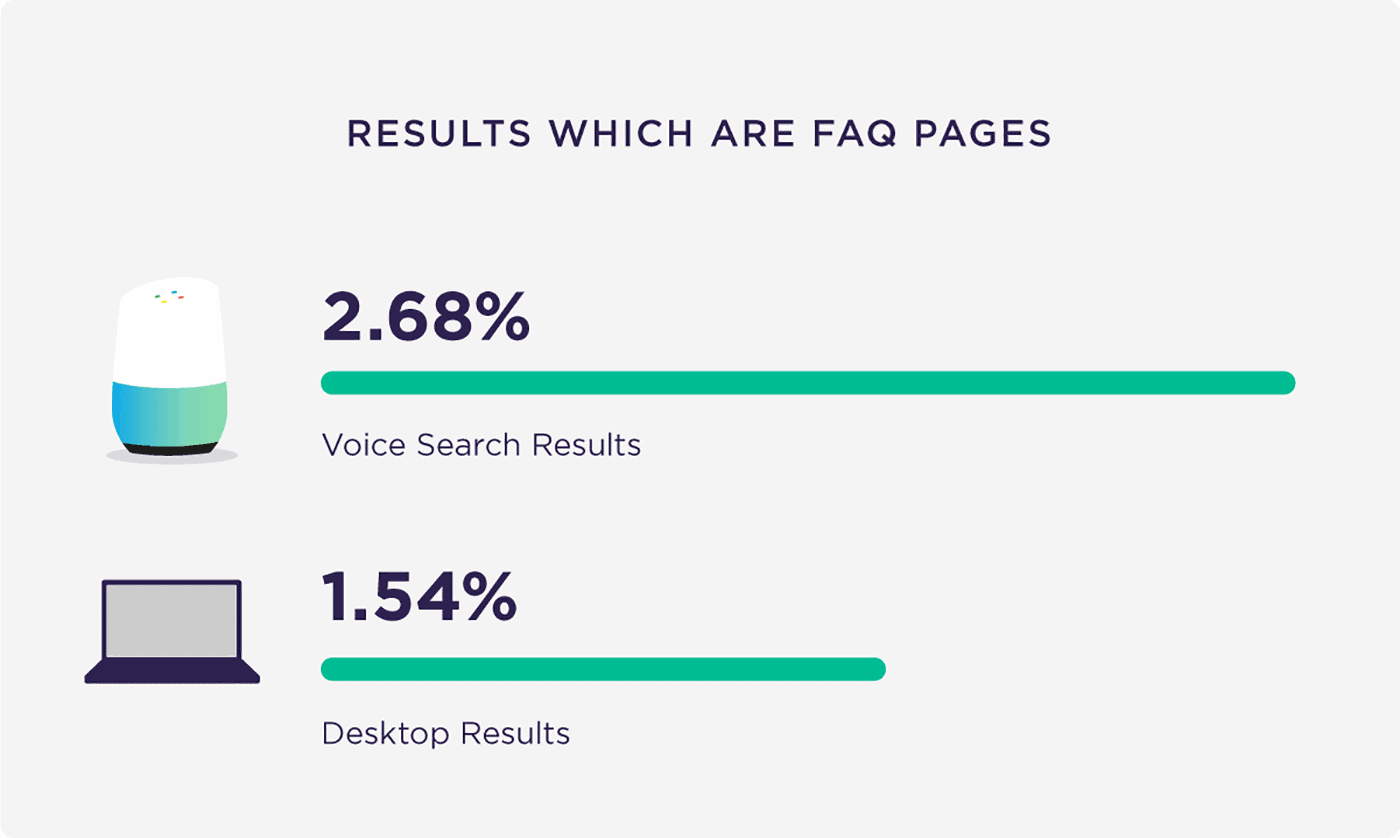
FAQ
What is the difference between off-page SEO and on-page SEO?
Off-page SEO focuses on optimizing signals that occur outside your website, such as building backlinks and establishing a social media presence. On the other hand, on-page SEO involves optimizing elements directly on your web pages, like content, meta tags, and internal links.
What is the difference between on-page SEO and technical SEO?
On-page SEO deals with optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and user experience. Technical SEO is a portion of on-page SEO that involves optimizing the technical aspects of your entire website, ensuring it’s crawlable, indexable, and performs well from a technical standpoint.
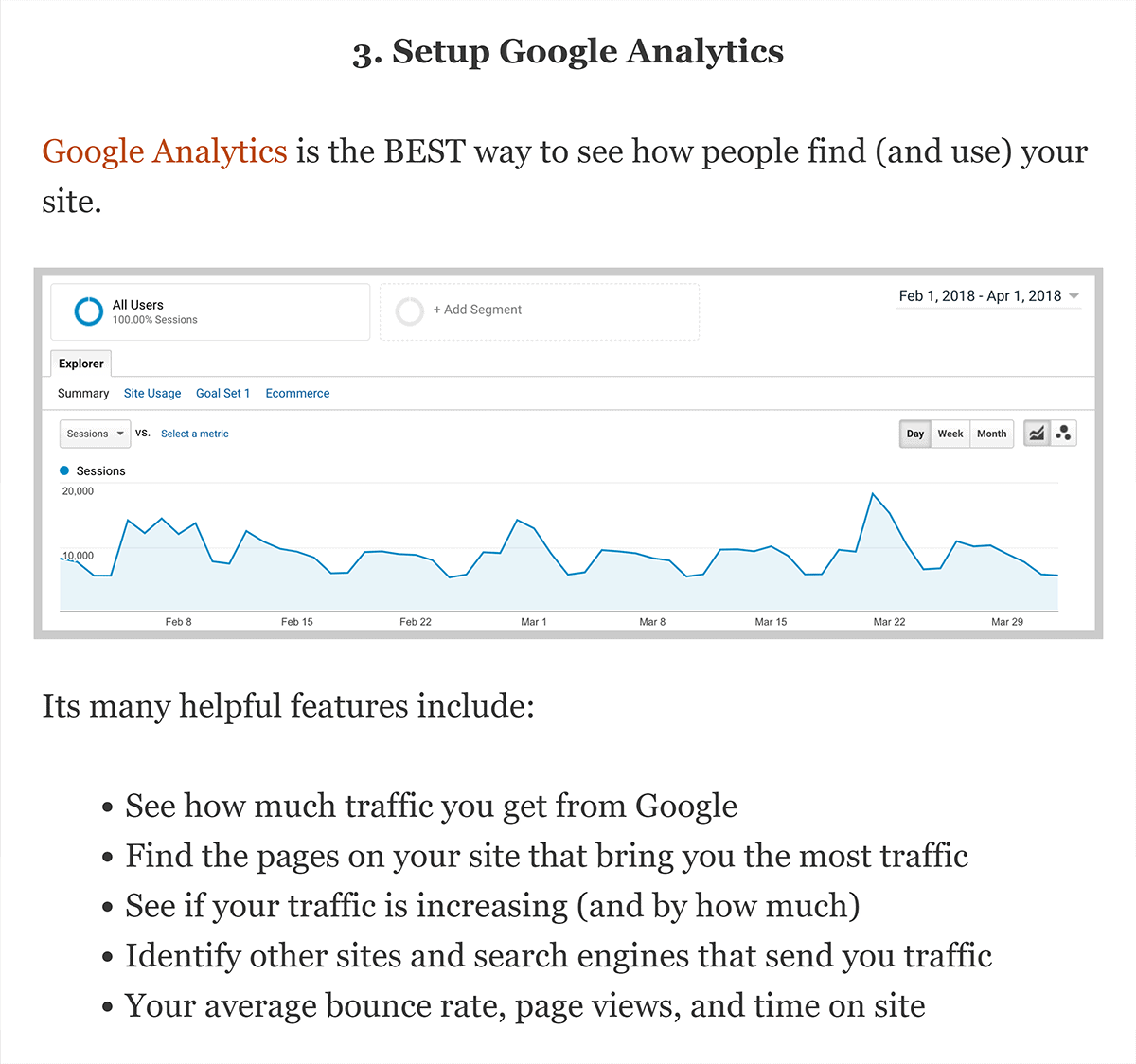
How often should I perform on-page SEO?
On-page SEO is not a one-and-done task. Regular monitoring and updates are essential, with a suggested frequency of at least once a month for routine checks. Conduct more in-depth assessments quarterly to ensure your content stays relevant and aligned with evolving search engine algorithms.
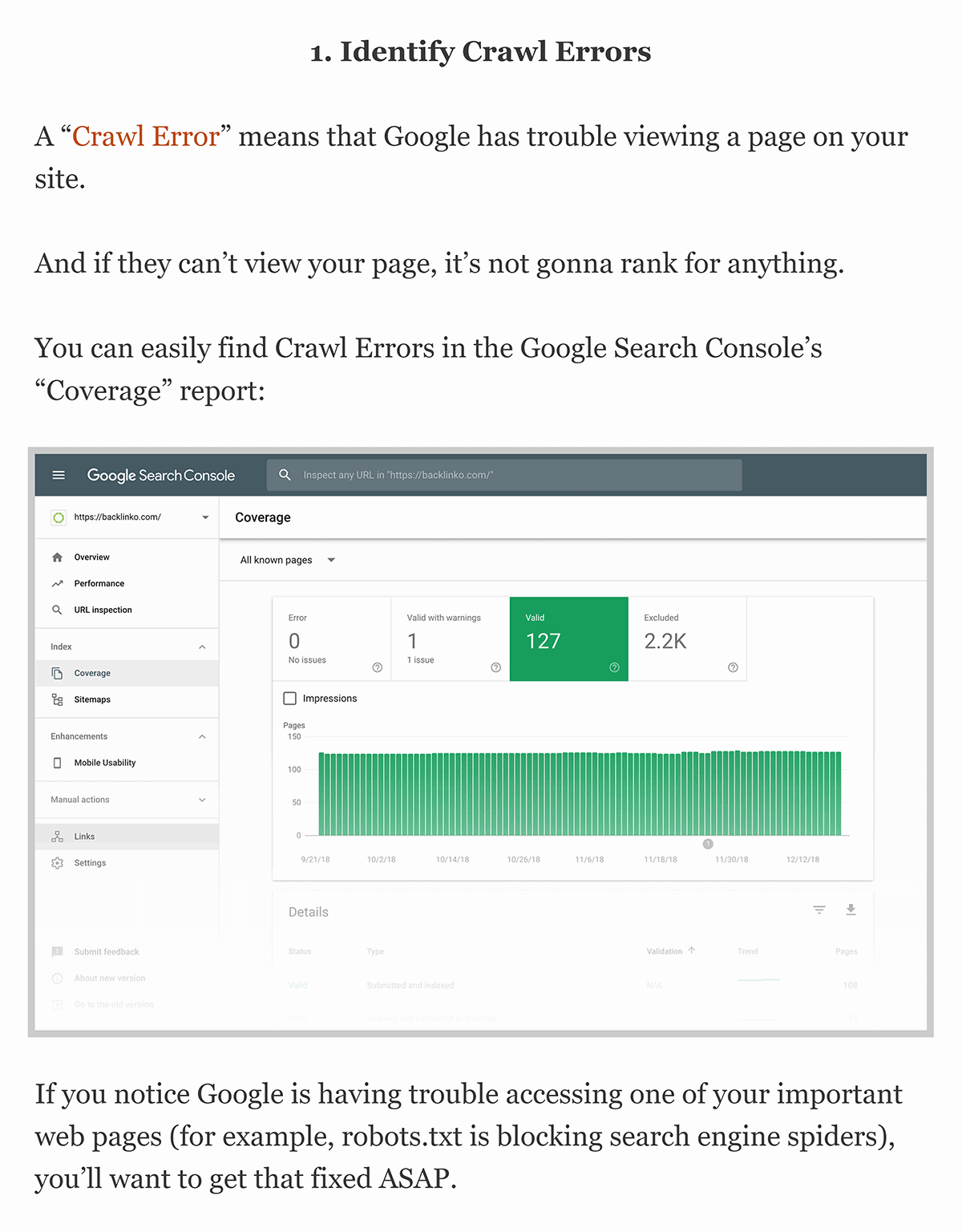
What are the key elements of on-page SEO?
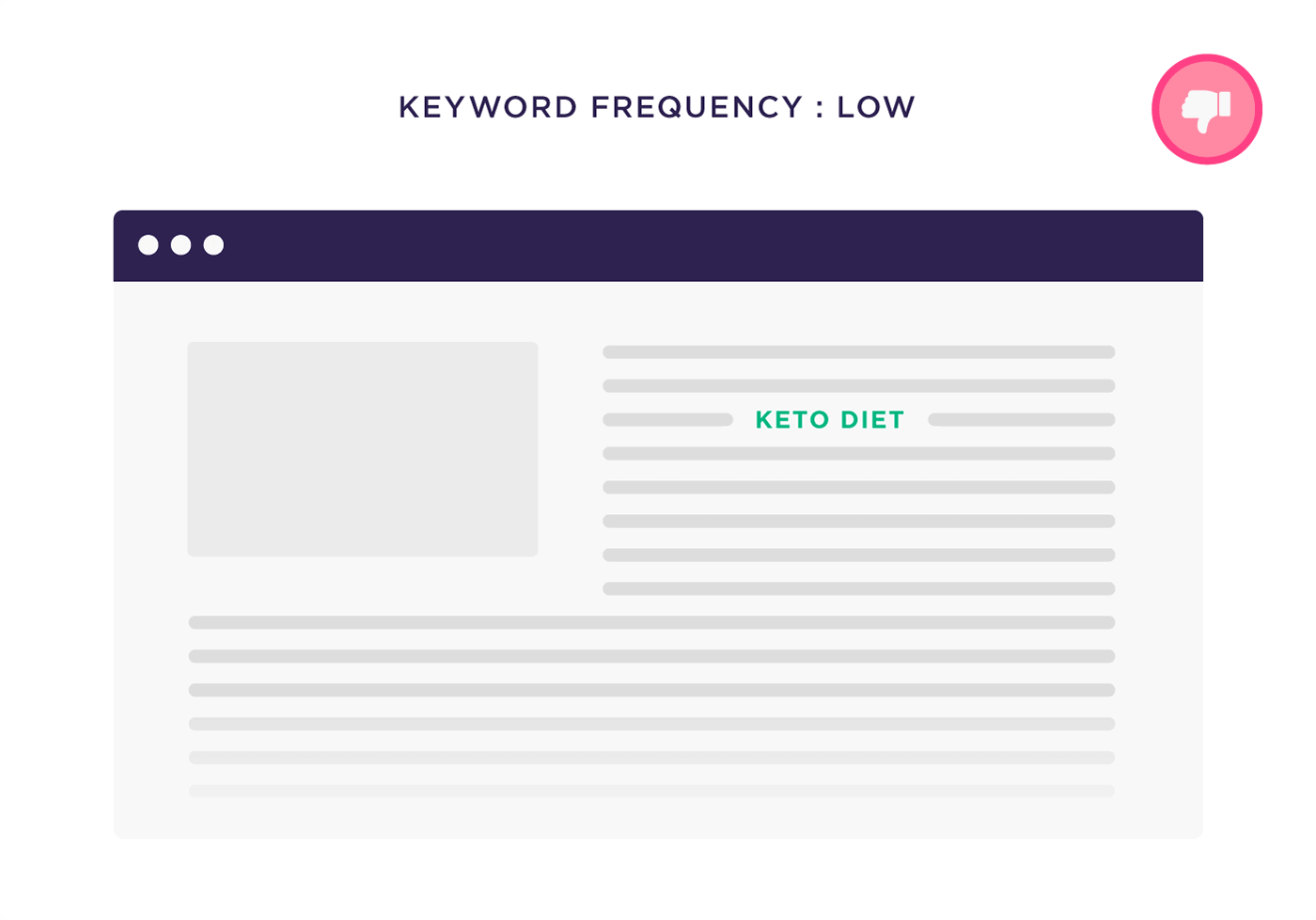
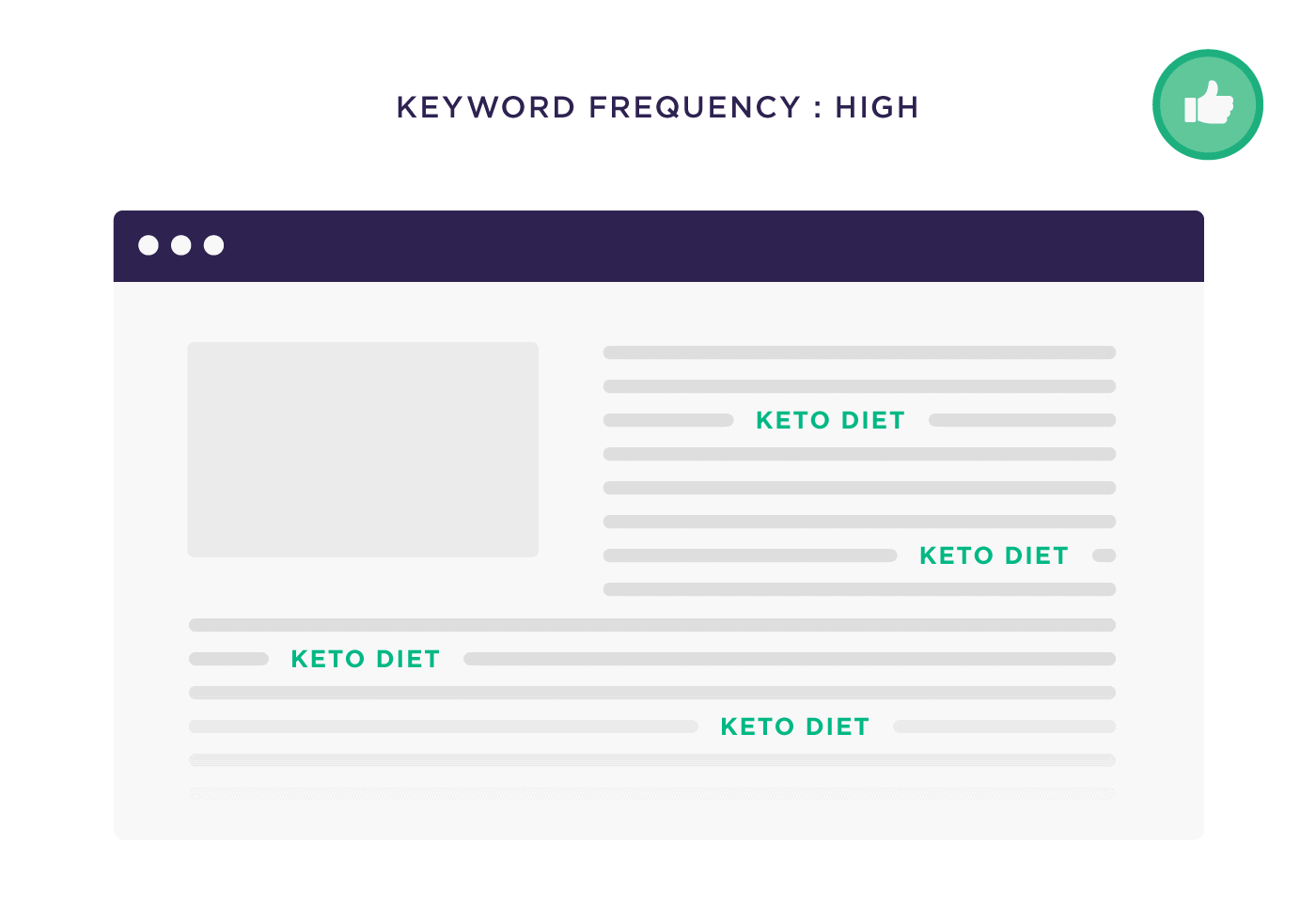
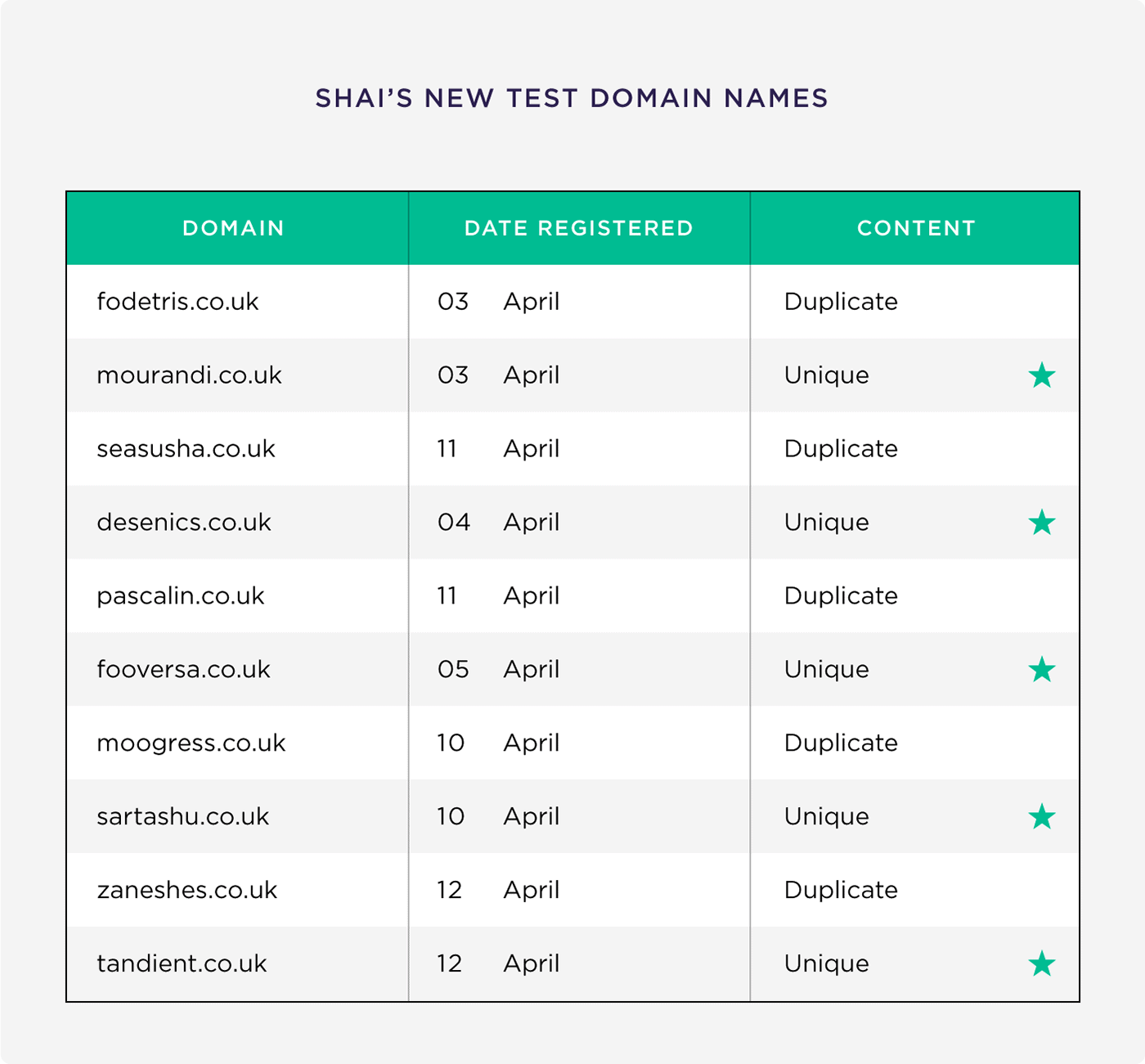
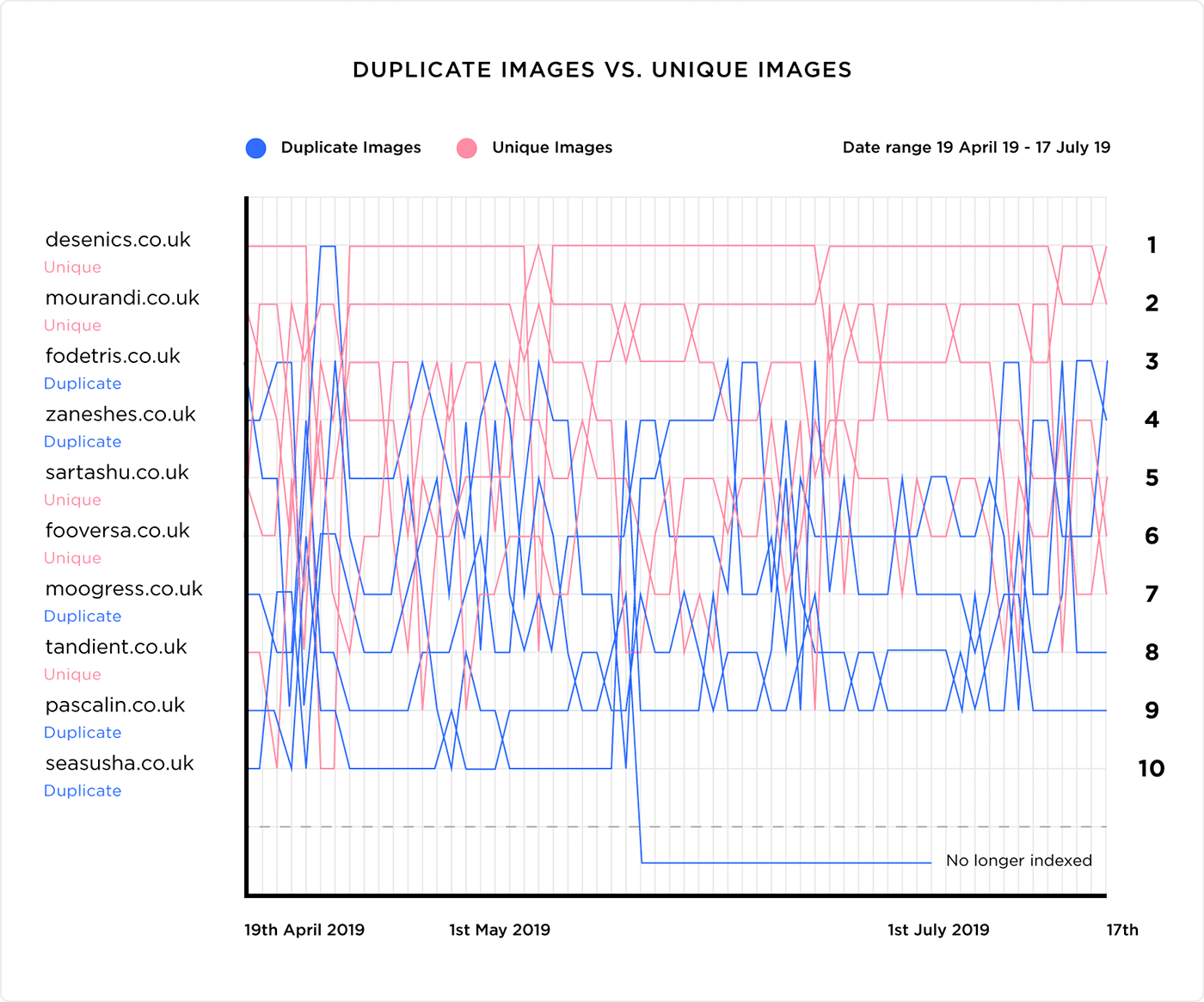
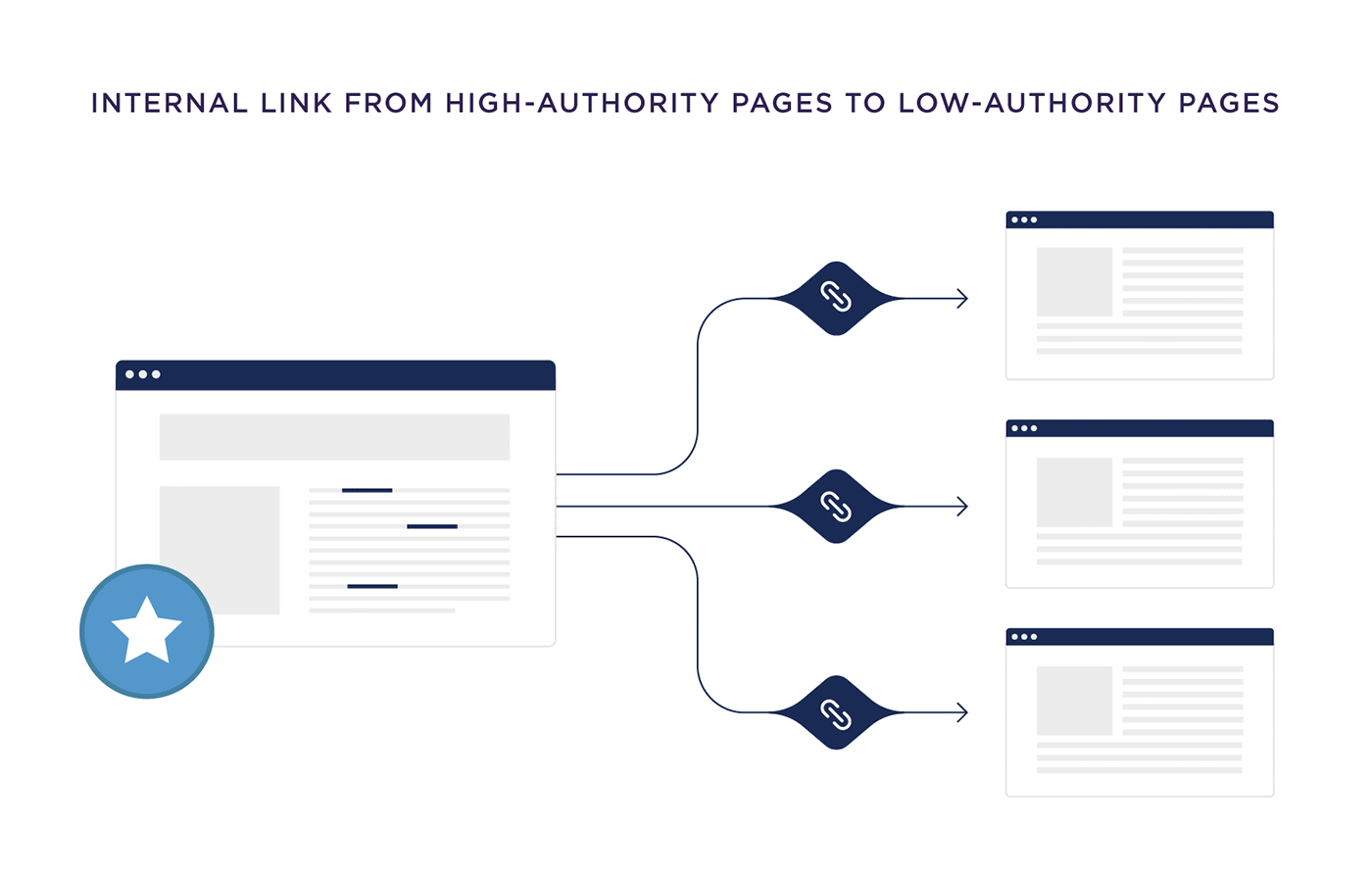
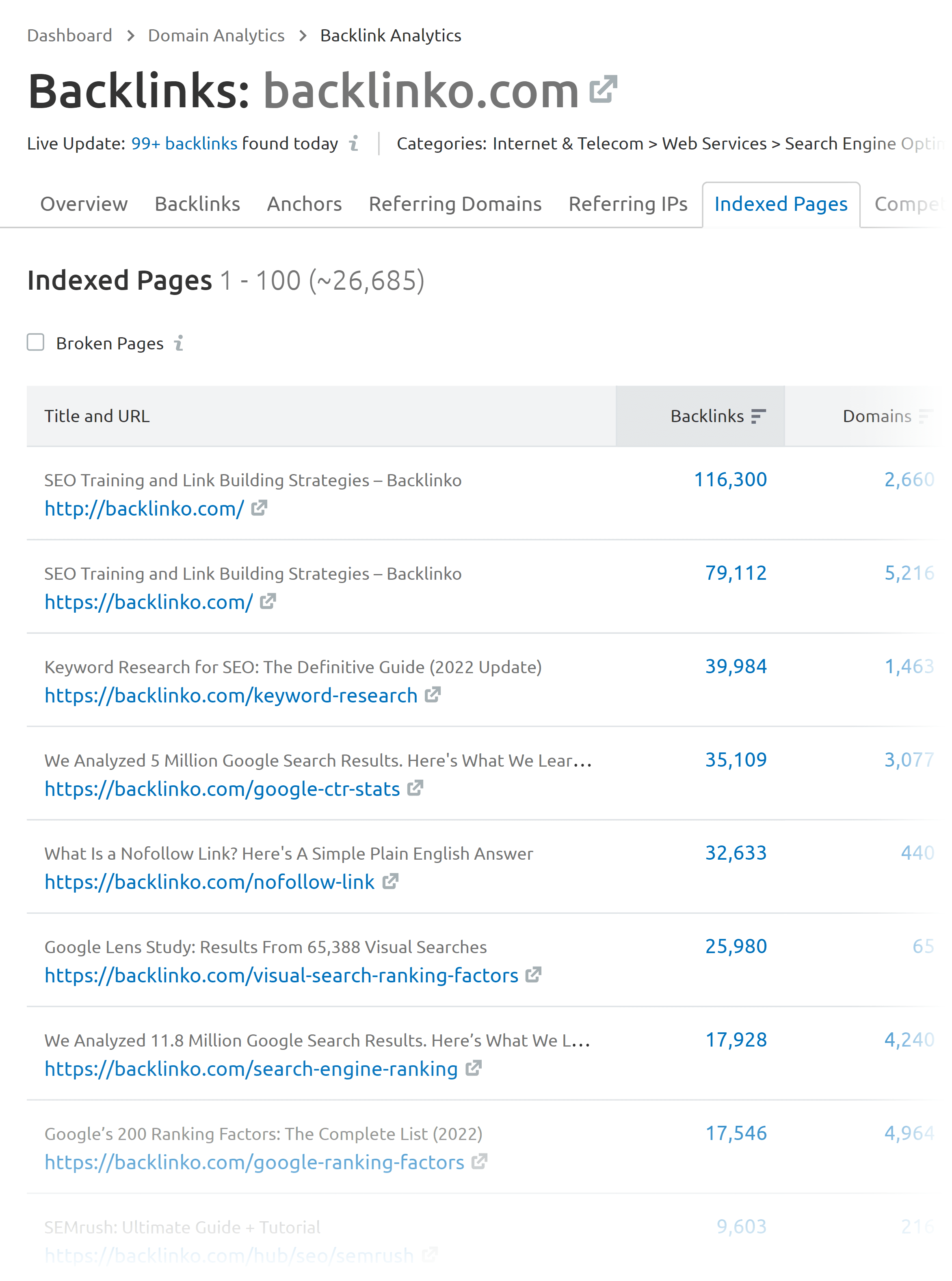
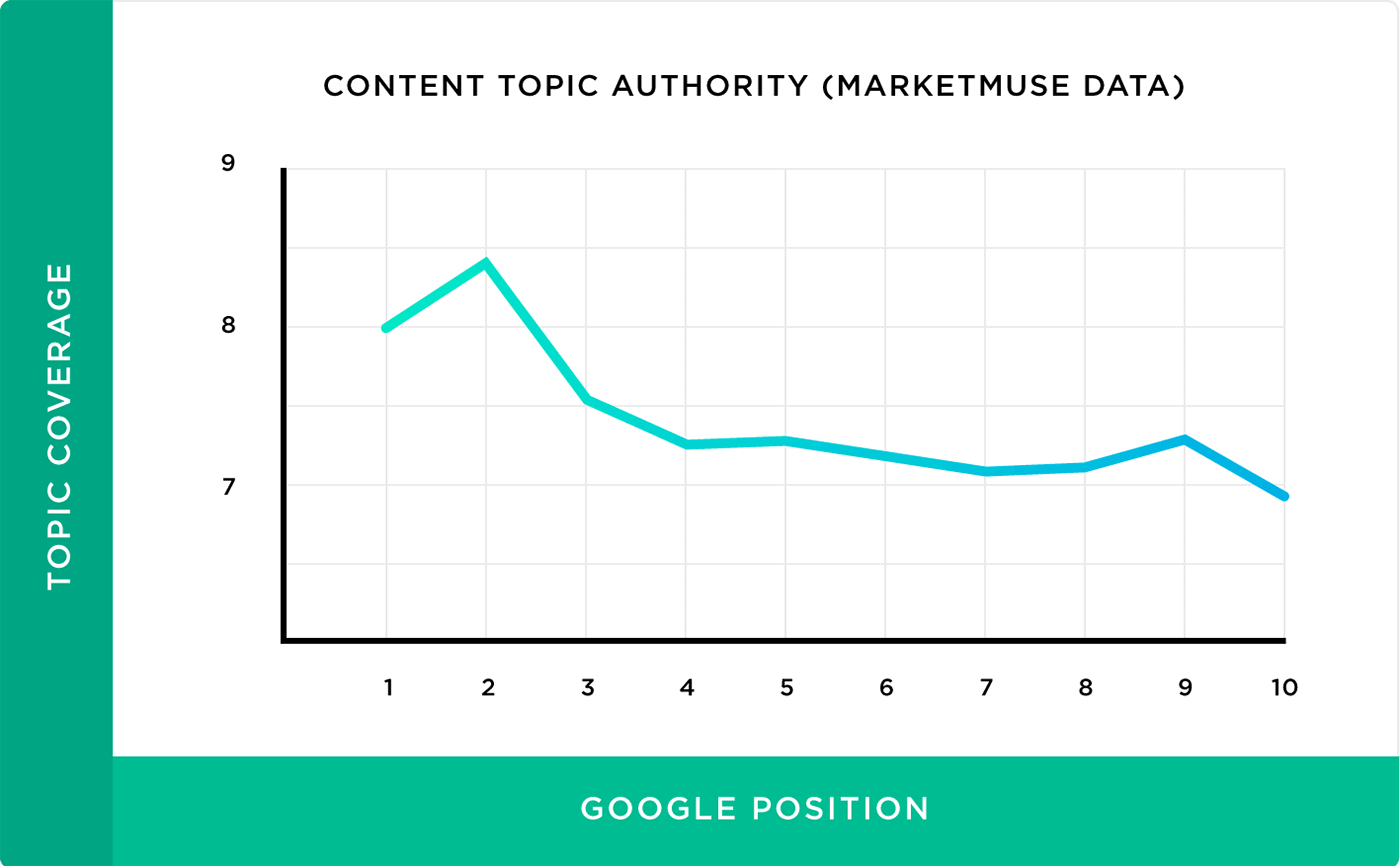
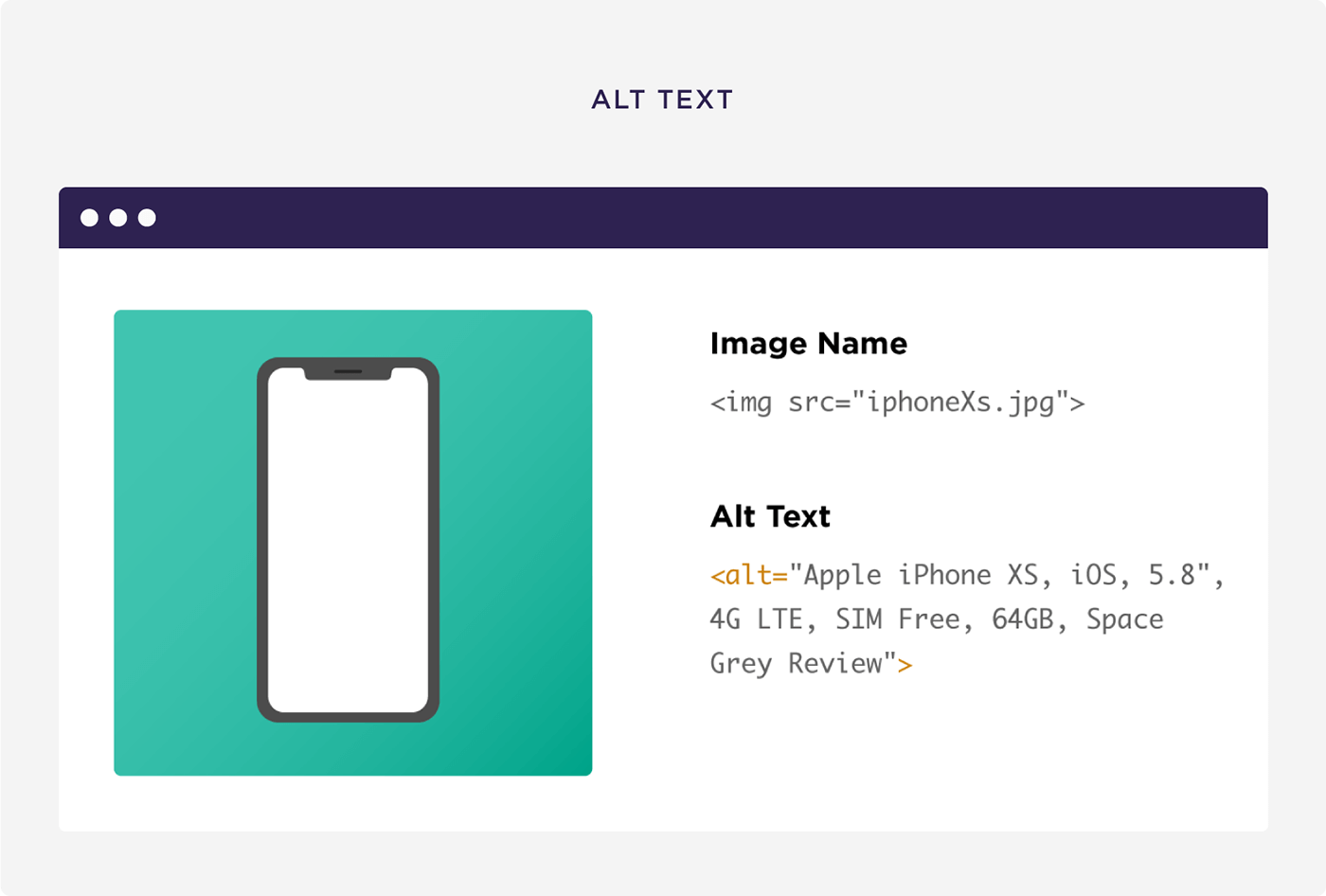
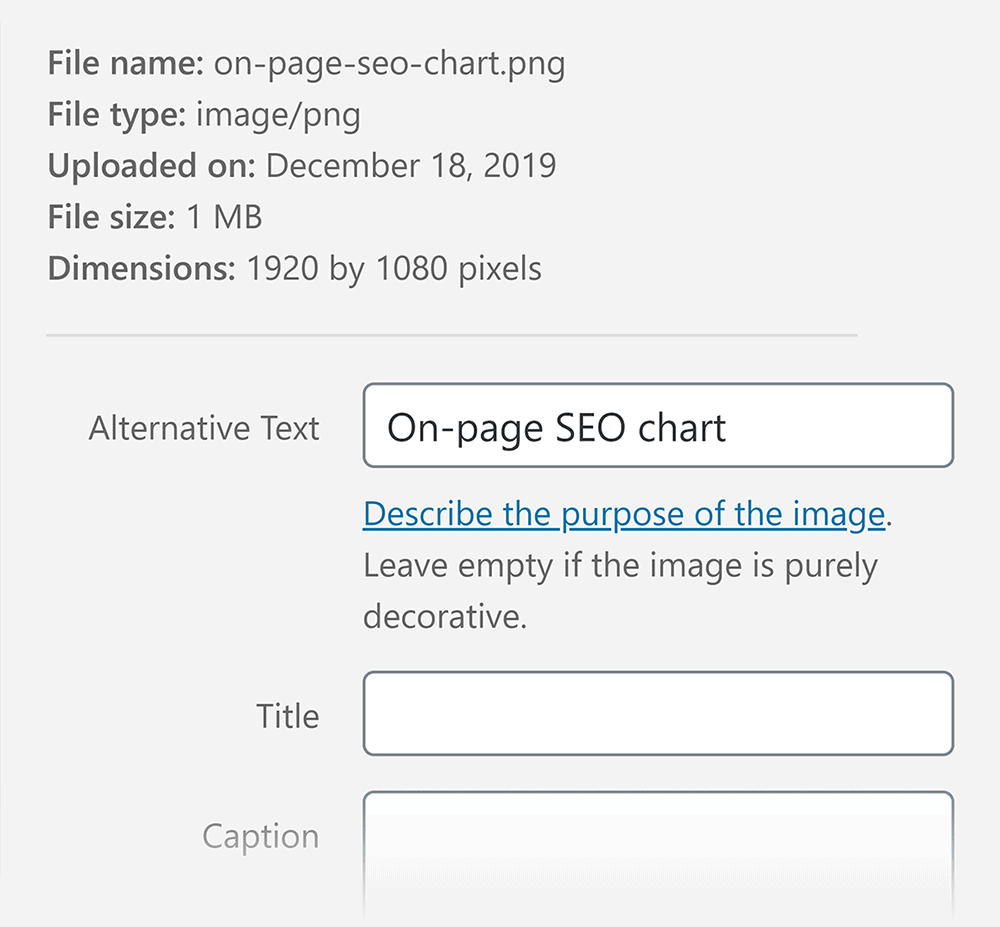
Key elements of on-page SEO include optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, content (including keyword usage), internal links, URLs, images, and ensuring a positive user experience. These elements collectively contribute to improved search engine rankings and user engagement.
How important is on-page SEO for overall website performance?
On-page SEO is integral to overall website performance. It directly impacts search engine rankings, user experience, and the discoverability of your content. Neglecting on-page SEO can hinder your site’s visibility and user engagement.
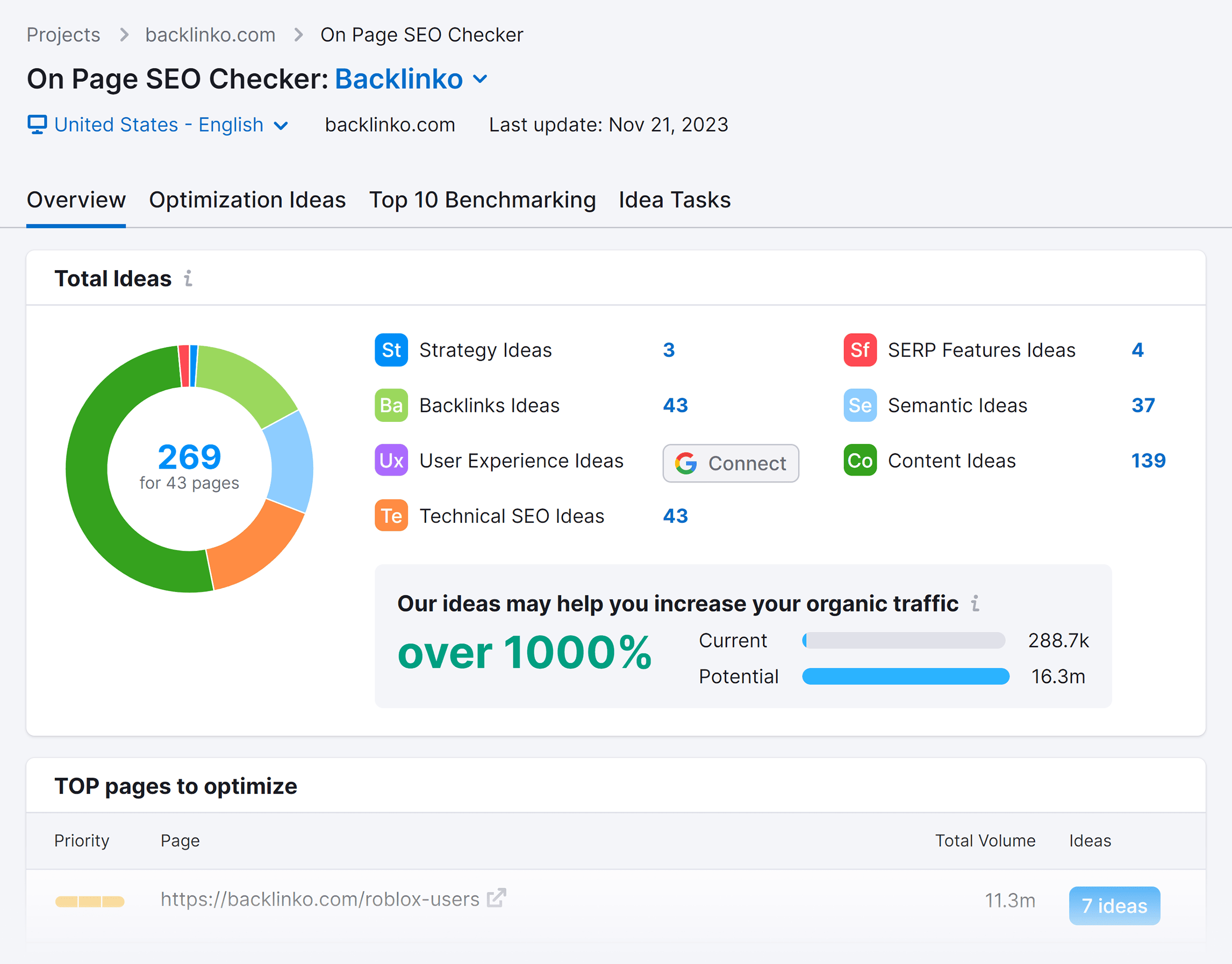
Are there tools available to assist with on-page SEO?
Yes, several tools can aid in on-page SEO efforts. Tools like Semrush, Moz, and Ahrefs offer features for keyword research, content optimization, and performance tracking. Utilizing these tools can streamline the on-page optimization process and provide valuable insights for improvement.