More of your customers are using AI to research products before they buy. Are you prepared?
To put this into perspective:
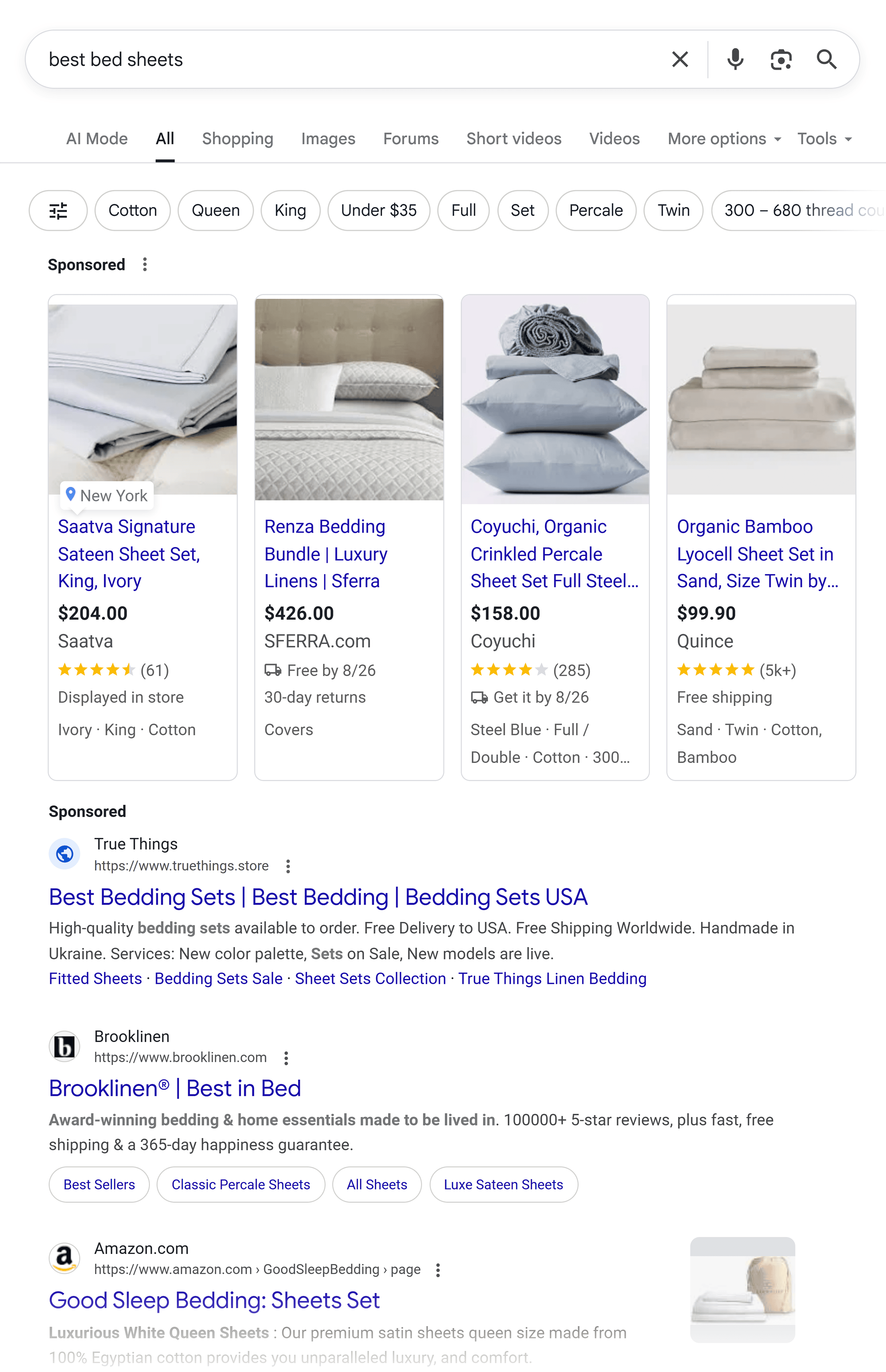
Last year, you might’ve searched “best bed sheets” on Google and scrolled through a few links or a Shopping ad.
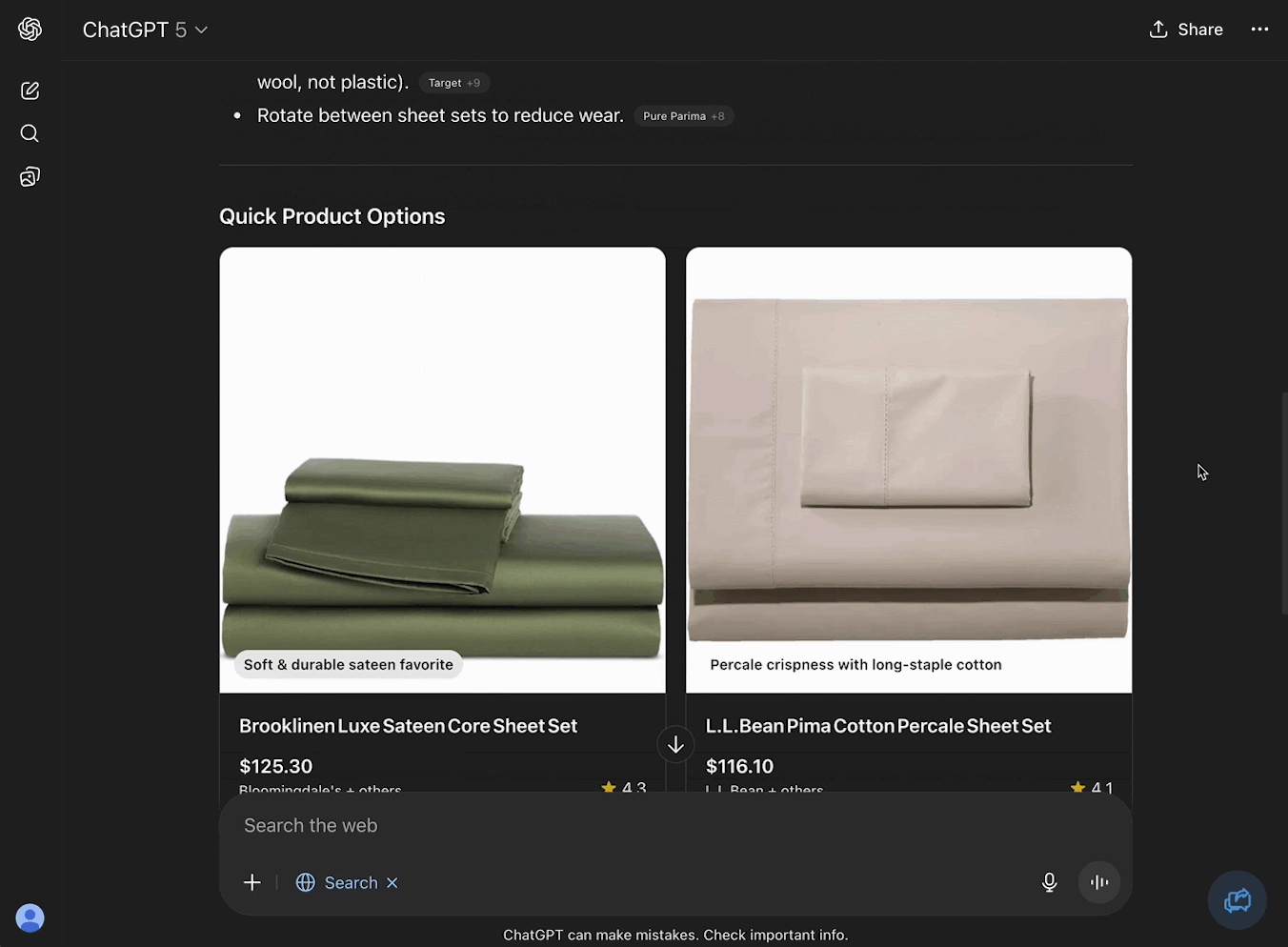
This year, you’re asking ChatGPT:
“I sleep hot and have sensitive skin. Can you recommend some breathable bed sheets that won’t irritate me?”
Totally different input. Totally different rules for showing up.
AI Search still cares about the fundamentals — content, crawlability, internal links, and high-quality backlinks. But now, your visibility is influenced by more than just your website.
AI models reflect the full picture:
- What people say about your brand
- Where you’re mentioned
- How your product is reviewed
It’s not just keyword targeting — it’s relevance engineering.
Shoutout to Mike King @ iPullRank for coining this term.
That’s where AI Search Optimization comes in.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to:
- Make your product pages visible and understandable to LLMs
- Structure your data with schema and product feeds
- Submit your catalog to AI search platforms
- Shift from keyword targeting to prompts and personas
- Build an AI-friendly brand presence across the web
- Track your visibility in a probabilistic, answer-first world
The future of ecommerce search isn’t about rankings. It’s about being part of the answer. This guide will show you how.
Step 1: Make Your PDPs Crawlable and Renderable
Before you do anything, start here: can bots actually see your product content?
When people started taking AI tools and chatbots seriously in 2022/23, some site owners turned to blocking their crawlers from accessing their site.
But if you block the crawler, it won’t be able to serve your pages in its responses.
Don’t Block AI Crawlers in Your Robots.txt File
Unless you actively took the step to block them, you shouldn’t need to do anything here. But it’s still worth verifying there are no lines in your robots.txt file like:
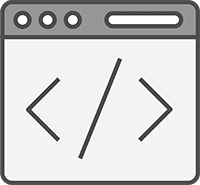
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /Don’t Serve Important Content Using JavaScript
The other aspect of crawlability to consider is how you’re serving your content.
Because right now, bots from the likes of ChatGPT and Perplexity do not appear to process JavaScript (although Google’s Gemini can). If your content is being loaded dynamically, they’re likely missing it completely.
That includes:
- Product descriptions
- Pricing
- Images
- Schema markup
If it’s not in the raw HTML, LLMs like these can’t see it. And if they can’t see it, you won’t show up in AI-generated product recommendations.
To make sure you’re not causing crawling issues here, you first need to understand how your ecommerce platform handles JavaScript. Every platform is different:
- Shopify: Generally fine, but watch out for third-party apps injecting schema or content via JS.
- WooCommerce: Depends heavily on your theme. Many use plugins that load parts of the page with JS.
- Custom stacks: If you’re using React, Vue, or similar frameworks, check whether product pages render server-side or after load.
Next, check your PDPs manually. You can do this by right-clicking and selecting “Inspect” in your browser.
Then press Command+Shift+P on Mac, or Control+Shift+P on Windows/Linux.
In the Command Menu, start typing “javascript” and then select “Disable JavaScript”:
Reload the page, and you’ll see how it looks without JavaScript enabled — in other words, how LLMs like ChatGPT see the page:
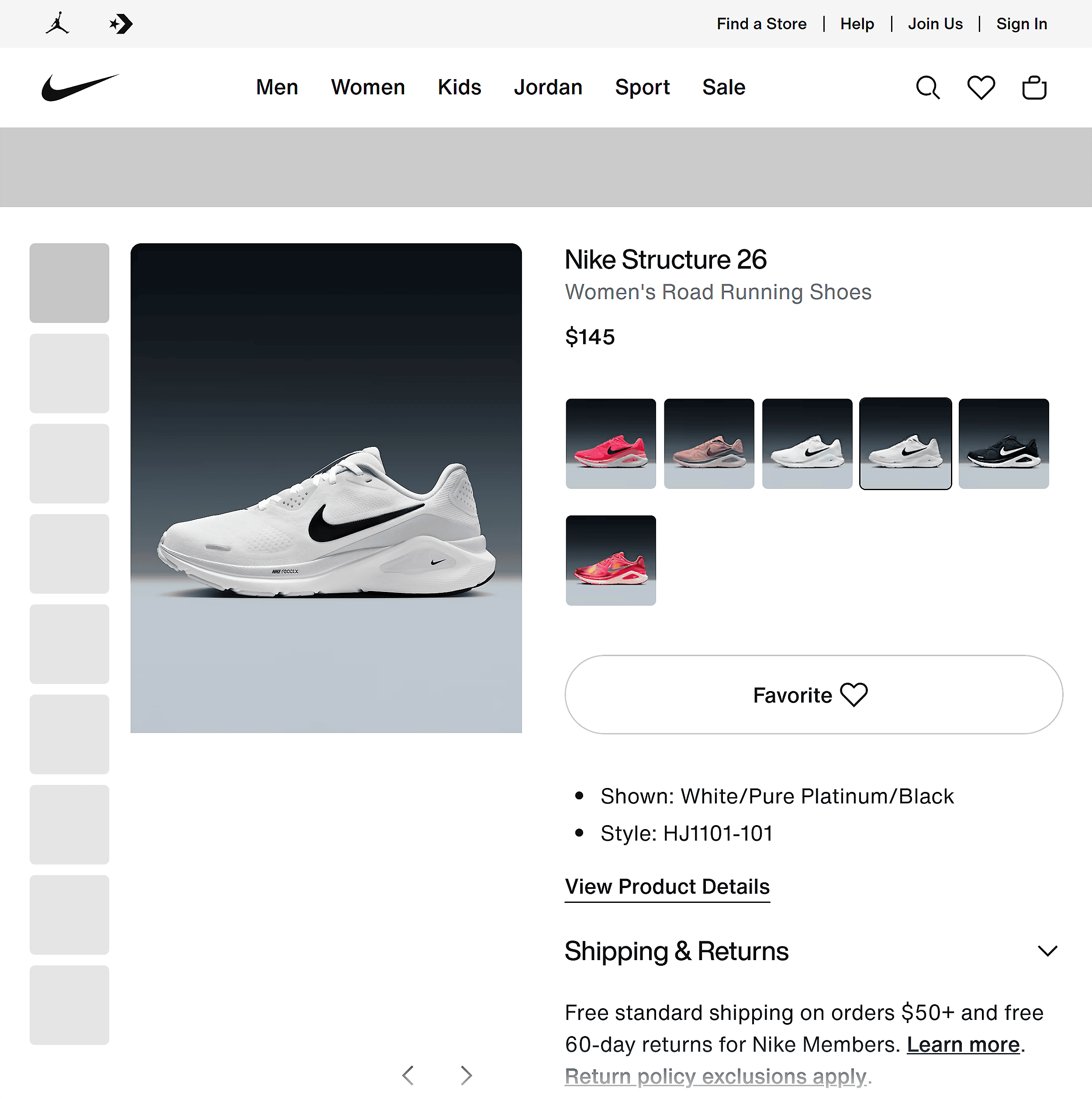
In the Nike example above, the LLM would still see key info like the product title, description, and price.
But in the example below…
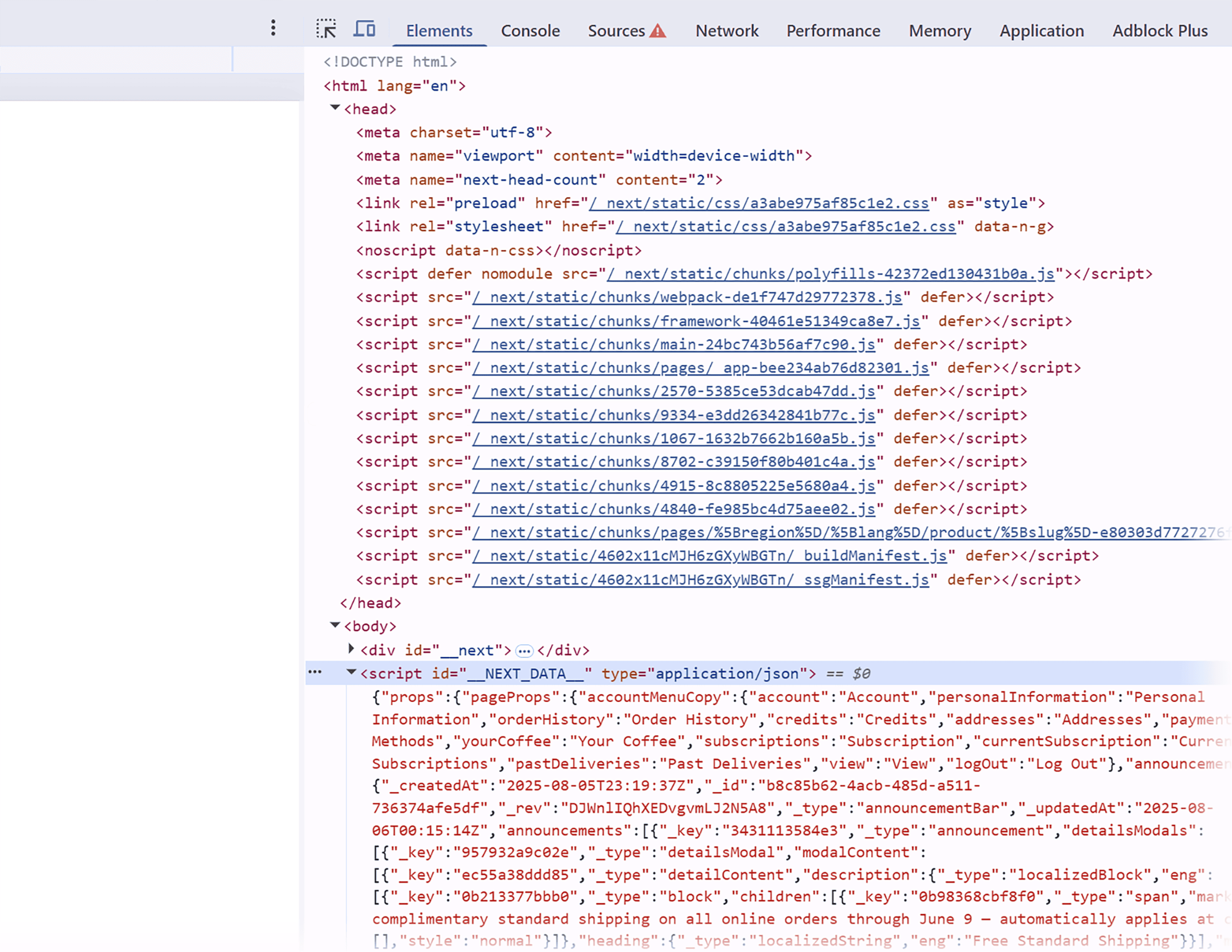
…it would see nothing.
You can see on the right that there’s still page code loading. But nothing is actually displayed to the user with JavaScript disabled. Meaning AI tools wouldn’t be able to pull any info from this page.
If you are using apps or components that rely on JavaScript to display key content, talk to your dev team about server-side rendering (SSR) or prerendering. The goal is to ensure all critical product info is delivered in the first HTML response.
Further reading: What Is JavaScript SEO? 6 Best Practices to Boost Rankings
Step 2: Add Structured Schema Markup
Once your product pages are crawlable, the next step is making them understandable.
Structured data — specifically Schema.org markup in JSON-LD format — helps systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google understand what your product is, how much it costs, whether it’s in stock, and more.
In the world of SEO, we’ve long used schema markup to improve how our pages appear in traditional search results.
Here’s an example of a traditional Google results enhanced with schema markup, appearing as a rich snippets:

But for LLM visibility, schema helps the AI tools understand key details about your products. Which makes it easier for them to pull in your products when they’re making recommendations for users.
How do we know this?
Because Microsoft has told us. The tech giant, a major investor in OpenAI (behind ChatGPT), said:
“[Structured data] makes it easier for search engines not only to index your content, but to surface it accurately and richly in search results, shopping experiences, and AI-driven assistants.”
(Interestingly, Microsoft/Bing recommends combining this with IndexNow — a service that automatically pings search engines when you update your content.)
Plus, using structured data just makes sense — it helps make it easier for complex machines to understand our content. Whether that’s a search engine or an LLM, providing more context is generally always going to be a good idea.
Here’s how to use structured data to improve your ecommerce store’s LLM visibility:
Focus on Product Pages First
While there’s value in marking up other templates (like category pages, blog posts, or FAQs), your product pages are where it counts most.
This is the data that LLMs and search engines will use to:
- Associate your product with relevant categories and attributes
- Match your offering to long-tail purchase prompts
- Feed structured knowledge into their product and shopping systems
Here are the fields to include:
- @type: Product
- GTIN, SKU, MPN
- Brand
- Description
- Offer block (price, currency, availability, URL)
- Review/rating info if available
Use your schema to reflect reality, not just fill fields. But also add as much context as you can.
If your product is eco-friendly, US-made, sweatproof — encode it. The better your markup, the more context LLMs have to surface your product in nuanced prompts.
Validate Your Schema and Confirm It’s Visible
Check your schema is valid with tools like:
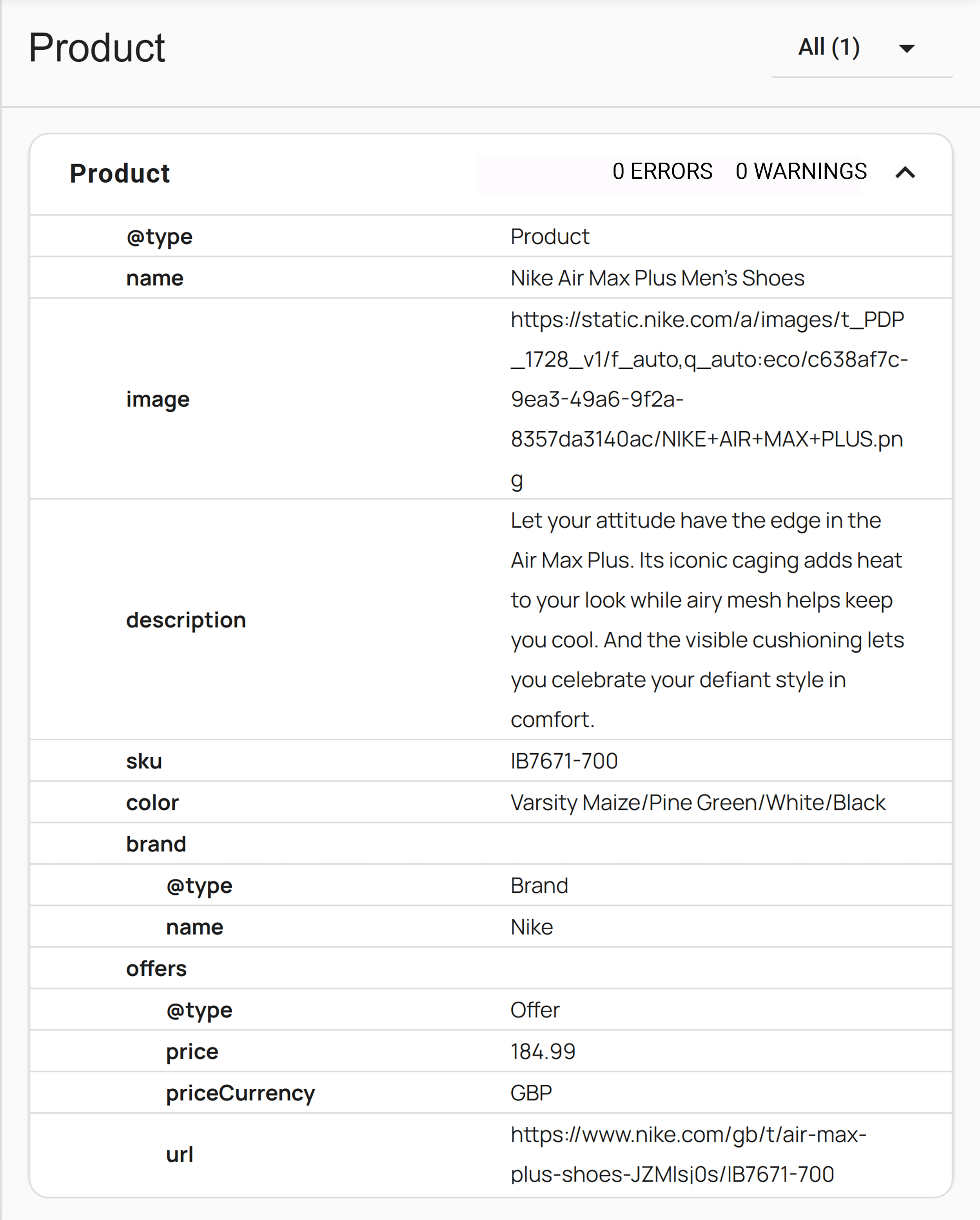
Make sure the schema is present in the raw HTML — not loaded with JavaScript.
Bonus: Extend to Reviews, FAQs, HowTo
Once your product markup is solid, consider adding:
- Review and AggregateRating blocks
- FAQPage markup for your PDPs or Help Center
- HowTo schema for tutorial content or sharing post-purchase use cases
These all help build context around your product and can influence how LLMs present or recommend it.
Once you’ve marked up your product pages, the next step is scaling an effective structure across your entire catalog. That’s where a high-quality product feed comes in.
Step 3: Build a High-Quality Product Feed
Structured feeds have been essential for Google Shopping, Meta Advantage+, and TikTok Shop for a while.
And now, they’re becoming equally important for AI-powered discovery. Especially as platforms like Perplexity and OpenAI build out product recommendation systems.
Think of your feed as the dataset LLMs will eventually pull from when answering questions like this:

Perplexity has launched a Merchant Program accepting feed uploads, called the Perplexity Merchant Program. This lets ecommerce sellers have even more control over how their products can appear in AI responses.
Plus, OpenAI is quietly testing ways to let store owners upload feeds to improve their AI responses for product recommendations.
These feeds will likely drive future AI shopping experiences across chat, search, and even voice interfaces.
So how do you set your product feeds up in an LLM-friendly way?
What to Include
To optimize your product feeds for AI, start with the essentials:
- Product title
- Description
- Price
- Availability
- Product URL
- GTIN or MPN + Brand
- Image URL
Note: Tools like ChatGPT may still generate their own versions of some of these (like titles). But it’ll still typically use information from places like your product feeds to inform its responses.
After you’ve added the basics, layer in high-value fields like:
- Category or taxonomy
- Color, material, and size variants
- Shipping cost and speed
- Review count and star rating
- Custom labels for campaigns or segmentation
Use the same language your customers use.
This means writing product information the way your customers actually talk and search, not how your internal teams or suppliers describe things. For example:
Instead of:
“Athletic footwear with moisture-wicking synthetic upper”
Write:
“Running shoes that keep your feet dry”
How do you find out how they talk?
Look at your customer reviews, support tickets, and search queries that already drive traffic to your store.
For example, they might search for “cozy sweater” not “knitted pullover.” This can inform your title and description choices.
How to Submit Product Feeds to LLMs
Here’s how to submit your product feeds for three of the biggest AI interfaces.
Perplexity:
In 2024, Perplexity launched their Merchant Program. This fuels the platform’s shopping experience for Pro users. Your products may appear in carousel-style answers and shopping-focused prompts, and shoppers can buy without leaving Perplexity.
You can find out more about the program and sign up here.
OpenAI (ChatGPT):
OpenAI is piloting product discovery via ChatGPT’s “Search + Product Discovery” initiative. They’re exploring using uploaded feeds to power future buying experiences inside ChatGP.
Fill out this interest form to apply.
Google Merchant Center (AI Mode and Gemini):
Google’s Merchant Center feeds power Shopping Ads, organic Shopping listings, and likely influence how Google’s AI systems interpret and surface your products in AI Mode and AI Overviews.
Step 4: Monitor LLM Crawlers
Once you’ve put all the steps in place to make your ecommerce store crawlable by LLMs, the next step is to make sure they’re actually accessing your content and product pages.
Here’s how to do that:
Set Up Bot Monitoring
Use server logs or your CDN (like Cloudflare, Fastly, or Akamai) to track requests from:
- GPTBot: This user agent is used by OpenAI to crawl web content that may be used in training their generative AI foundation models.
- OAI-SearchBot: Used by OpenAI to link to and surface websites in search results in ChatGPT’s search features.
- PerplexityBot: Identifies Perplexity’s AI search crawler when it accesses websites.
- Google uses various Googlebot user agents to crawl the web, depending on the type of content being crawled (e.g., desktop, mobile, images). You can find a detailed list of common Googlebot user agent strings and their purposes in resources from Google for Developers.
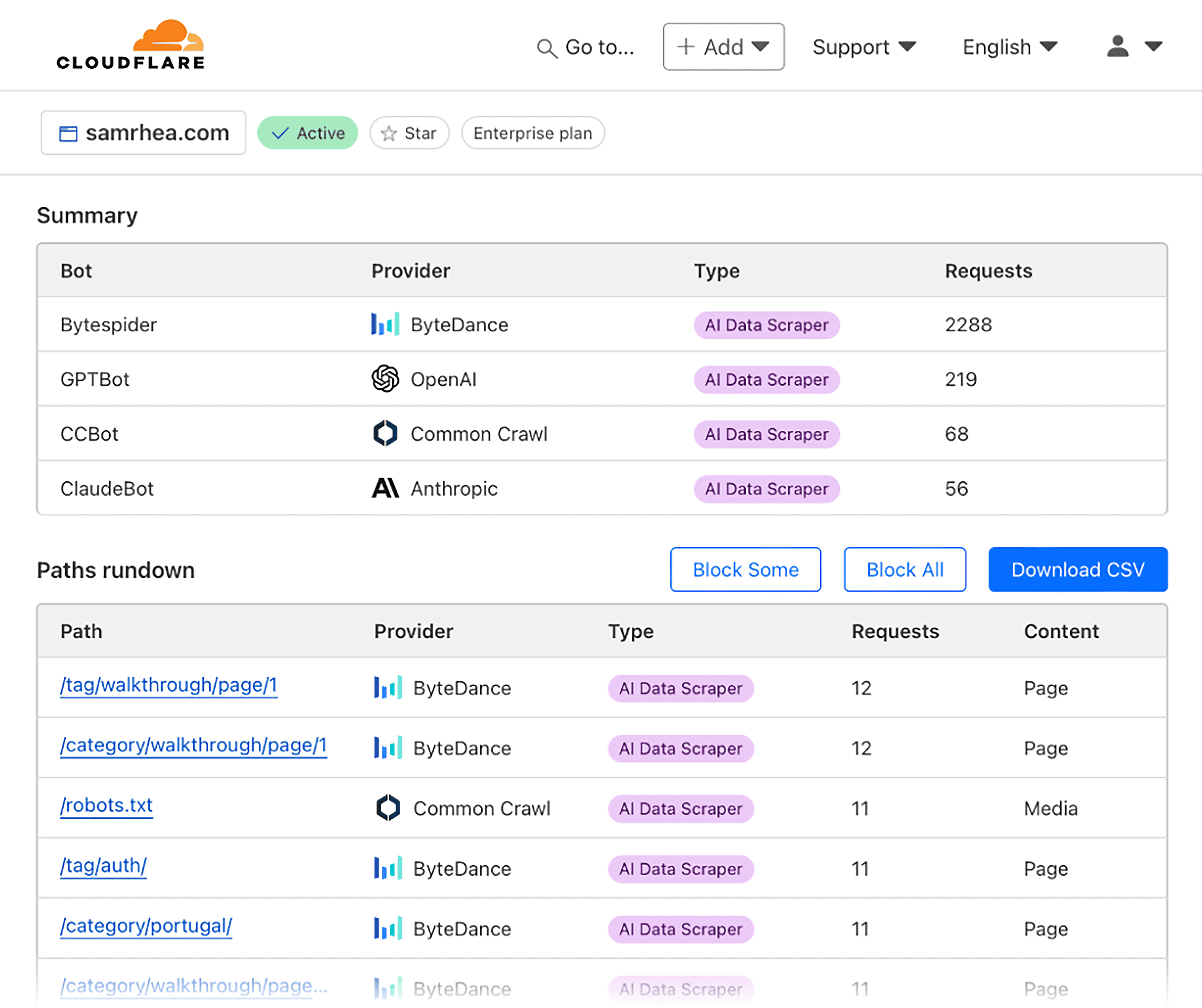
For each of these bots, track:
- Which pages they’re crawling (PDPs, collection pages, sitemap, feed)
- How often they come back
- How crawl patterns evolve over time
This helps confirm they’re discovering your content and gives you a baseline to measure progress.
Step 5: Shift from Keyword Lists to Prompts and Personas
Keyword research is still important. But you also need to think about how your customers are likely to prompt AI tools when looking for products like yours.
LLMs answer questions, interpret context, and make recommendations based on how people naturally speak.
That means you need to rethink how you optimize for product discovery. Not by keywords alone, but by personas, use cases, and prompt formats.
Start With What You Know
Your best-performing SEO and paid search keywords are still the foundation. They tell you:
- Which products and categories convert
- How people describe their intent in short-form searches
- Which attributes drive action (e.g., “cooling sheets,” “queen size,” “organic cotton”)
Use these to anchor your prompt strategy — but expand outward.
Think in Prompts, Not Just Queries
As people become more savvy with how AI tools work, more and more shoppers are going beyond just typing in “best bed sheets.” They’re asking:
Medium-length prompts:
- “Best cooling sheets for hot sleepers”
- “Softest bed sheets under $100”
- “What kind of sheets stay on the bed all night?”
Longer, context-rich prompts:
- “I’m a side sleeper who gets hot at night. What bed sheets will stay cool and not cling to my skin?”
- “Looking for breathable, hypoallergenic sheets that work well in humid climates”
- “I have sensitive skin and eczema. What’s a good sheet material that won’t irritate me?”
Your goal is to build context around your products that lines up with this kind of language and framing.
Note: You can’t predict exactly what your customers will ask, and there are infinite ways they can do it. But thinking about prompts — not just keywords — will put you in a good place to be able to optimize your ecommerce pages for LLMs.
Map Your Catalog to Prompt-Based Use Cases
Think in layers:
- By need: cooling, breathable, wrinkle-resistant, organic
- By persona: hot sleeper, allergy sufferer, luxury buyer, college student
- By situation: new apartment, guest bedroom, summer refresh, wedding registry
- By problem: sheets come loose, feel scratchy, trap heat, shrink in the wash
This is how you start to think of your items like answers and solutions, not just products.
Use These Prompts to Guide Content and Merchandising
Let this prompt structure inform your:
- Product page copy and comparison points
- Blog posts and videos
- Social media posts
- FAQs and Help Center content
- Category names and filters
- Product feed descriptions and attributes
LLMs can pull from all of it — so make sure you’re using the kind of language your real customers use everywhere.
Step 6: Seed Your Brand Across the Web
Even if your site is crawlable, your schema is perfect, and your feed is super optimized — LLMs still learn about your brand based on what people are saying about you elsewhere.
They’re trained on massive web-scale datasets, so third-party content — like reviews, Reddit mentions, YouTube transcripts, forums, blog posts — can carry as much (or more) weight than your owned channels.
If you want to show up in AI answers, your brand needs to already exist in the wider conversation.
Where You Want to Show Up
AI tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude all lean on third-party review sites and forums in their answers to brand and product-related queries.
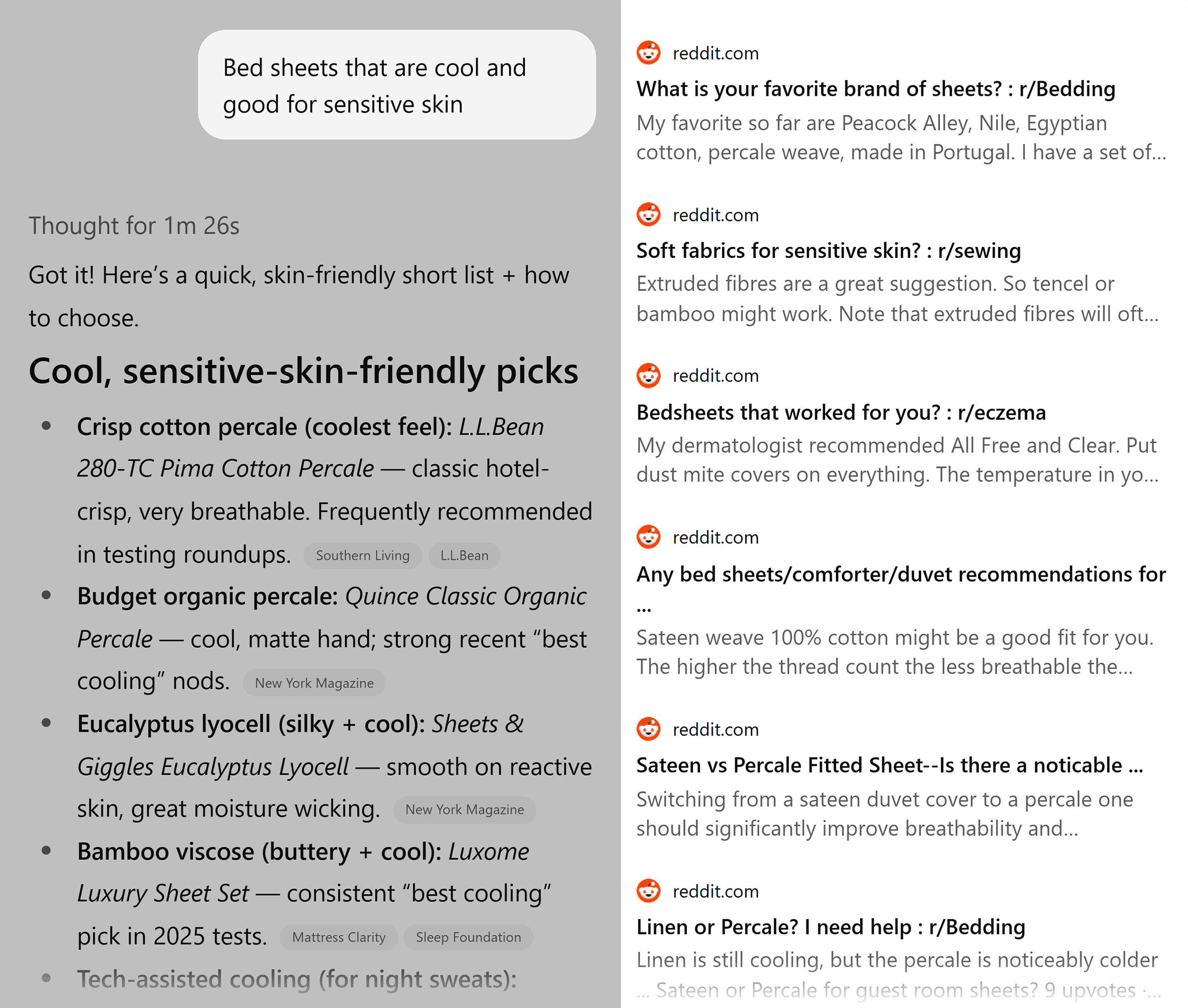
These are the places you’ll want to show up in order to be included in those answers:
- Review sites: Trustpilot, Amazon, Google Reviews, BBB, niche review sites
- Reddit, Quora, & niche forums: Participate in threads and subtly seed your product category (without being spammy)
- YouTube: Appear in titles, transcripts, and product comparisons — even if you’re not the creator (consider partnering with creators to do this)
- Affiliate content: Get included in roundups, listicles, and side-by-side comparisons
Showing up in these places is half the battle. The other component is how you show up.
Ideally, you’ll want to be mentioned alongside competitors (“like Brooklinen but…”). And in the right, relevant context (“these are some of the best cooling sheets for eczema”).
A lot of this is going to be completely out of your control (especially on platforms like Reddit). But good marketing practices can make it more likely that people will naturally talk about your brand in the way you want them to.
This Is Just Good Marketing
Gaining LLM visibility is a byproduct of an effective multichannel marketing strategy.
If you’re running a strong content program, building brand awareness, and actively participating in your category — you’re already seeding relevance.
What’s new is the urgency: LLMs are already using these signals to decide which brands deserve to be recommended.
Related: See our LLM Seeding Playbook for tactics, templates, and outreach strategies.
Step 7: Track Your AI Search Visibility
In traditional SEO, visibility was deterministic: rank #1 for a keyword, get X% of clicks.
That model is breaking.
AI-powered discovery works differently. Your brand might appear in one version of a response, but not the next.
Whether your ecommerce store is included depends on how the user phrases their prompt, how much brand recognition you have, and how often you’re referenced across the web.
So, your measurement strategy needs to adapt.
What to Track
Start by building a prompt library — real questions your customers might ask:
- Organize prompts by topic (e.g., cooling sheets, organic materials, luxury bedding)
- Group them by persona (e.g., hot sleepers, allergy sufferers, budget-conscious buyers)
- Then choose a tool to test visibility: like Semrush AI Visibility Toolkit, Peec.AI, or Profound
Here’s how it looks in Semrush’s AI Visibility Toolkit:
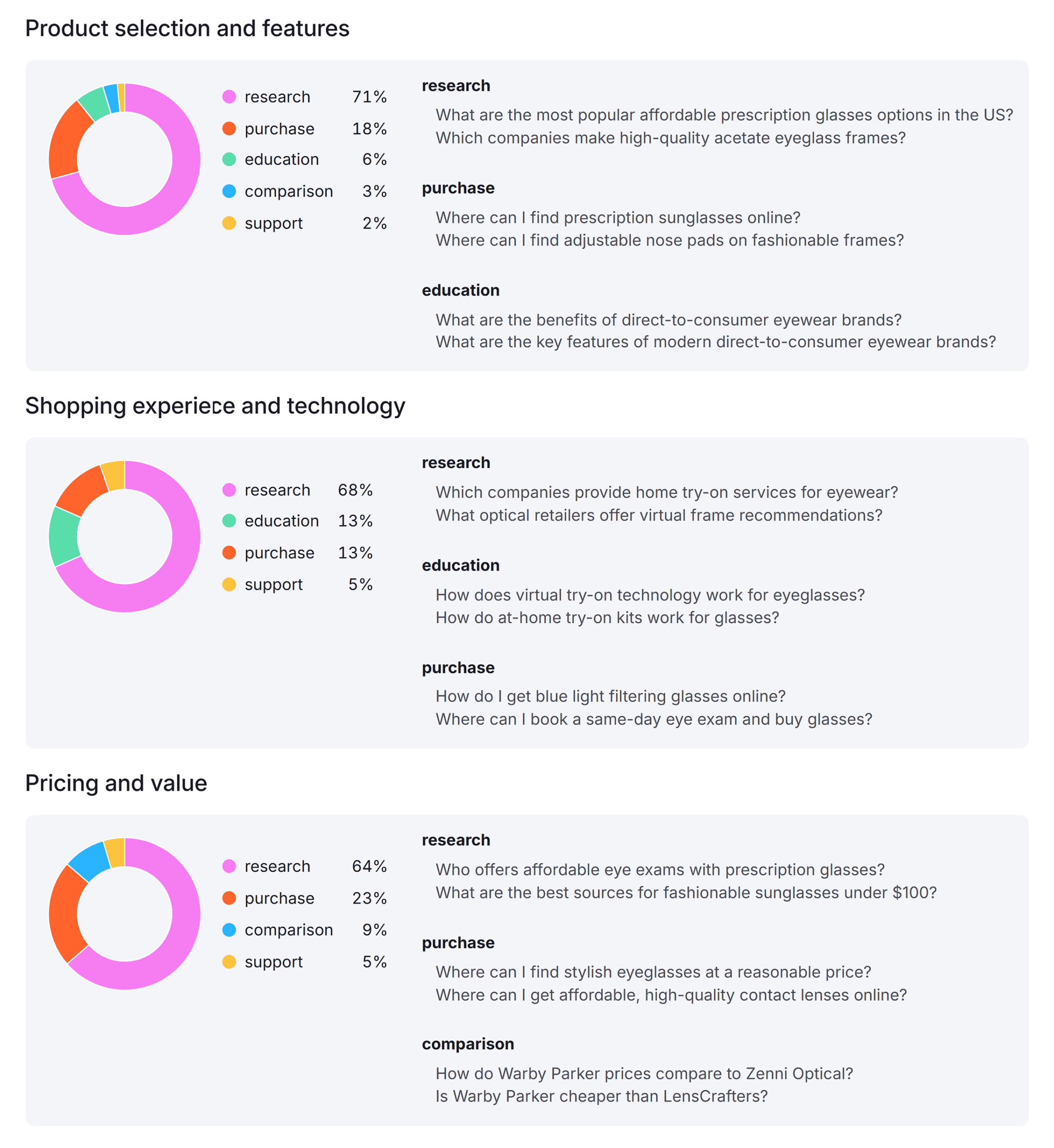
For each prompt, ask:
- Does your brand show up?
- If not, who does?
- What sources are the tools citing?
- What kind of language are the tools using?
Over time, this gives you a clearer picture of how visible your brand is across different use cases.
LLM Optimization Is Still New, But It’s Gaining Traction Fast
AI-driven search is already reshaping how people discover products. The shift is subtle now, but it won’t stay that way for long.
What used to be a clear SEO vs. paid search strategy is now blending into a broader question:
When someone asks a smart machine what to buy… will it know you exist?
This guide gave you a playbook to start answering that question:
- Clean up your technical foundation (crawlability, schema, product feeds)
- Rethink your discovery strategy around prompts and personas
- Show up across the web in ways that reinforce what makes your brand unique
It’s a lot. But the good news?
If you’ve already invested in great products, strong messaging, and a multi-channel strategy, you’re not starting from scratch.
Still need help nailing the fundamentals?
Check out these guides:
Backlinko is owned by Semrush. We’re still obsessed with bringing you world-class SEO insights, backed by hands-on experience. Unless otherwise noted, this content was written by either an employee or paid contractor of Semrush Inc.