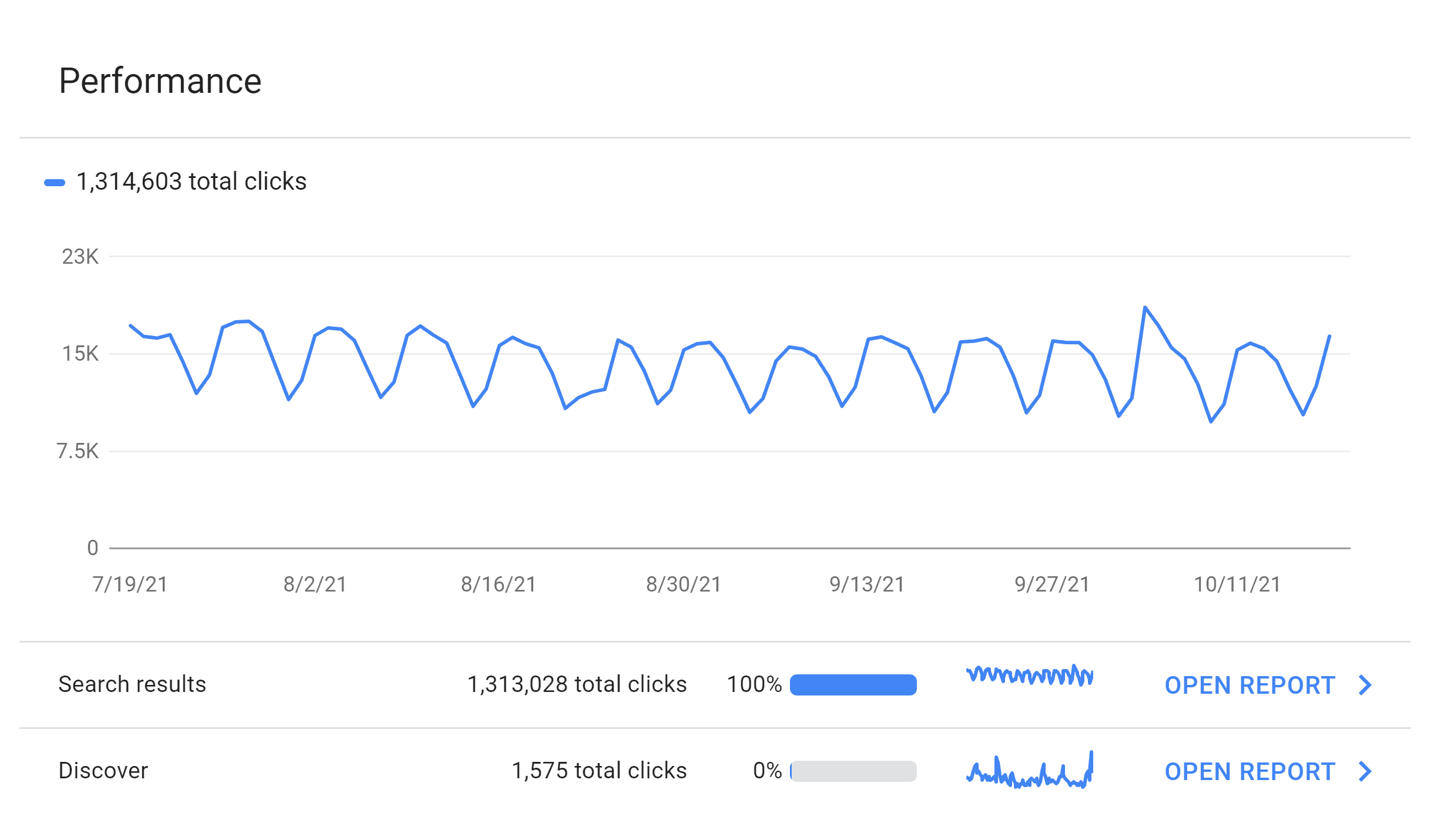
But it also tells you the exact keywords people used to find your site…
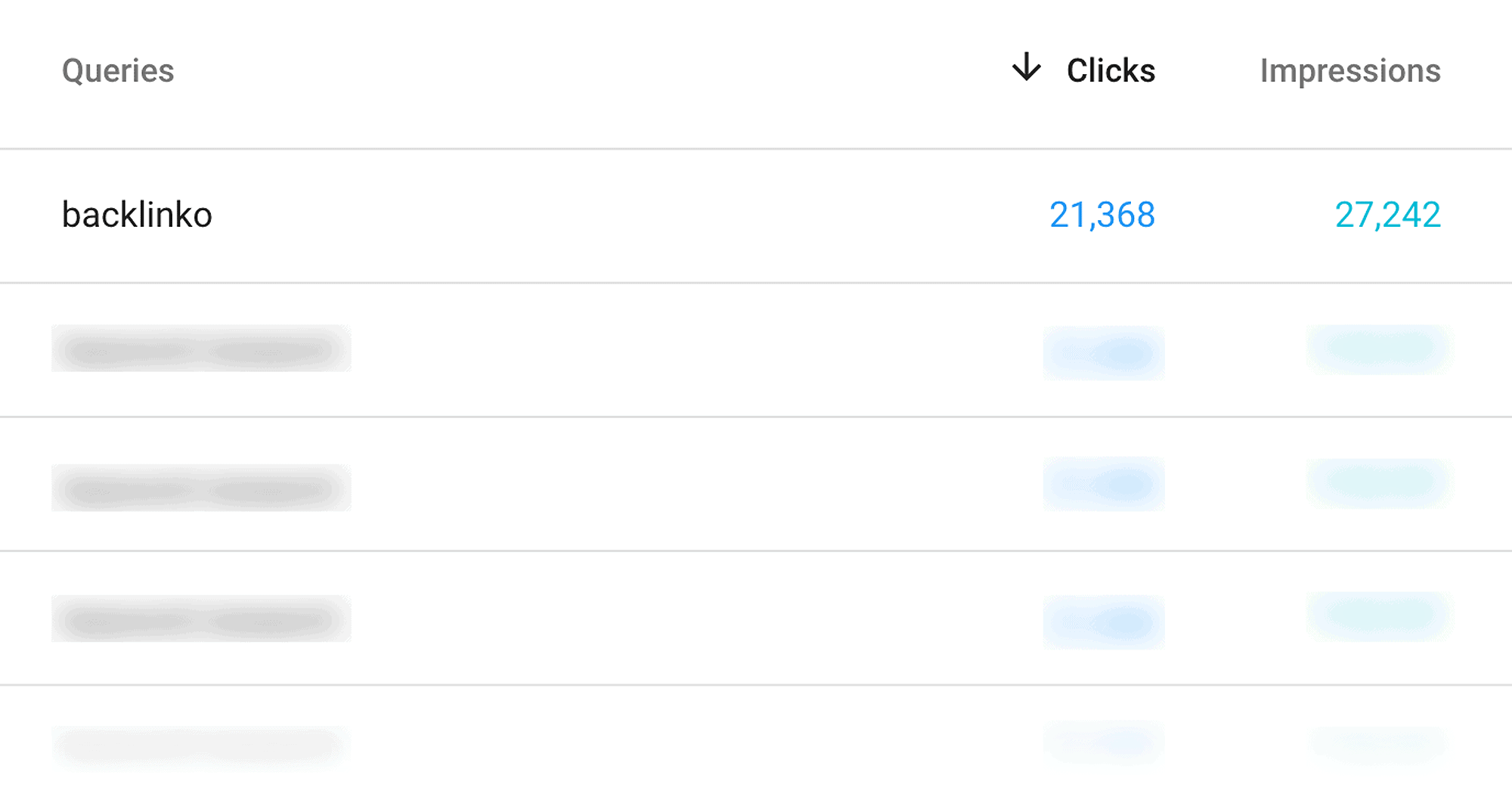
…and the pages that bring in the most organic traffic:
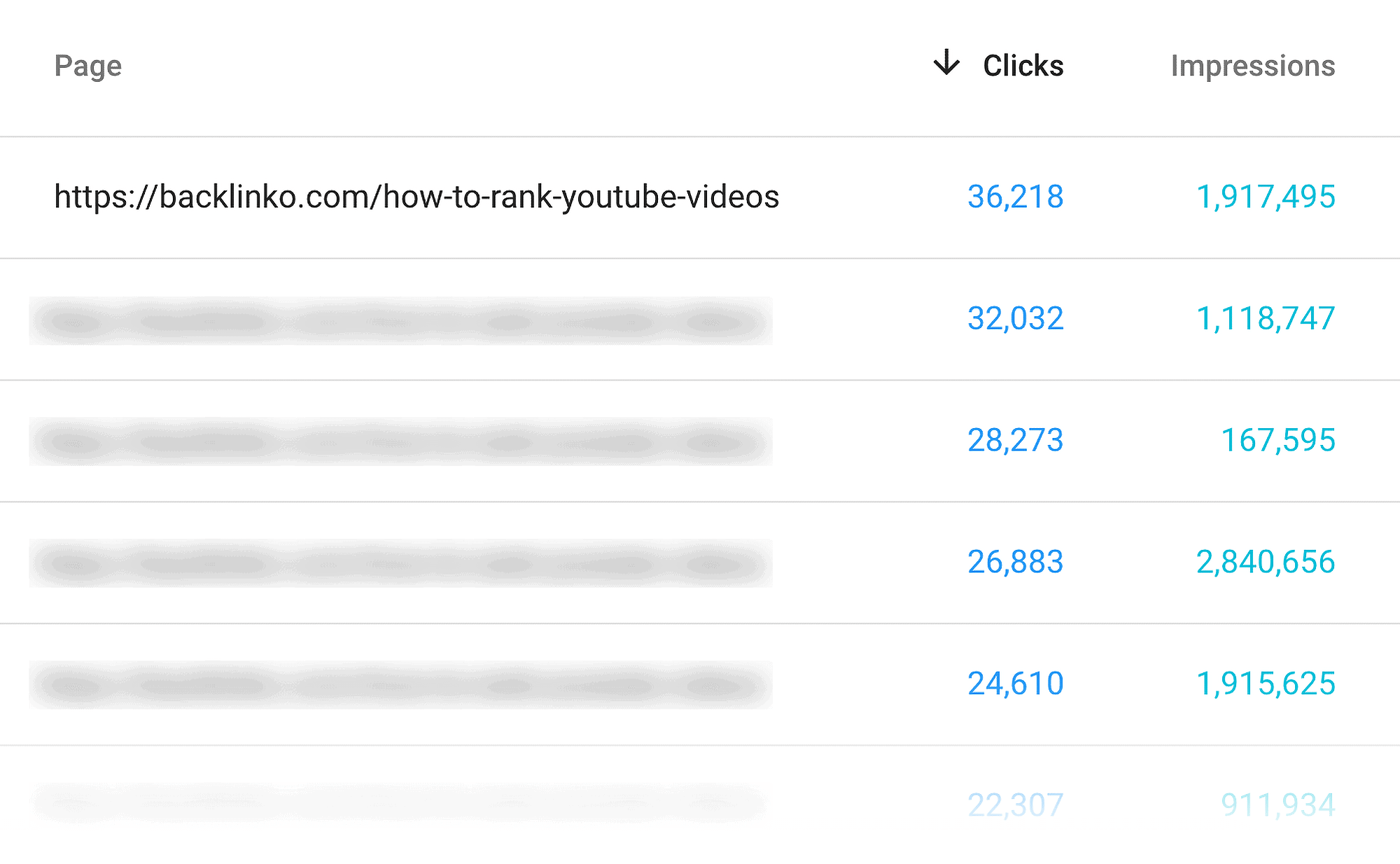
Step #6: Prune “Zombie Pages”
“Zombie Pages” are pages on your site that don’t add any value.
In other words, they’re pages that don’t bring in any traffic… or sales.
And when done carefully, removing Zombie Pages can help improve your site’s Google rankings.
(Why? Google updates like Panda mean that Google penalizes sites that have lots of low-quality pages.)
For example, Sean Falconer is a Backlinko reader that wanted to improve his site’s SEO.
And the first thing he did was delete over 10k web pages from his site.
Deleting those 10k pages is one of the main reasons that he improved his site’s organic traffic by nearly 90%:

Sean isn’t alone…
Blogger James Pearson recently axed hundreds of blog posts from his site… and his organic traffic increased by 30%:
Step #7: Optimize for RankBrain
An AI algorithm called RankBrain is now an important part of Google’s new-and-improved search algorithm.

So, how do you optimize your content for Google’s RankBrain algorithm?
Optimize for “User Intent”.
Google uses RankBrain to determine whether or not someone’s happy with the search results.
If a searcher likes a specific page in the SERPs, Google gives that page a boost:
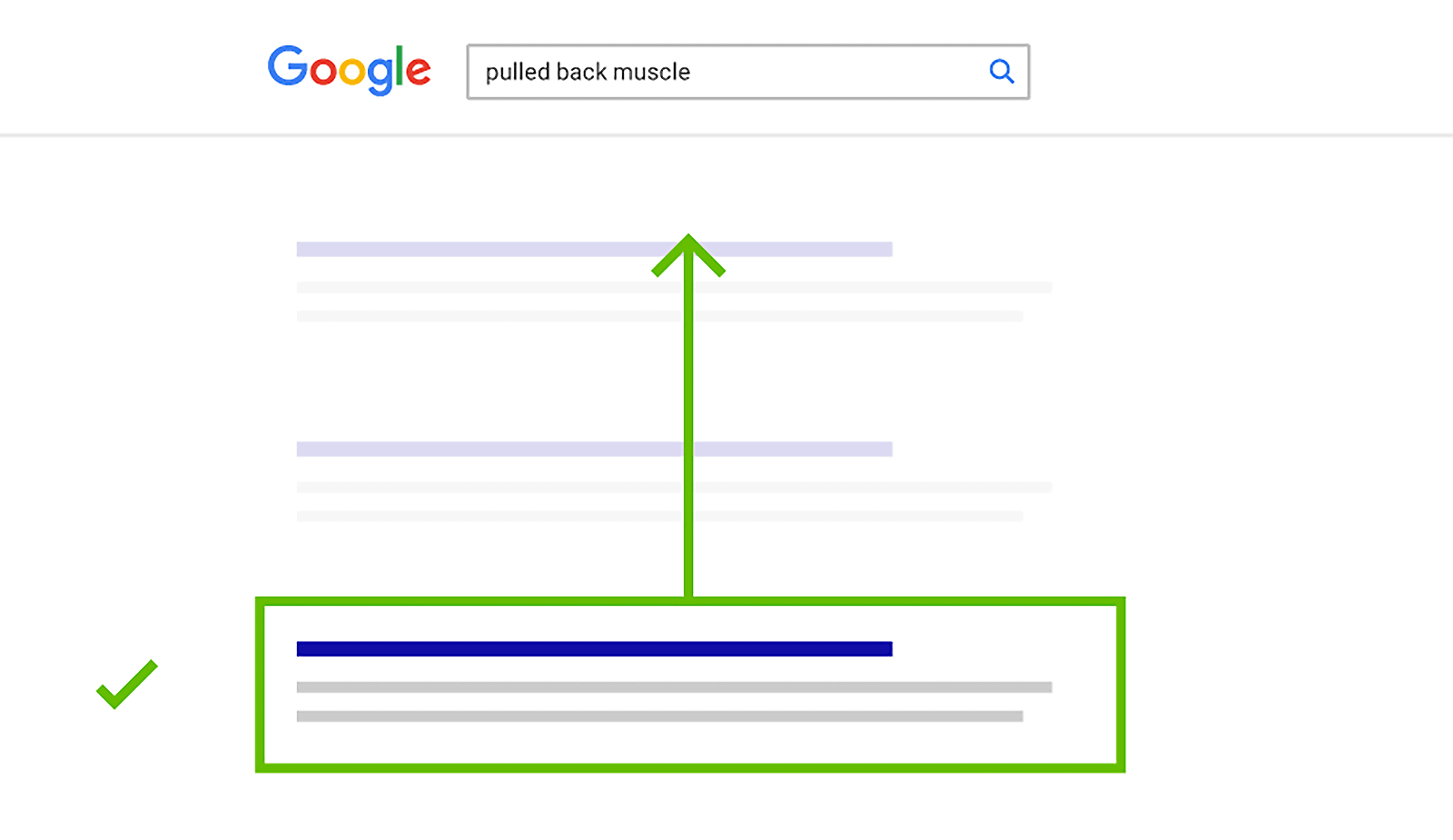
If not, they drop it down a few spots:
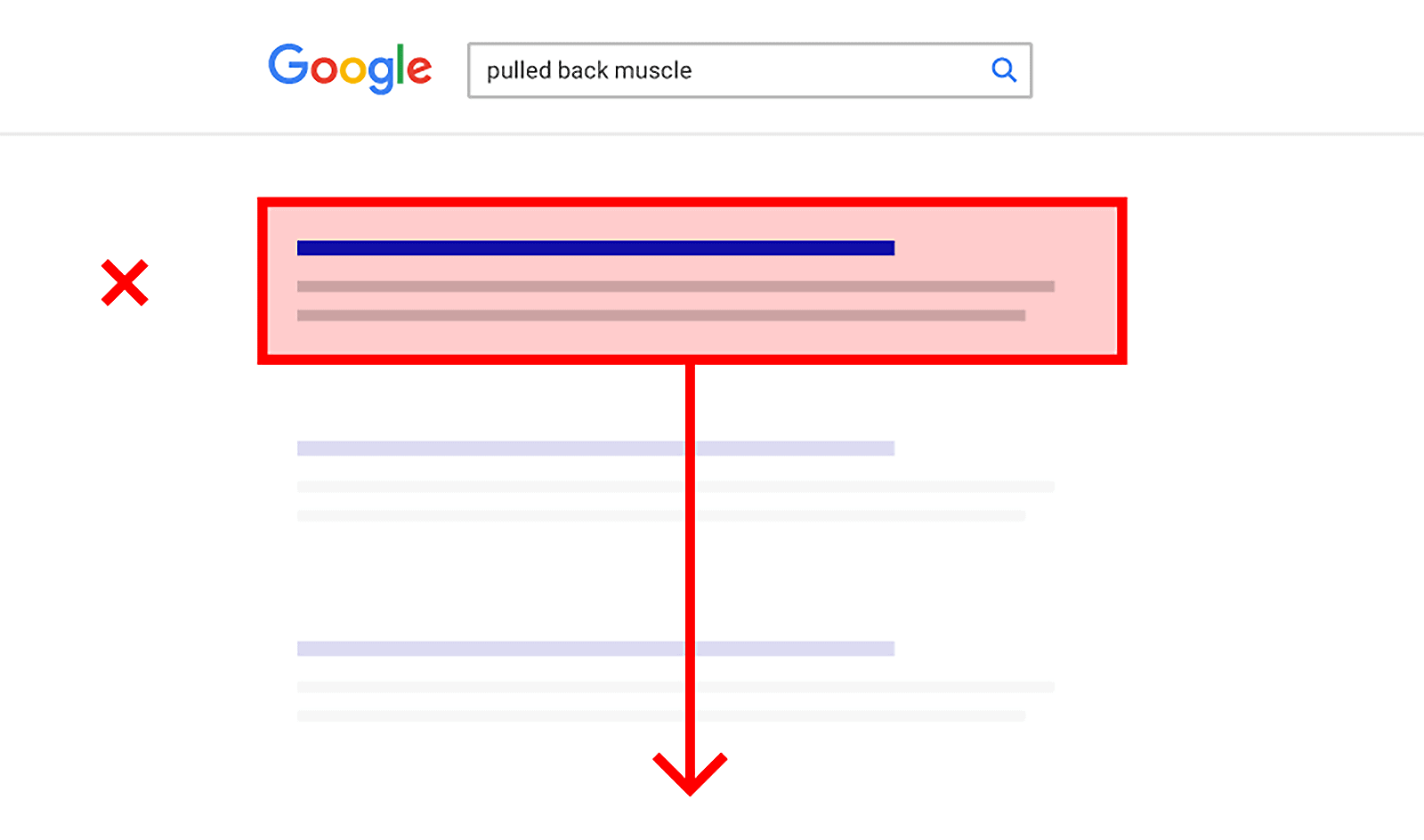
That’s why it’s important that your page satisfies “User Intent”.
In other words:
Does your content give the searcher what they’re searching for?
For example, a while back I wanted to rank for the keyword “SEO tools”.
But before I wrote a single word of content, I asked myself: “What does someone searching for ‘SEO tools’ actually want”?.
And I realized the answer was: a thorough list of the best SEO tools on the market.
So I created a post optimized for that user intent: 41 Best SEO Tools (Free & Paid).

Because the page is optimized for User Intent, it ranks in the top 5 for my target keyword:

Backlinko is owned by Semrush. We’re still obsessed with bringing you world-class SEO insights, backed by hands-on experience. Unless otherwise noted, this content was written by either an employee or paid contractor of Semrush Inc.

