SEO Basics: How to Rank #1 on Google

Written by Ankit VoraIn collaboration with Semrush

SEO can feel overwhelming when you’re just starting out.
With so much jargon and endless advice online, it’s hard to know where to begin.
But here’s the truth: mastering the basics of SEO is simpler than you think—and it can transform your website.
Take Traffic Think Tank. In just 12 months, the team increased organic traffic from just a few hundred visits per month to over 10K—all while driving new customer signups profitably.

It’s not magic. SEO works because search engines reward helpful content and great user experiences. Get these right, and you’re already 90% of the way there.
SEO boils down to a handful of main areas:
- Keyword Research
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
- Technical SEO
In this guide, you’ll learn the essentials of each area, plus how to explore them further when you’re ready.
Let’s start with the foundation.
What Is SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving your website’s visibility in organic (non-paid) search results on platforms like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Higher rankings mean more traffic to your site—and more traffic can lead to increased sales and revenue.
Unlike paid ads, which let businesses buy top positions, SEO focuses on earning those rankings by creating helpful content and providing a great user experience.

To understand the basics of SEO, it helps to understand how search engines work.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Keywords are words or phrases that users type into search engines to find information.
Search engines like Google aim to provide the most relevant information to users based on the keywords they enter in their search.
For instance, when someone searches on Google (let’s say for “on-page seo”), Google’s algorithm sifts through countless webpages to present the ones most relevant to that user’s query in the results.
For “on-page seo” query, the top two results are Semrush and Backlinko.

But how does Google decide which results to show?
It has a complex algorithm, which takes into account hundreds of ranking factors. They work together to determine the most useful and relevant results.
Google uses a multi-step process to discover, store, and rank web pages.
It goes like this:
- Crawling: This is how search engines discover new content and keep tabs on updated content. They deploy automated bots to scan the internet. These “crawlers” or “spiders” visit different web pages and follow links on those pages to find new and updated content.
- Indexing: This is how search engines store and organize the content found when crawling. Once a crawler visits a page, Google stores the data it collects (like text, images, and video content) in a massive database known as an index. This index contains details from all the web pages Google has explored.
- Ranking: This is how search engines determine where to place a web page in the search results for a given query. When you enter a query, Google looks through its index to find pages that match your query best. The pages that seem most relevant to your search terms appear higher in the search results.

With this understanding of how search engines rank pages, let’s explore how SEO works.
How Does SEO Work?
To show up in search results for relevant keywords, you need to first target those keywords on your site.
SEO involves creating and publishing helpful, reliable, and people-first content on a particular topic. And optimizing it for search engines so that when your potential customers search for relevant queries, your business can appear in front of them.
You can create different forms of content. Like blog posts, case studies, ebooks, whitepapers, and landing pages.
For example, if your company sells a project management software, you could create a blog post that targets the query “best project management tools.”

SEO also involves improving your site’s technical performance so that it offers a great user experience.
This includes focusing on elements like security, mobile-friendliness, accessibility, and speed.

The more user-friendly your website is, the better the experience for visitors. And the more likely it is to rank higher in search results.
SEO is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process.
Since search engine algorithms frequently change, tactics that are effective today might not be as effective tomorrow.
So, it’s important to consistently produce new content, update existing web pages, and continually optimize your website’s performance.
Why SEO Matters
There are three reasons why learning the SEO basics is worthwhile:
- You can drive more traffic to your website
- You can increase your brand awareness
- You can improve user experience
Let’s quickly review some examples.
1. Drive More Traffic to Your Site
At any given moment, billions of people use search engines to find information. In fact, Google processes 4.9 billion searches every minute.
This means that improving your website’s visibility on search engines can put your business in front of more customers. Potentially a lot more customers. And drive more traffic to your website.
Our study of over four million Google search results proves it. Results showed that the first organic search result receives 27.6% of all clicks. The number falls down to 15.8% for the second result and 11% for the third. And so on.
Here’s a complete click-through rate (CTR) breakdown for organic results on the first page of Google:

Keep in mind that driving more traffic to your site isn’t the only key to business growth.
The traffic quality and how you engage visitors once they land on your site are also major determining factors in whether they turn into customers or not.
2. Increase Brand Awareness
SEO can put your business on the radar of potential customers who might not know you yet.
When your website appears in search results, it introduces your brand to those searching. And each time your site shows up, it reinforces your brand in their minds.
To make the most of this exposure, focus on publishing high-quality, valuable content that genuinely helps your visitors.
When your content is useful and informative, it builds trust and positions your brand as an authority. This trust makes visitors more likely to remember you and eventually purchase from you down the road.

Overall, SEO not only increases your brand’s visibility but also helps in establishing trust and credibility by making valuable content more discoverable.
3. Improve User Experience on Your Site
When you optimize your site for search, you’re also improving the overall user experience.
This includes focusing on website elements that contribute to the overall user experience. Like how fast your site loads, how easy it is to navigate, and how mobile-friendly it is. And more.

This positive experience makes visitors more likely to stay longer and make a purchase.
So, it’s important to publish high-quality content that is also pleasant to consume on a fast-loading, mobile-friendly, and secure site.
Essential SEO Terms to Know
Before we dive deeper, let’s review some key SEO terms you’ll encounter:
Search engine results page (SERP): The SERP is displayed after a user enters a keyword or phrase—it contains ranked results the search engine has deemed most relevant to that query.

Organic search results: The section of the SERP that displays unpaid, naturally ranking results.

Organic search traffic: The number of visitors who land on your website by clicking on organic (unpaid) search results.

Authority score: A metric that predicts how well a website can rank on SERPs. It ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a greater ability to rank.
Use Backlinko’s Free Website Authority Checker to find out your website’s authority score.

Page authority (PA): Similar to authority score (AS), PA measures the predictive ranking strength but focuses specifically on a single page rather than an entire domain.

SERP features: Special boxes or enhancements within the SERPs, such as AI overviews, featured snippets, local packs, and knowledge panels.

Featured snippets: Highlighted boxes at the top of Google search results that provide direct answers to queries.

People Also Ask: A feature in Google’s search results that shows a list of related questions that people search for frequently, providing quick access to additional information.

Keyword Research Basics
Keyword research is the process of identifying the most relevant and promising keywords for your business.
For example, if you run a backyard website, you may want to rank high for “best pergola covers.”

By incorporating relevant keywords into the content on your site, you improve your chance of appearing in search results for queries that use those keywords. This can further improve your business’ visibility and attract more customers.
Keyword Research Terminology
Seed keywords: Broad terms related to your industry, business, product and/or service that form the foundation of your keyword research. You can use these terms to generate more keyword ideas. For example, if your company sells online video editing software, a seed keyword can be “video marketing.”

Monthly search volume: The average number of times a specific keyword is searched on search engines each month. In the image below, “Volume” shows location-specific searches, while “Global Volume” represents the total searches worldwide.

Keyword difficulty (KD%): A metric that indicates how hard it would be to create content that ranks in the top 10 results on the SERP for a specific keyword.

Search intent: The likely purpose behind a keyword search. For instance, there are informational, commercial, navigational, and transactional searches.

Keyword Research Tactics
Use a Keyword Research Tool
Keyword research tools let you discover and analyze keywords based on the seed keywords you enter.
These tools have access to massive databases of keywords. Tap into them to find a wide range of related keywords. Plus, additional information for each keyword like their search volume, KD%, search intent, and more.
Keyword research tools also let you filter keywords by different parameters (search volume, KD%, search intent, questions) to help you narrow down your search.
For instance, use the KD% filter to identify keywords that are easier to rank for.

Here are some top recommended keyword research tools:
| Tool | Best For | Top Feature | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword Research Tool by Backlinko | Beginners and those seeking free access to keyword data | Leverages Semrush’s extensive keyword database (25.5 billion keywords) | Free |
| Google Search Console | Identifying and improving existing rankings | Integration with Google Analytics | Free |
| Semrush | Comprehensive competitor and keyword analysis | Keyword Magic Tool | Starts at $117.3 per month; offers a 7-day free trial (use our special link for a 14-day trial) |
| Jaaxy | In-depth analysis of keyword competition | Quoted Search Result (QSR) | Starts at $49 per month; free trial available |
Further Reading: 17 Best Free and Paid Keyword Research Tools for SEO
Start with Seed Keywords
You begin the keyword research process by adding seed keywords to your keyword research tool. So, it’s important to first identify seed keywords relevant to your industry, business, product, and/or service.
How to identify seed keywords:
- Brainstorming: Start with a brainstorming session. Think about the terms your potential customers might use to describe your products or services.Break down your products or services into basic categories and subcategories. Each of these can be a potential seed keyword. For example, if you sell a video editing software, a seed keyword can be “video marketing.” Because video marketing is a great use case.
- Check competitors’ websites: See which keywords your competitors are targeting. Visit their websites and note the main terms they use, especially those in titles and headers.
- Industry terms: Note down standard industry terms that are commonly known and used. These can be technical terms, brand names, or even common jargon in your field.
Once you identify your seed keywords, use them to find related keywords using a keyword research tool. Like Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool.
Simply launch the tool. Enter a seed keyword. In this example we’ll use “Excel”. Then select a country from the drop-down, and click “Search.”

The tool will display a list of related keywords for you to review.
For each keyword, you’ll find relevant information. Like its monthly search volume, KD%, and search intent.

Use filters to narrow down your search.
For instance, you can use the “Intent” drop-down filter to identify keywords with high purchase intent. Targeting these keywords can potentially bring in more sales and revenue.

Apply a combination of filters to identify the most promising and relevant keywords for your business.
Identify Low-Competition, High-Volume Keywords
These are keywords that get a significant amount of searches each month yet aren’t very competitive. By targeting these keywords, you can rank higher in search results and attract more visitors to your site.
For example, “excel formula generator” is a great low-competition, high-volume keyword.
As per Semrush’s Keyword Overview tool, it has a 5.4K US and 13.9K global search volume (as of this writing). Yet its KD% is only 22%, which makes it easy to rank for.

Use Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool to identify such keywords.
Begin by adjusting the drop-down “Volume” filter to above 1,000. This is the threshold generally recommended for sufficient search traffic.

Then, from the “KD%” (Keyword Difficulty percentage) drop-down menu, select either “Easy” or “Very Easy” to focus on keywords that are less competitive and easier to rank for.

Keep in mind that not all keywords will fit your needs, so make sure to manually review them to ensure they are relevant to your specific goals.

Find Keywords Your Competitors Are Targeting
This method involves spotting keywords your competitors are targeting yet you aren’t. Helping you identify new keyword opportunities and potentially increase your market share.
Use a tool like Semrush’s Keyword Gap to compare your keyword profile against up to four competitors.
Start by opening the SEO tool. Enter your website URL along with the URLs of up to four competitors. Then click “Compare.”

In the results, the “Top Opportunities” section will show you the keywords you’re missing out on (“Missing”). And those where your competitors have a higher ranking (“Weak”).

To see a comprehensive list of keywords that your competitors target but you do not, scroll down to the “All keyword details for:” section. Select the “Missing” tab.

On-Page SEO for Beginners
On-page SEO is about optimizing a website’s pages and the content on those pages for search engines. So that they rank higher in the results for the keyword(s) they target.
This includes focusing on on-page SEO elements like title tags, meta descriptions, and alt text.
Let’s review what these elements are.
On-Page SEO Terminology
Title tag: An HTML element that specifies the title of a web page. The title tag appears in the browser tab and as the headline for the page in search engine results.

Meta description: An HTML element that gives a brief summary of a web page’s content. It appears below the title in search engine results and can influence click-through rates.

Alt text: An HTML element that specifies what an image represents. Alt text helps search engines understand the content of the images and can improve image search rankings.

H1 tag: An HTML element used to define the main heading or subject of a web page.

URL slug: The part of a URL that comes after the domain name and identifies a specific page. Like this:

On-Page SEO Tactics
Perform an SEO Site Audit
An SEO site audit can help you identify on-page (and technical) SEO issues that may impact your website’s rankings. Issues can include missing alt text, poor internal linking structure, broken links, poorly optimized title tags and meta descriptions, and inadequate use of keywords.
Use Semrush’s Site Audit tool to analyze the health of your website. This tool evaluates your website for over 140 on-page and technical SEO issues.
Simply launch the tool. Enter your website URL and click “Start Audit” to create a new project.
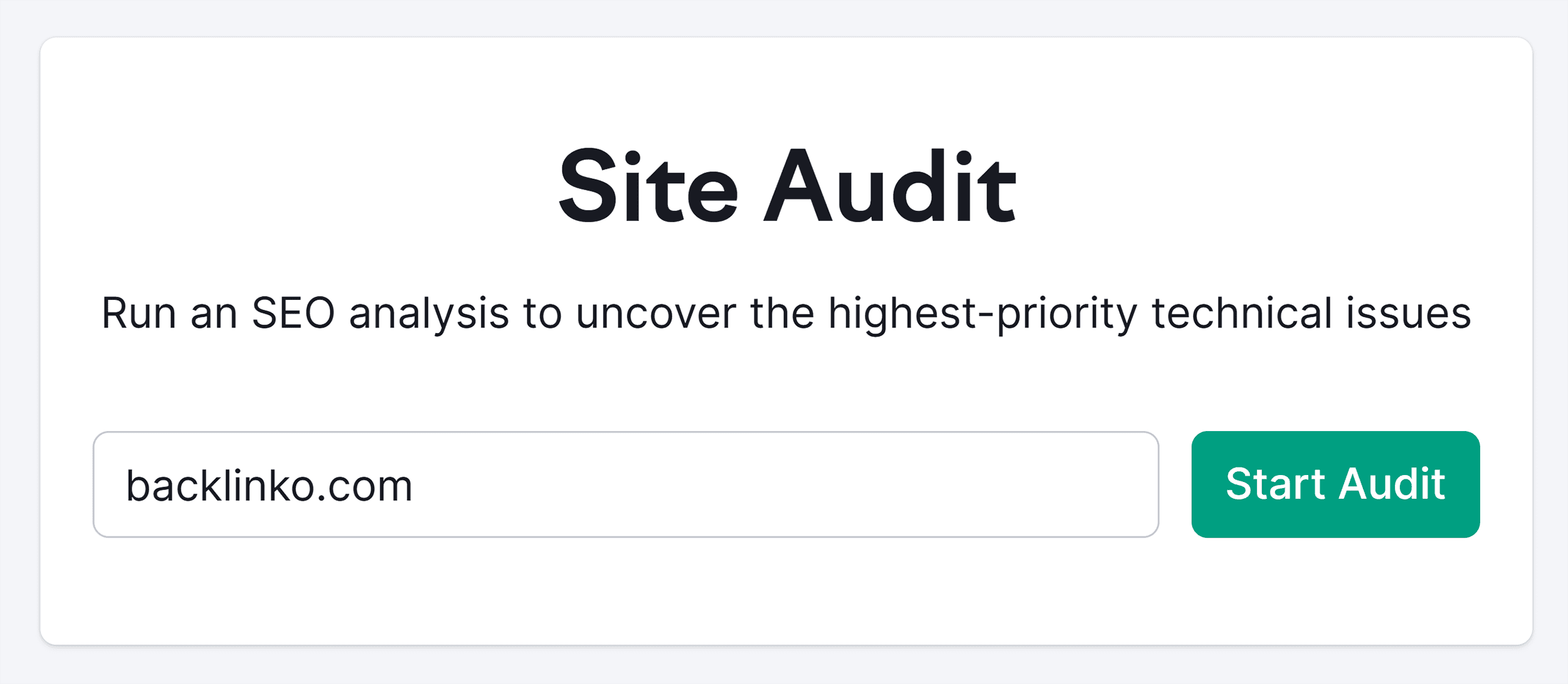
Next, specify how many pages you want to include in the audit. For example, 100 pages. Then select “Website” as your crawl source, like this:

At this point, you have two options: Further configure your settings (crawler settings and URL parameters) or stick to default ones. For now, let’s proceed with the default settings.
Click “Start Site Audit” to initiate the audit process.
Once it’s complete, navigate to the “Issues” tab. Here, you can find a comprehensive list of on-page SEO and technical issues impacting your website’s search performance.
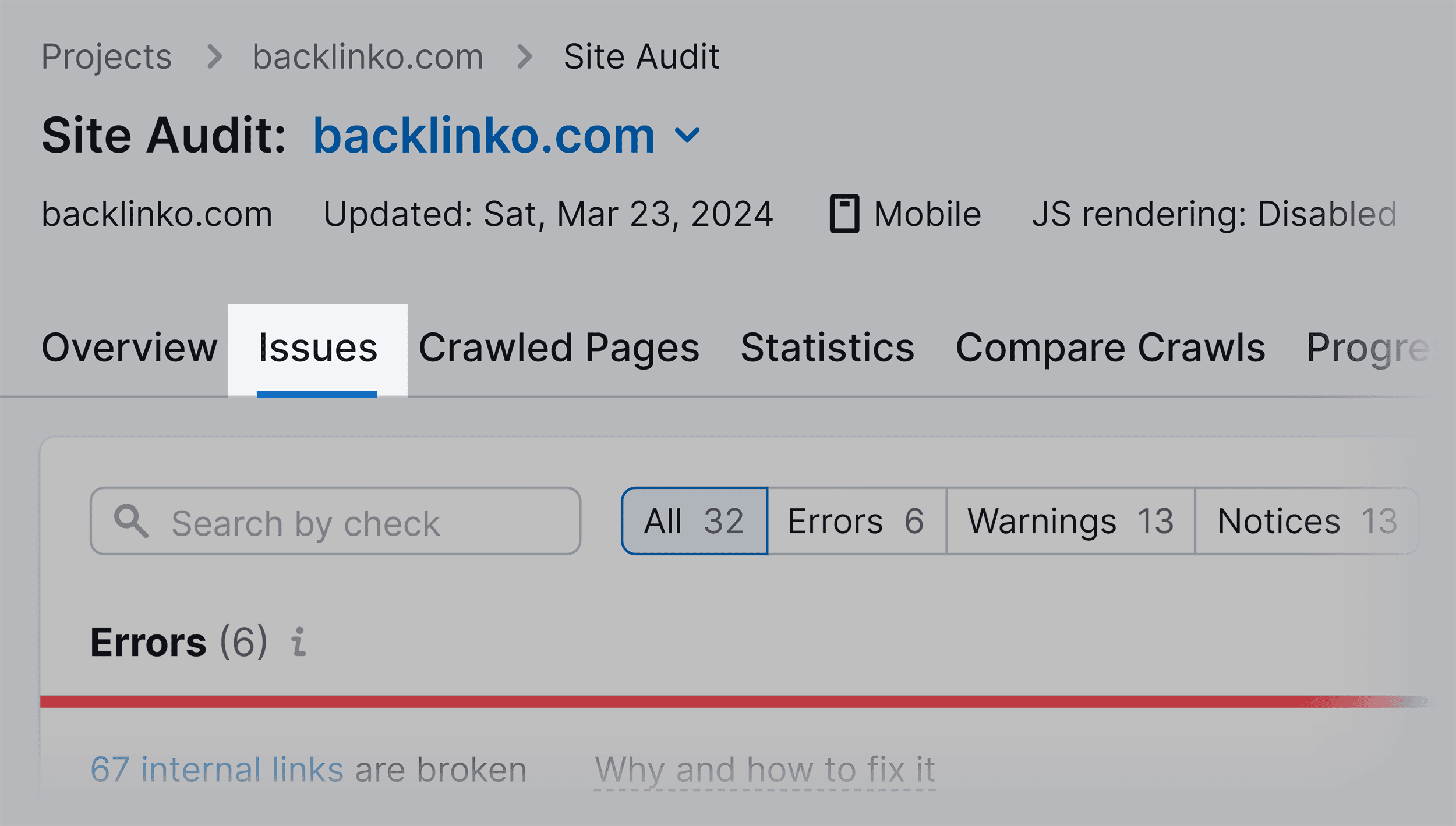
To specifically focus on on-page SEO elements, use the search bar to identify the issues directly related to on-page optimization. Type keywords such as “title tag,” “meta description,” or “H1 tag” into the search bar to filter and display only the relevant results.
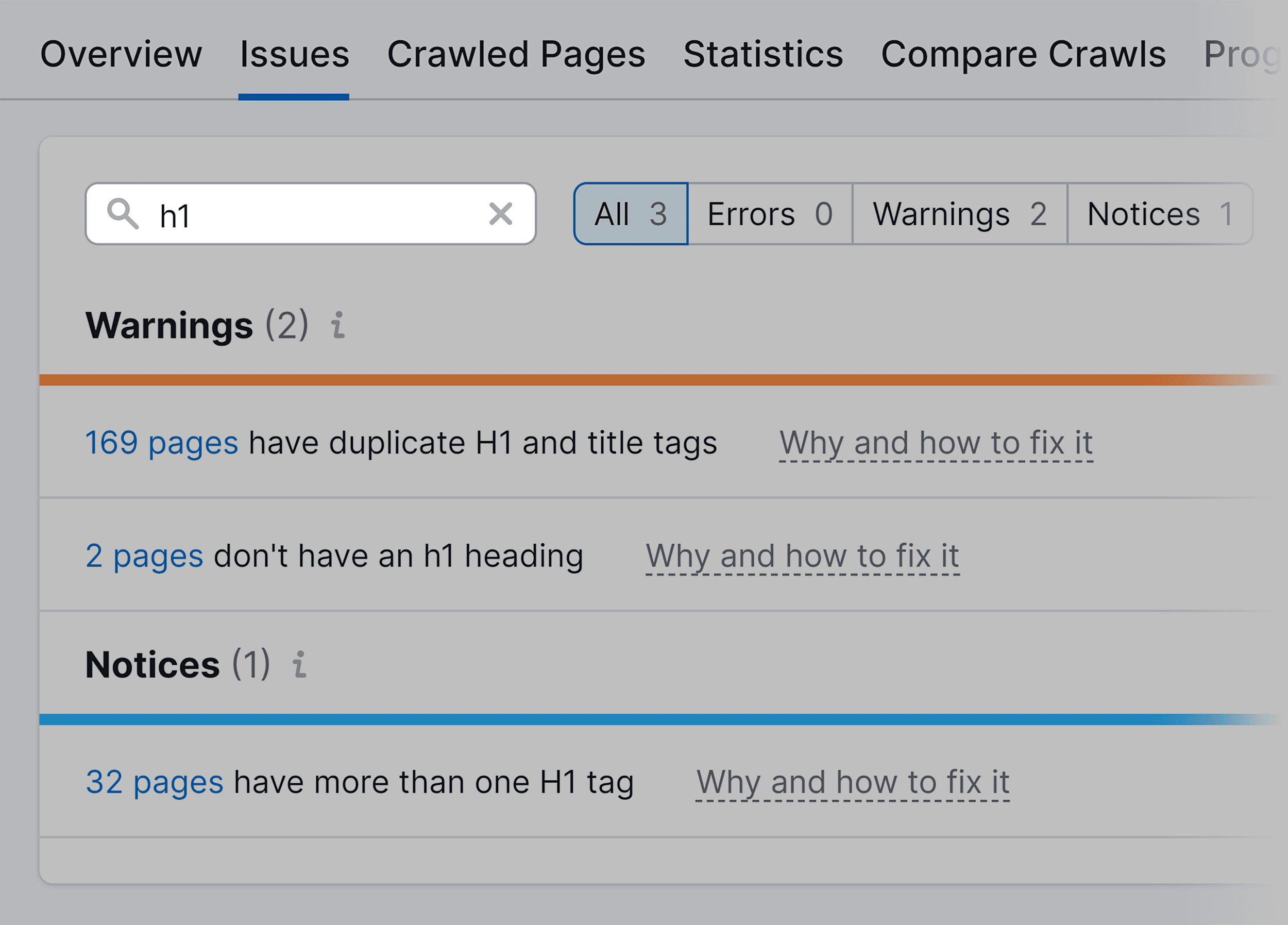
Fix these issues to improve your website’s on-page SEO.
Further Reading: The 15-Step SEO Audit Checklist
Create High-Quality Content That Matches Search Intent
Search engines like Google aim to present the most relevant information to users.
So, for every keyword you target, make sure the content you create aligns with the search intent of that query. And offers value to the readers.

There are four main kinds of search intent:
Informational: Users are seeking information. For example: “what is influencer marketing.”

Navigational: Users are trying to reach a specific website or webpage. For example: “amazon.”

Transactional: Users are looking to make a purchase or engage in another type of transaction. For example: “buy website domain.”

Commercial: Users are considering a purchase and are looking for the best option or comparison information. For example: “best influencer marketing tools.”

A blog post targeting the keyword ‘best video editors’ should primarily focus on top video editing software. Rather than extensively covering what video editors are or their general benefits.
Because the search intent behind the keyword “best video editors” is commercial. Users are looking for video editing software options rather than a definition for what a video editor is.

Many keyword research tools like Semrush and Backlinko display search intent of keywords. Making it easier to understand what users are likely looking for. That way, you can create content accordingly.

Optimize On-Page SEO Elements of Important Web Pages
Title tags, meta descriptions, H1 tags, and alt text are important elements of on-page SEO.
They not only help search engines understand the content and context of your pages but also improve the user experience by providing clear and descriptive information about what your content is about.
Read our on-page SEO guide to learn how to optimize the on-page SEO elements of important pages on your site.
Technical SEO 101
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing your website’s technical performance. So that it delivers a great user experience. And makes it easier for search engines to discover, understand, and store your content.
Technical SEO Terminology
Crawlability: The ability of search engine bots to access and navigate your website. Good crawlability ensures that all your pages can be discovered by search engines.

Indexability: The ability of a web page to be stored in a search engine’s index. Proper indexability ensures that your content is eligible to appear in search results.

Page speed: The time it takes for the content on your web page to load. It’s a confirmed ranking factor.

Mobile-friendliness: How well your website performs on mobile devices. It’s a confirmed ranking factor.

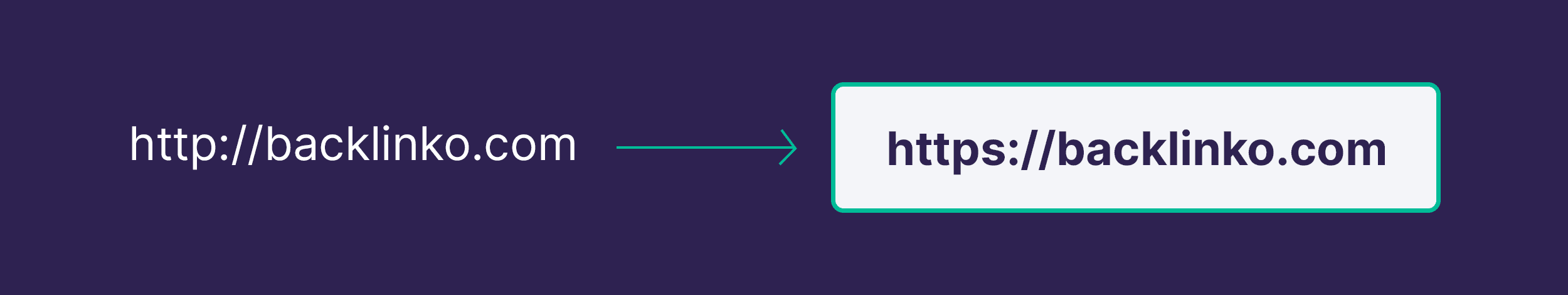
HTTPS: A secure version of HTTP that encrypts data between the user’s browser and the website. It’s a confirmed ranking factor.
Technical SEO Tactics
Improve Your Website’s Crawlability & Indexability
For your website to appear in search results, search engines must be able to crawl and index your pages. So, it’s important to identify any crawlability and indexability issues. And resolve them as soon as possible.
To further improve indexation, create and submit an XML sitemap. Use a tool like XML Sitemaps Generator to create an XML sitemap for your website.
Simply enter your website URL and click “Start” to generate a sitemap.
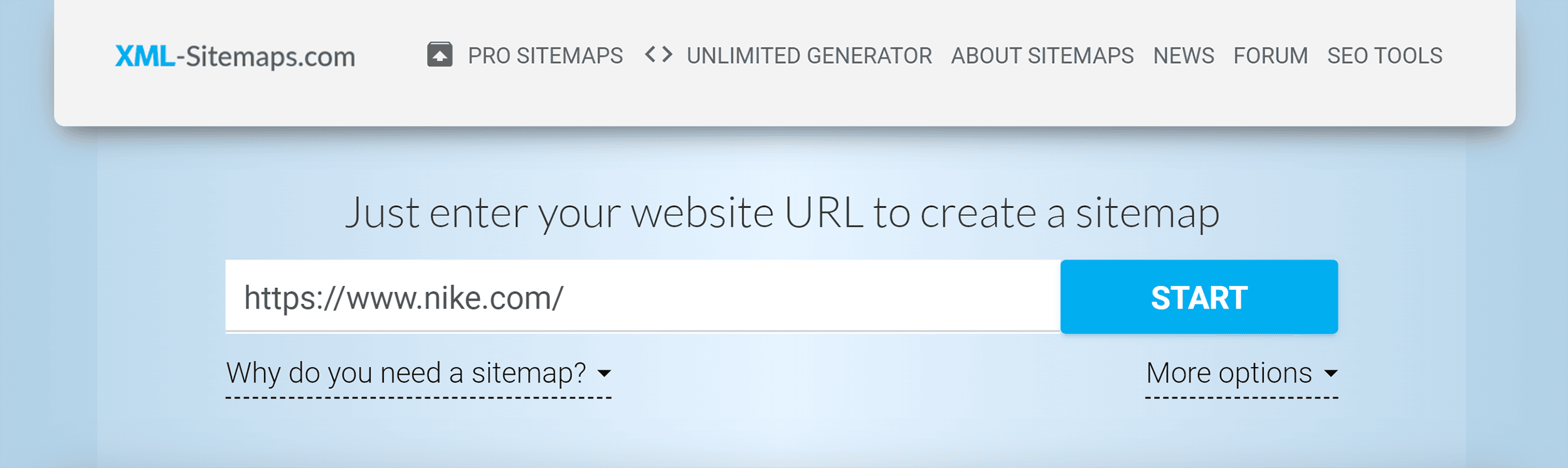
Download and upload the sitemap to your website’s root directory. For example, nike.com/sitemap.xml.

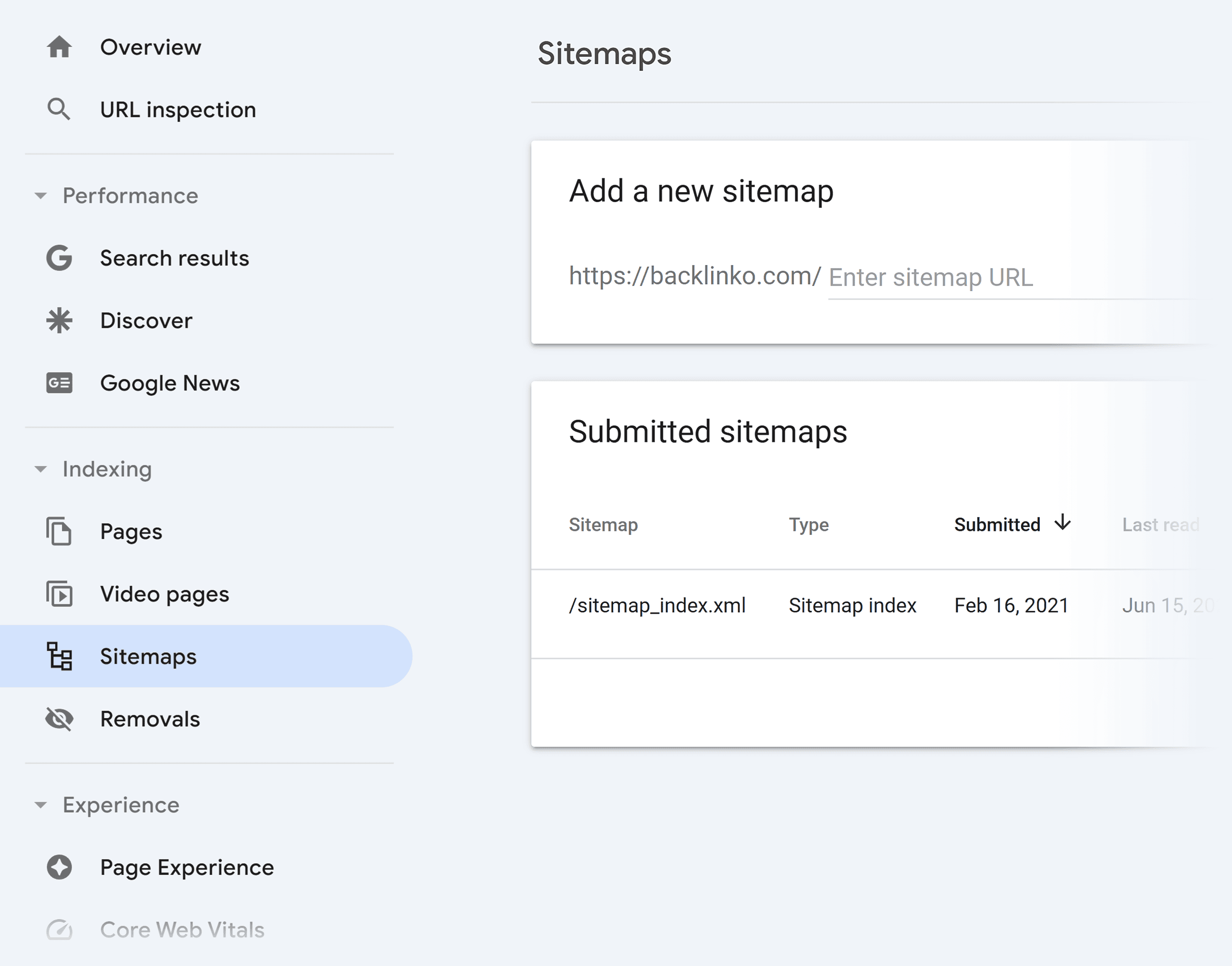
Then, submit it through Google Search Console (GSC).
In GSC, select “Sitemaps” from the sidebar, enter your sitemap URL, and click “Submit.”
Further Reading: Top 8 Sitemap Generator Tools
Improve Your Website Page Speed
Faster page speed improves user experience and can positively impact search engine rankings. Google uses Core Web Vitals metrics to assess page speed. These include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the main content on a page to load
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Evaluates the time from when a user interacts with your page to when the visual response is noticeable
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Monitors how often users experience unexpected layout shifts during page interaction
Use Site Audit to improve your website’s page speed. After setting up your project, find the “Core Web Vitals” section under “Thematic Reports” in the default “Overview” tab. Click “View details.”
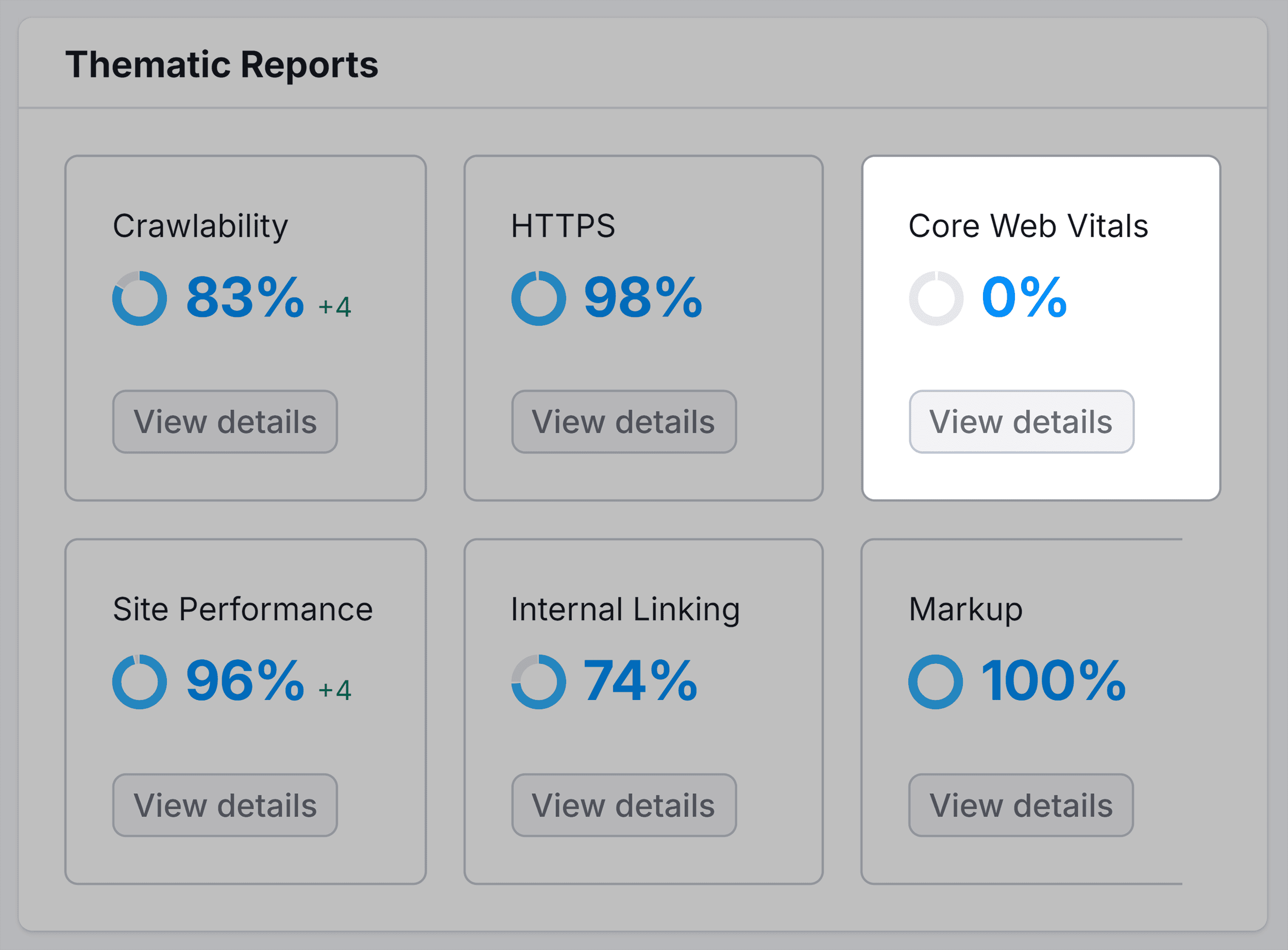
This report will provide a snapshot of your pages’ performance in terms of Core Web Vitals.
Go through this report and act on the recommendations to improve your website’s page speed.
Secure Your Site with HTTPS
A secure connection (HTTPS) can directly influence your search engine rankings.
To check if your website uses HTTPS, look at the URL in your browser’s address bar. Click on the icon next to the URL. If it says “Connection is secure,” your site uses HTTPS.

To use HTTPS, you need an SSL or TLS certificate on your website.
Use the Site Audit to identify HTTPS implementation issues.
After setting up your project, go to the “HTTPS” section under “Thematic Reports” and click “View details.”

This report shows information on:
- Security Certificate (which verifies your site’s identity)
- Server protocol (rules for data exchange between your server and users)
- And your Website’s Architecture (how your website is organized)

Optimize Your Site for Mobile Devices
Search engines like Google default to the mobile version of a website for crawling. That means if your website isn’t optimized for mobile devices, it might not perform well in SERPs.
Wondering how to optimize your site for mobile devices?
Implement a mobile-friendly website theme. Many content management systems or website builders, like WordPress, offer themes that automatically adjust to different screen sizes.
Or implement a responsive design. Use CSS media queries to adjust the layout for different screen sizes.
Consider using Site Audit to identify issues impacting your site’s performance on mobile devices.
After setting up your project, navigate to the “Issues” tab and search keywords like “mobile” in the search bar.

As you can see, Backlinko doesn’t have any mobile issues.

But if your site does, you can fix the issues that appear to improve your website’s mobile performance.
Off-Page SEO Basics
Off-page SEO is about improving a website’s search engine visibility without performing any changes on that website.
This involves doing activities that earn links and mentions from other reputable websites.
Off-Page SEO Terminology
Backlinks: Links from an external website back to yours. Search engines consider these an important ranking signal. Because they demonstrate to the search engine that other websites find your content valuable.

Guest blogging: Writing articles for other websites to earn more exposure, backlinks, and authority in your industry.

Off-Page SEO Tactics
Get Backlinks from High-Authority Sites
The more backlinks a web page gets from high-authority sites, the better its chances of ranking higher in the SERPs.
Because search engines like Google consider backlinks as votes of confidence. Meaning, when a high-authority site links to your page, it’s like that site is vouching for the quality and relevance of your content.
So, focus on winning backlinks from websites with high authority scores.
But it’s easier said than done. For another website to link to yours, there needs to be a good reason.
Here’s why they might do it:
- Quality content: If your website offers valuable, well-researched, and unique content (research reports, infographics, eBooks), other sites will find it useful to link to your pages. Because they want to provide their readers with reliable and insightful resources. For instance, if you publish an in-depth report on industry trends, a blog in the same field might link to your report when discussing those trends.
- Expertise and authority: When your website is recognized as a trusted and authoritative source in your niche, others are more likely to link to it.
- Mutual benefit: Websites often link to each other as part of a collaboration or partnership. For instance, if you write a guest post for a site, they might include a link back to your website in return.
If you’re new to building backlinks, it can be confusing to figure out where to start or which websites might link to yours.
A smart approach is to study how your competitors are earning their backlinks. By examining which sites are linking to them, what type of content is attracting those links, and the context in which the links are being shared, you can develop a strategy that works for your own site.
Use Semrush’s Backlink Analytics to evaluate your competitors’ backlink profiles.
Simply launch the tool. Enter a competitor’s website. For example: www.lunya.co. And click “Analyze.”

Navigate to “Backlinks.” Here you’ll find a comprehensive table with data on the competitor’s backlinks.

This table will show you details like the source of the backlink, the anchor text used, the type of link (follow or nofollow), and the authority score of the linking domain.

Use this information to identify potential backlink opportunities for your own website.
Look for high-authority domains that regularly link to your competitors and examine the content they find valuable enough to link to. Pay attention to the anchor text, as this can give you clues about the context in which the link was shared and what specific aspect of the content appealed to the linking site.
Run a Link Building Campaign
Running a link building campaign is a great way to get backlinks to your site. It involves identifying and manually reaching out to prospects (sites) for your link building campaign.
Use Semrush’s Link Building Tool to run a winning link building campaign. This tool lets you plan, manage, and execute your link building campaign from a single interface.
Simply launch the tool. Enter your website (e.g., www.fitnessguru.com) and click “Start Link Building.”

Enter the keywords for which you want to improve your ranking.

Along with your competitors’ sites (e.g., www.healthline.com, www.bodybuilding.com, and www.menshealth.com).

Click “Start Link Building” again.
Next, navigate to the “Prospects” tab to see a list of suggested prospects for your link building campaign.

Carefully review the list. Move the most promising prospects to the “In Progress” tab by clicking the “To In Progress” button next to each one.

In the “In Progress” tab, start conversations with your chosen prospects directly from the Semrush tool. You may find email addresses for some of the company contacts.

Initiate and follow up on conversations with each prospect using Semrush’s interface.

Finally, keep an eye on the progress of your link building campaigns in the “Monitor” tab.
Submit Guest Posts to High-Authority Sites in Your Niche
Guest blogging is another great way to build high-quality backlinks to your site. It also helps you increase your brand awareness and build authority in your niche.
How it works:
Research potential sites: Identify high-authority blogs and websites in your industry that accept guest posts. Look for sites with strong domain authority.

Pitch your topic: Reach out to the people who manage content operations at these publications/websites with a well-crafted pitch. Pitch a topic that aligns with the topics they’re publishing currently.

Create valuable content: Write a high-quality post that provides real value to the readers of the publication you’re writing for. Thoroughly read their content guidelines to make sure your post meets their standards.

Include backlinks: Naturally incorporate backlinks to your site within the content. Most publications that accept guest posts allow one or two link insertions. However, it’s a good idea to thoroughly review the section (in their guidelines) where they talk about link insertions.

Find good guest post opportunities using these strings on Google:
- Your keyword + “guest post”
- Your keyword + “guest article”
- Your keyword + “write for us”
- Your keyword + “contribute to our site”
- Your keyword + “contributing writer”
For example, if you sell influencer marketing software, you can find relevant publications in your niche by using the string “influencer marketing” + “guest post” on Google.

Local SEO Basics
Local SEO is the process of optimizing your business’ local presence on search engines. So that it appears for location-based searches.
Local SEO Terminology
Google Business Profile: A free tool that allows businesses to manage their online presence across different Google services. Like Search and Maps.
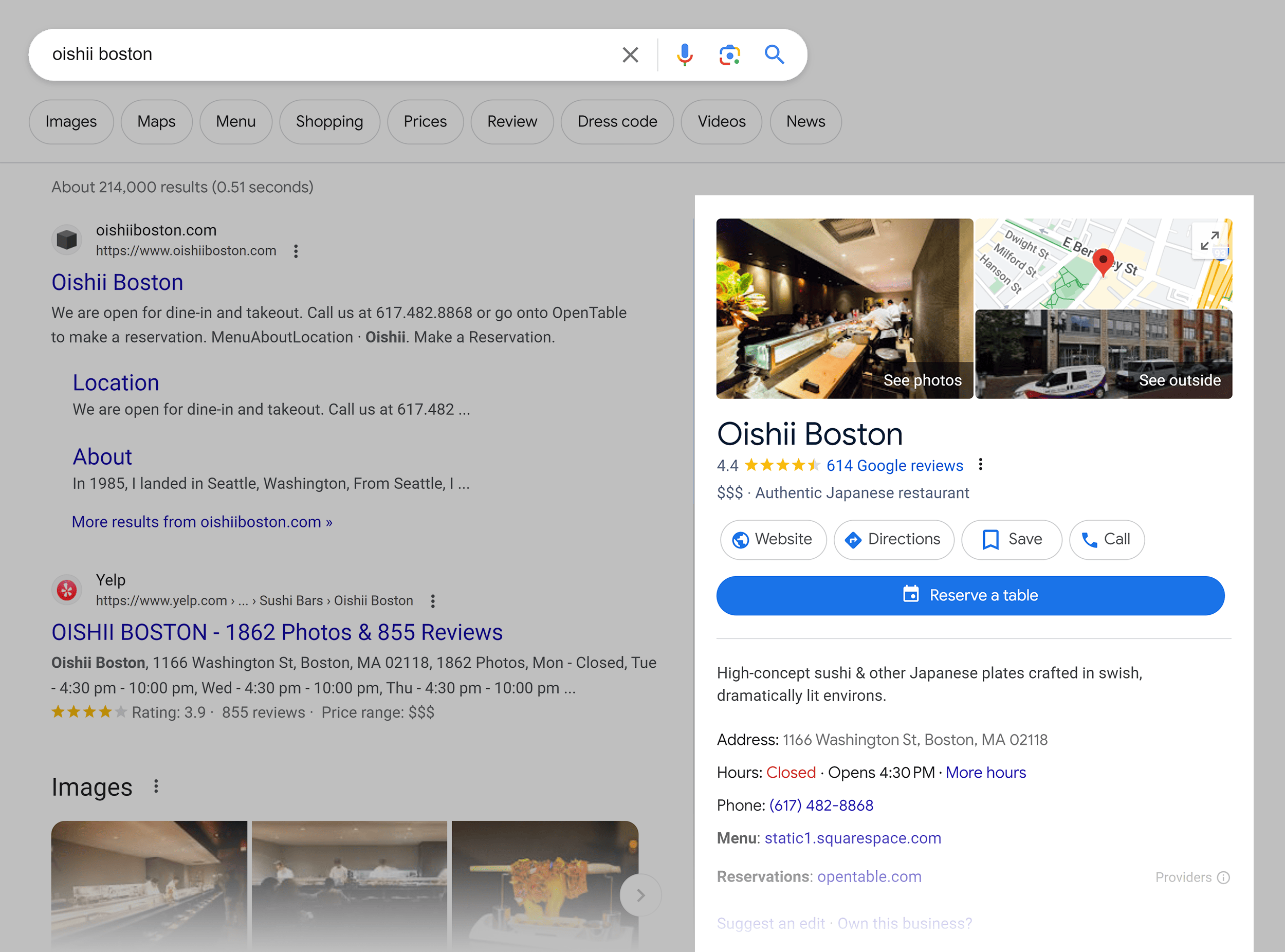
Local pack: A section in Google search results that displays a map and a list of top local businesses relevant to the search query.

Local keywords: Keywords that include location-specific terms. For example, “indian restaurant in new york.” For more on this, read our guide on how to perform local keyword research.

Local directories: Online platforms where businesses can list their information, like Yelp.

Location Pages: These are dedicated location pages on your website for each of your business locations.

Local SEO Tactics
Create a Google Business Profile
Google fetches information from Google Business Profile for local search results. Like the local pack.
So, if you haven’t yet created a Google Business Profile for your business, sign up for one. It’s a simple and straightforward process.
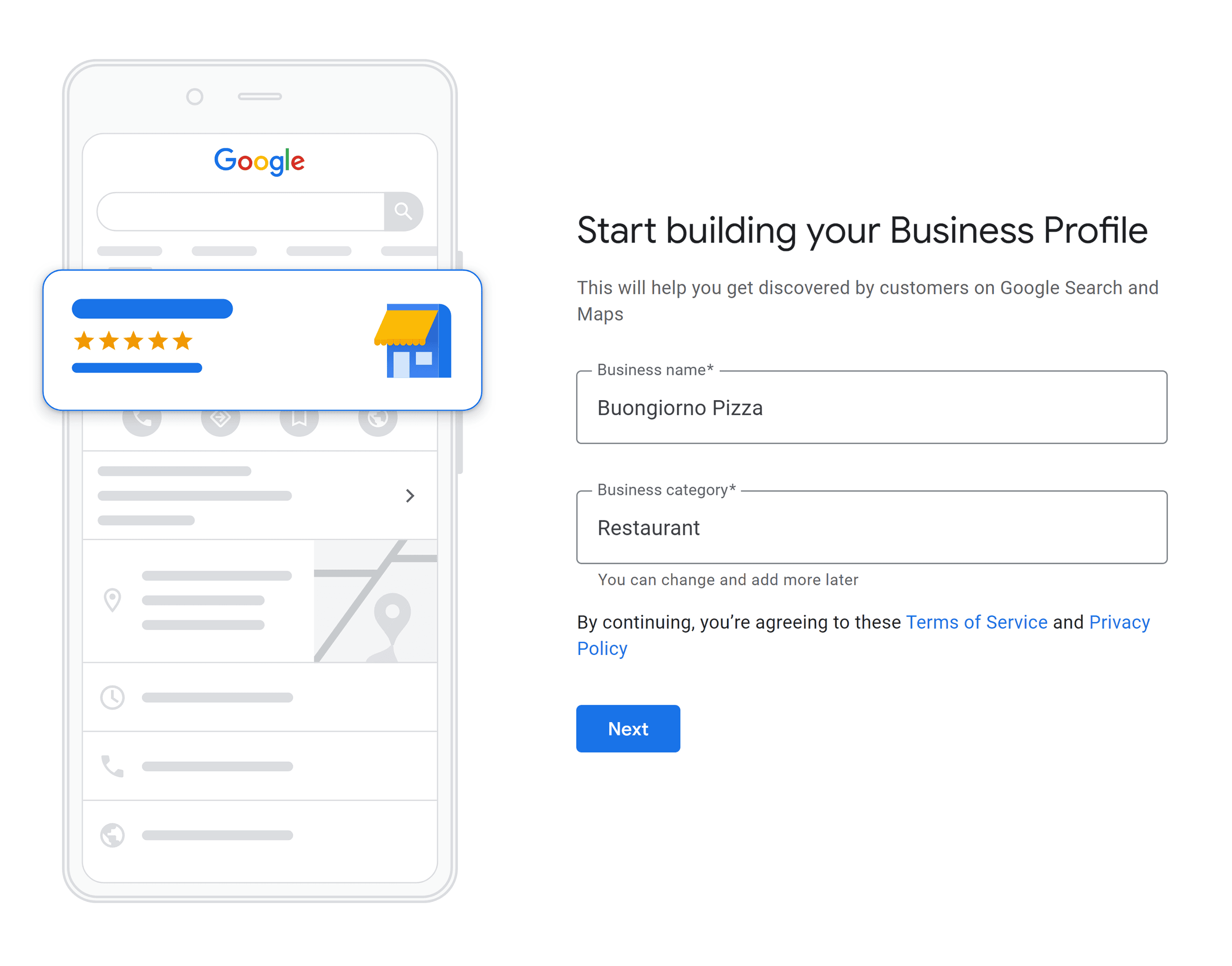
Optimize your profile so that it appears higher than your competitors in local pack for relevant keywords.
This includes:
Business Details: Write a concise and informative description of your business. Enrich your listing with phone number, address, hours of operation and your website URL. That way, your target audience can easily find you.

Photos and Videos: Add high-quality photos and videos of your business, products, or services.
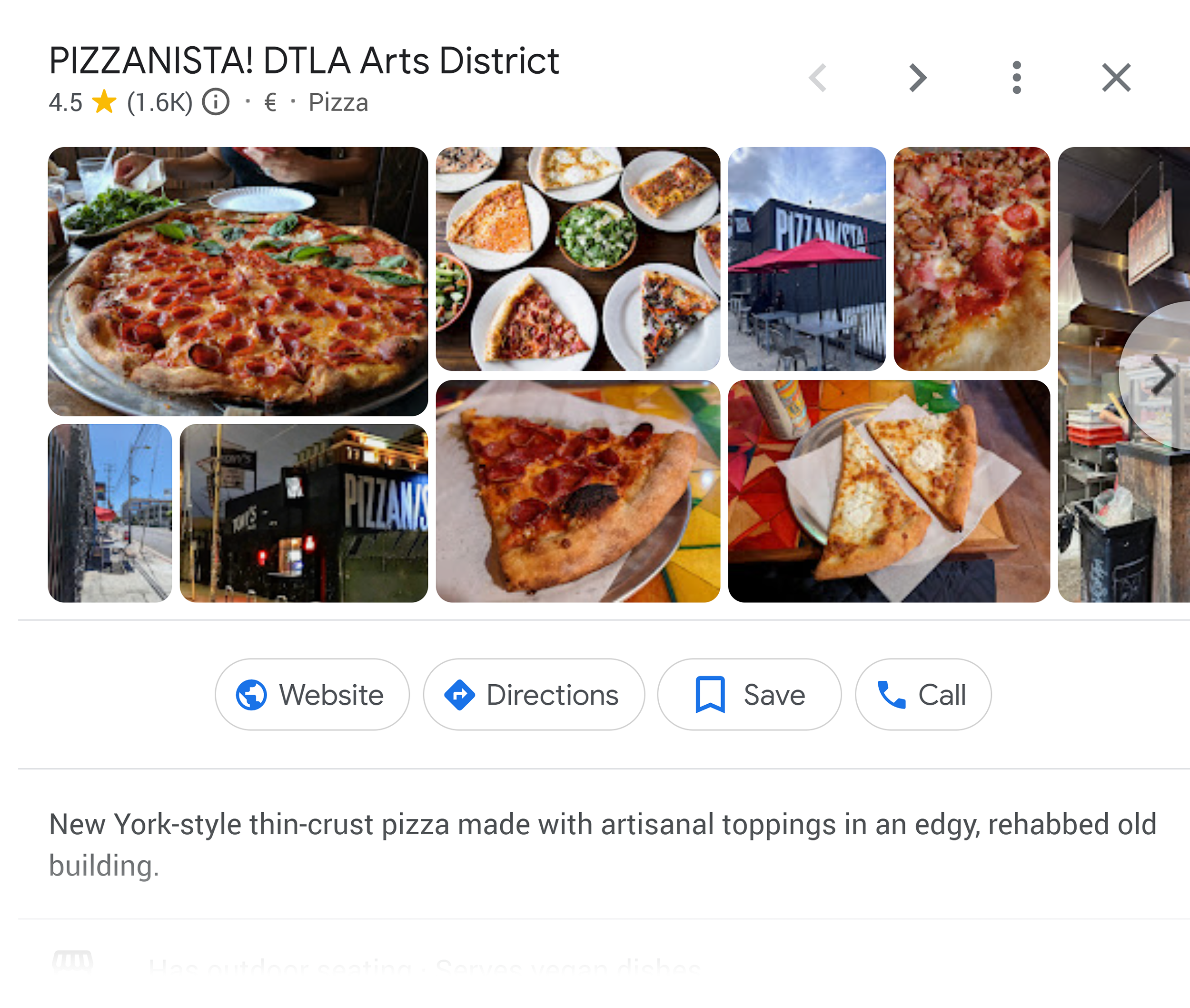
Services: Highlight specific products/services you offer. This can increase your chances of appearing in local search results when users type these services.

Customer Reviews: Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews. Respond to reviews (even to the negative ones) to show you value customer feedback and are laser-focused on improving your offering.
Also, make sure that your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) are correct and consistent with other listings. Because NAP citations are a key ranking signal.
Create Location Pages
If your business serves multiple locations, it’s a good idea to create dedicated pages for each location you serve. These pages help search engines understand where you operate and make it easier for potential customers to find you.
For example, Wasson Nursery has dedicated pages for each of its locations in Indiana.

Each page includes specific details like address, contact information and hours of operation relevant to that location. And the keyword it targets. In this case, it’s “muncie garden center.”

This page ranks #1 for the target keyword “ muncie garden center.”

Build an SEO Strategy to Get Started
Phew! You’ve learned a lot about SEO basics. You might be wondering, “What’s next?”
Now, it’s time to channel all this knowledge into a solid SEO strategy for your website.
An effective SEO strategy will not only give direction to your efforts but also help you focus on activities that offer the most benefit to your site’s visibility and search rankings.
It’s about applying what you’ve learned in a structured way, so you can systematically improve your site and measure the results.
Read our comprehensive SEO strategy guide that walks you through the essential steps for crafting an effective SEO plan tailored to your goals.
Also, make it a habit to stay on top of the latest SEO trends. Because of the ever-changing search engine algorithms and fierce competition.
